Overview
R-Bench is a graduate-level, multi-disciplinary benchmark designed to evaluate complex reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). The benchmark addresses limitations of existing evaluations like MMLU and MMMU, which show saturation effects with advanced models (OpenAI o1 achieves >90% on MMLU). R-Bench focuses on system-II thinking—slow, deliberate reasoning—rather than quick knowledge recall, providing a more challenging assessment across 19 university departments and over 100 subjects in both English and Chinese.
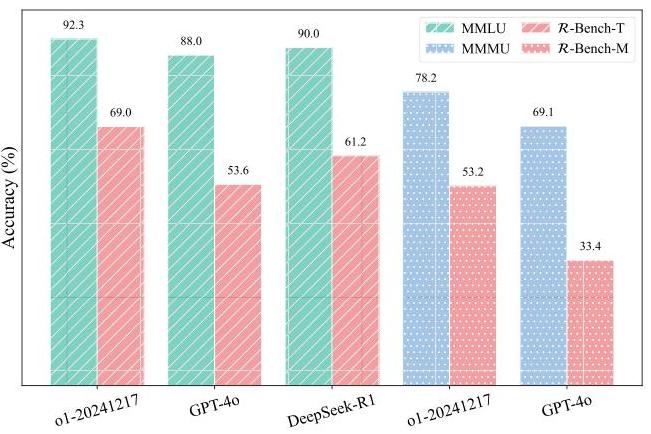
Performance comparison showing R-Bench's increased difficulty compared to MMLU and MMMU across different models, with lower accuracy scores indicating greater challenge.
Key Specifications
R-Bench consists of four sub-benchmarks:
- R-Bench-T: 1,094 English text-only questions across 108 subjects from 18 departments
- R-Bench-T(zh): Chinese translation of R-Bench-T
- R-Bench-M: 665 English multimodal questions (text + images) across 83 subjects from 18 departments
- R-Bench-M(zh): Chinese translation of R-Bench-M
All questions follow a six-option multiple choice format (A-F) and are evaluated using Top-1 accuracy. The benchmark filters questions through expert curation and OpenAI o1 screening (requiring >2,000 reasoning tokens) to ensure focus on complex reasoning rather than memorization.
Data Examples
Text-only Computer Science Example (Data Structures): In the undirected graph G=(V,E) where V={1,2,3,4,5,6,7} and E={(1,2), (1,3), (2,3), (4,5), (3,6), (4,7), (5,7)}, how many different spanning forests does the graph G contain? Note: If the edge sets of two spanning forests are different, they are considered different spanning forests.
Options: A: 14 B: 9 C: 10 D: 12 E: 11 F: All other answers are incorrect
Answer: B
Multimodal Mechanical Engineering Example (Theoretical Mechanics): The width of the brick clamp is 25 cm, and the curved rods AGB and GCED are hinged at point G, with dimensions as shown in the figure. Suppose the weight of the brick is Q=120N and the force P that lifts the brick acts along the centerline of the brick clamp. The coefficient of friction between the brick clamp and the brick is f=0.5. Determine the maximum value of distance b required to lift the brick using the clamp.
[Image shows technical diagram of brick clamp mechanism]
Options: A: 9 cm B: 11 cm C: 15 cm D: 20 cm E: 25 cm F: All other answers are incorrect
Answer: B
Significance
R-Bench addresses critical gaps in current AI evaluation by providing a comprehensive, challenging benchmark that remains discriminative for advanced models. Key contributions include:
- Higher Difficulty: Even top models achieve moderate accuracy (OpenAI o1: 69% on text, 53% on multimodal), providing room for improvement
- Multimodal Assessment: Reveals significant performance gaps between text and visual reasoning capabilities
- Cross-lingual Evaluation: Enables assessment of reasoning consistency across languages, reducing language-specific overfitting
- Multi-disciplinary Coverage: Spans diverse academic fields, promoting general rather than domain-specific intelligence
The benchmark reveals that multimodal reasoning significantly lags behind text-only reasoning and that current models show substantial variation across different academic disciplines.
Usage
R-Bench is publicly available with associated code and evaluation tools. Models are evaluated in zero-shot settings with Chain of Thought prompting. The benchmark uses OpenCompass for LLM evaluation and VLMEvalKit for MLLM assessment. Current leaderboards show OpenAI GPT-5 leading both language (77.4%) and multimodal (68.4%) evaluations, though performance remains moderate across all models, confirming the benchmark's continued relevance for driving AI reasoning capabilities forward.