Overview
MultiVENT-G (MultiVENT-Grounded) is a multimodal benchmark designed to evaluate AI systems' ability to extract "partially-defined events" from collections of unstructured video and text data. Unlike traditional event extraction tasks where events are fully contained within the data, MultiVENT-G focuses on events that exist outside the provided media - each video-text pair offers only partial observations of larger, ongoing real-world events. The benchmark formulates event extraction as a three-stage span retrieval task across text, temporal, and spatial modalities.
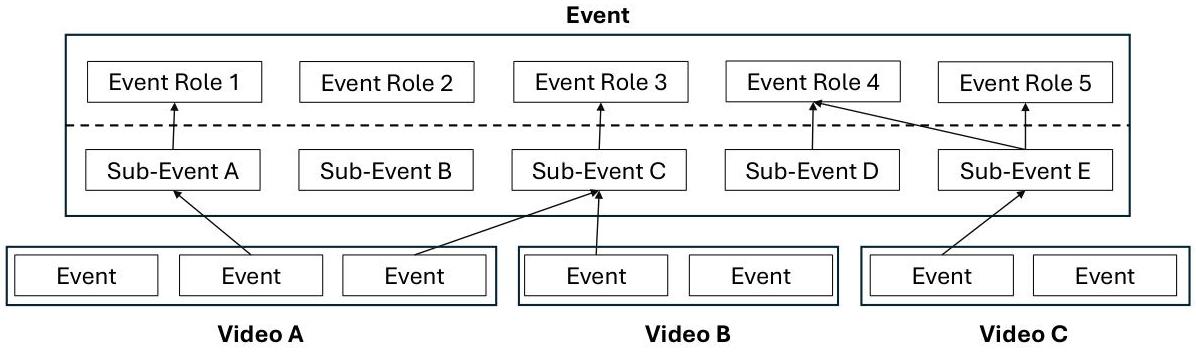 Figure 1: Illustration of partially-defined events where multiple videos (A, B, C) provide incomplete observations of a larger event through different sub-events and roles.
Figure 1: Illustration of partially-defined events where multiple videos (A, B, C) provide incomplete observations of a larger event through different sub-events and roles.
Key Specifications
Dataset Size: 1,168 densely annotated video-text pairs across 5 languages (Arabic, Chinese, English, Korean, Russian)
Languages: Multilingual coverage with English comprising the largest subset (414 videos), followed by Chinese (234), Korean (208), Russian (187), and Arabic (125)
Event Categories: Seven event templates covering Emergency/Disaster, Election, Political Development, Demonstration, Social Event, Sports, and Discovery/Launch
Annotation Density: 22,800+ labeled event-centric entities with professional linguist annotations, including natural language descriptions, OCR flags, and human confidence scores
Task Structure: Three sequential stages:
- Stage 1: Text span retrieval from accompanying documents
- Stage 2: Temporal span retrieval from video content
- Stage 3: Spatial span retrieval via bounding box localization
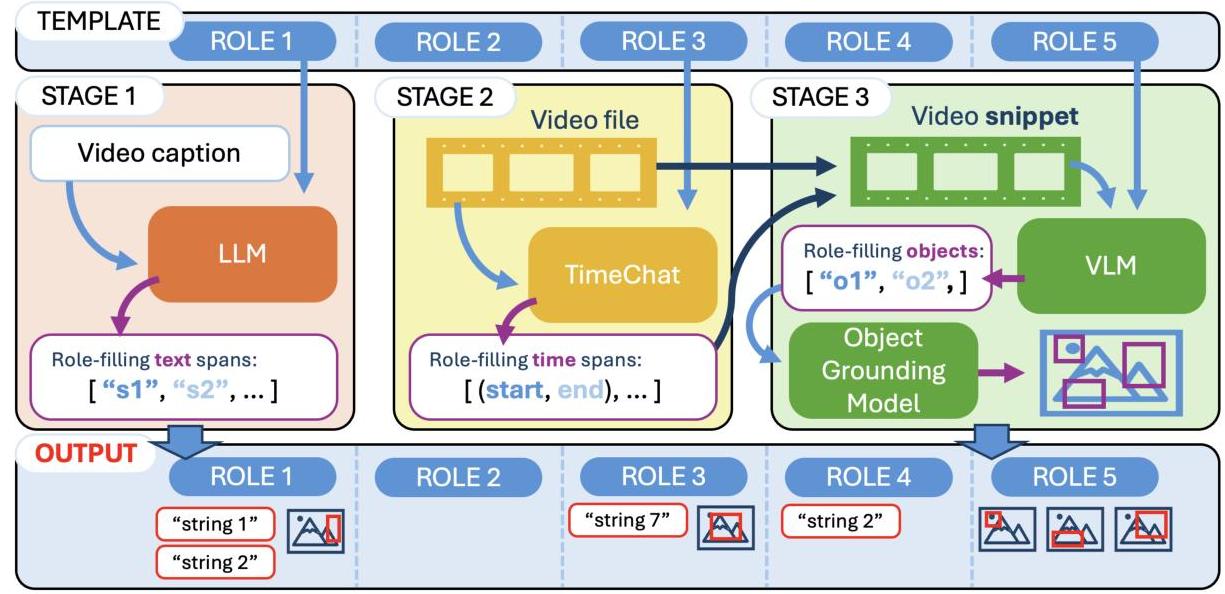 Figure 2: The three-stage span retrieval pipeline showing how each stage processes different modalities to extract role-filling information.
Figure 2: The three-stage span retrieval pipeline showing how each stage processes different modalities to extract role-filling information.
Data Examples
Example 1 - Emergency Event (Notre Dame Fire):
Text Input: "Massive plumes of smoke and intense flames pouring from the centuries-old #NotreDame cathedral in #Paris were captured on camera."
Template Question: "What emergency/disaster is occurring?"
Text Span Output: ["fire", "flames"]
Temporal Question: "Where is the emergency/disaster occurring?"
Temporal Span Output: ['15.2 - 28.0 seconds']
Spatial Question: "What was the outcome of the emergency/disaster?"
Spatial Output: Bounding boxes around "smoke plumes" and "cathedral damage"
Example 2 - Demonstration Event:
Video showing protest scene with police presence
Template Questions:
- "Who are the protesters?" → Text/Visual spans: ["demonstrators", "crowd"]
- "What law enforcement was involved?" → Spatial spans: Bounding boxes around police officers
- "When did the protest occur?" → Text spans: ["afternoon", "October 2023"]
Significance
MultiVENT-G addresses a critical gap in multimodal AI evaluation by focusing on realistic, incomplete information scenarios that mirror human news consumption and event understanding. The benchmark's key contributions include:
Novel Task Formulation: Shifts from template-filling to span retrieval, requiring models to ground conclusions in specific data segments rather than generating answers from implicit knowledge.
Multilingual Multimodal Coverage: Provides one of the first dense multilingual video-text datasets for event extraction, crucial for global AI applications.
Granular Evaluation Framework: The three-stage decomposition allows detailed analysis of model capabilities across different modalities and reasoning types.
Real-world Complexity: Uses authentic news content with inherent noise, ambiguity, and partial information that reflects genuine information processing challenges.
Usage
MultiVENT-G is released as an open dataset for academic research. The benchmark includes standardized evaluation metrics for each stage:
- Text: Span-based precision/recall/F1 and CEAF-RME scores
- Temporal: Role-filling IoU at multiple thresholds (0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
- Spatial: Modified IoU metrics and semantic similarity scores for caption grounding
Initial baselines show significant room for improvement: GPT-4o achieves 67.2 F1 on text retrieval, TimeChat variants reach ~33 F1 on temporal grounding, and spatial grounding remains challenging with best IoU scores around 24. The benchmark establishes that current multimodal models struggle with partial event understanding, particularly in cross-modal reasoning and precise spatial localization.