Johannes Gutenberg–Universität Mainz
We use molecular dynamics (MD) to simulate an unstable homogeneous mixture of binary fluids (AB), confined in a slit pore of width D. The pore walls are assumed to be flat and structureless, and attract one component of the mixture (A) with the same strength. The pair-wise interactions between the particles is modeled by the Lennard-Jones potential, with symmetric parameters that lead to a miscibility gap in the bulk. In the thin-film geometry, an interesting interplay occurs between surface enrichment and phase separation.
We study the evolution of a mixture with equal amounts of A and B, which is rendered unstable by a temperature quench. We find that A-rich surface enrichment layers form quickly during the early stages of the evolution, causing a depletion of A in the inner regions of the film. These surface-directed concentration profiles propagate from the walls towards the center of the film, resulting in a transient layered structure. This layered state breaks up into a columnar state, which is characterized by the lateral coarsening of cylindrical domains. The qualitative features of this process resemble results from previous studies of diffusive Ginzburg-Landau-type models [S.~K. Das, S. Puri, J. Horbach, and K. Binder, Phys. Rev. E {\bf 72}, 061603 (2005)], but quantitative aspects differ markedly. The relation to spinodal decomposition in a strictly 2-d geometry is also discussed.
11 Jul 2024
This text summarizes and expands the content of a general audience talk given in 2018 at the University of Mainz. Motivated by recent developments in dependent type theory and infinity category theory, it presents a history of ideas around the concepts of truth, proof, equality, and equivalence as well as their relation to human thought. We describe a few selected ideas of Platon, Aristoteles, Leibniz, Kant, Frege and others and then pass to the results of Gödel and Tarski about incompleteness, undecidability and truth in deductive systems and their semantic models. The main focus of this text, however, is the development of dependent type theory through the work of Per Martin--Löf and recent developments in homotopy type theory, i.e., the univalent foundations program of Vladimir Voevodsky and others. These theories allow the notion of identity types, which gives new possibilities for handling equality, symmetry, equivalence and isomorphisms in a conceptual way. Martin--Löf type theories have semantic models in (infinity,1)-categories, which are related to simplicial localizations of Quillen model categories. The interaction of type theory with infinity category theory is a new paradigm for a structural view on mathematics which is superior to set theory. It also supports the recent emerging trend for computer assisted proofs in mathematics and verification of algorithms and software in computer science.
16 Nov 2014
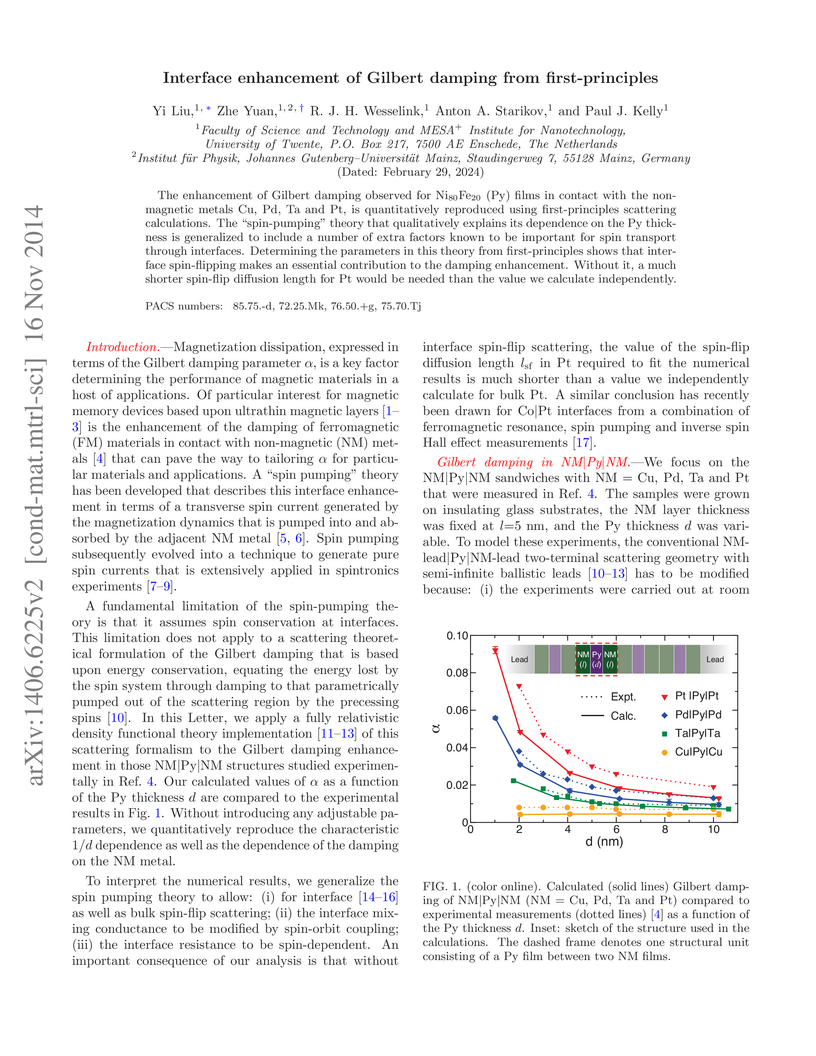
The enhancement of Gilbert damping observed for Ni80Fe20 (Py) films in
contact with the non-magnetic metals Cu, Pd, Ta and Pt, is quantitatively
reproduced using first-principles scattering theory. The "spin-pumping" theory
that qualitatively explains its dependence on the Py thickness is generalized
to include a number of factors known to be important for spin transport through
interfaces. Determining the parameters in this theory from first-principles
shows that interface spin-flipping makes an essential contribution to the
damping enhancement. Without it, a much shorter spin-flip diffusion length for
Pt would be needed than the value we calculate independently.
University of Victoria Nagoya UniversityINFN Sezione di PisaPacific Northwest National Laboratory
Nagoya UniversityINFN Sezione di PisaPacific Northwest National Laboratory University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Université Paris-SaclayWayne State UniversityHigh Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)Universität BonnThe Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI)Hiroshima UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iMax-Planck-Institut für PhysikGeorg-August Universität GöttingenElettra-Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A.J. Stefan InstituteDeutsches Elektronen–SynchrotronUniversity of Valencia-CSICUniv. of Naples Federico IIJohannes Gutenberg–Universität MainzUniversità di Trieste Dipartimento di FisicaUniversit
de StrasbourgUniversit
di Pisa
Université Paris-SaclayWayne State UniversityHigh Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)Universität BonnThe Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI)Hiroshima UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iMax-Planck-Institut für PhysikGeorg-August Universität GöttingenElettra-Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A.J. Stefan InstituteDeutsches Elektronen–SynchrotronUniversity of Valencia-CSICUniv. of Naples Federico IIJohannes Gutenberg–Universität MainzUniversità di Trieste Dipartimento di FisicaUniversit
de StrasbourgUniversit
di Pisa
 Nagoya UniversityINFN Sezione di PisaPacific Northwest National Laboratory
Nagoya UniversityINFN Sezione di PisaPacific Northwest National Laboratory University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Université Paris-SaclayWayne State UniversityHigh Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)Universität BonnThe Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI)Hiroshima UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iMax-Planck-Institut für PhysikGeorg-August Universität GöttingenElettra-Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A.J. Stefan InstituteDeutsches Elektronen–SynchrotronUniversity of Valencia-CSICUniv. of Naples Federico IIJohannes Gutenberg–Universität MainzUniversità di Trieste Dipartimento di FisicaUniversit
de StrasbourgUniversit
di Pisa
Université Paris-SaclayWayne State UniversityHigh Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)Universität BonnThe Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI)Hiroshima UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iMax-Planck-Institut für PhysikGeorg-August Universität GöttingenElettra-Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A.J. Stefan InstituteDeutsches Elektronen–SynchrotronUniversity of Valencia-CSICUniv. of Naples Federico IIJohannes Gutenberg–Universität MainzUniversità di Trieste Dipartimento di FisicaUniversit
de StrasbourgUniversit
di PisaThe high design luminosity of the SuperKEKB electron-positron collider will
result in challenging levels of beam-induced backgro\ unds in the interaction
region. Understanding and mitigating these backgrounds is critical to the
success of the Belle~II experi\ ment. We report on the first background
measurements performed after roll-in of the Belle II detector, a period known
as SuperKE\ KB Phase 2, utilizing both the BEAST II system of dedicated
background detectors and the Belle II detector itself. We also repor\ t on
first revisions to the background simulation made in response to our findings.
Backgrounds measured include contributions f\ rom synchrotron radiation,
beam-gas, Touschek, and injection backgrounds. At the end of Phase 2,
single-beam backgrounds origina\ ting from the 4 GeV positron Low Energy Ring
(LER) agree reasonably well with simulation, while backgrounds from the 7 GeV
elect\ ron High Energy Ring (HER) are approximately one order of magnitude
higher than simulation. We extrapolate these backgrounds for\ ward and conclude
it is safe to install the Belle II vertex detector.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.