Overview
VLURes is a multilingual benchmark designed to evaluate Vision Language Models (VLMs) on fine-grained visual and linguistic understanding tasks across four languages: English, Japanese, Swahili, and Urdu. The benchmark includes eight vision-language tasks and provides article-length textual contexts rather than short descriptions, addressing limitations in existing VLM evaluation frameworks that primarily rely on English-centric, brief text descriptions.
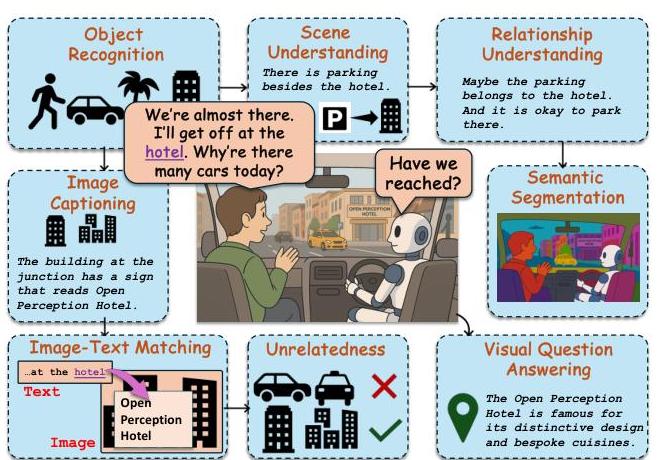
The benchmark evaluates VLMs on both image-only reasoning tasks (Object Recognition, Scene Understanding, Relationship Understanding, Semantic Segmentation, Image Captioning) and image-text reasoning tasks (Image-Text Matching, Unrelatedness, Visual Question Answering).
Key Specifications
VLURes contains approximately 4,000 image-text pairs distributed across four languages:
- English: 1,000 pairs
- Japanese: 1,000 pairs
- Swahili: 1,130 pairs
- Urdu: 996 pairs
Text characteristics:
- Average length ranges from 270-447 words per language
- Maximum text lengths reach 1,716-7,766 words
- Content spans 10 diverse image categories including cultural and regional contexts
The benchmark supports multiple evaluation settings:
- Zero-shot and one-shot prompting
- With and without rationale generation
- Fine-tuning scenarios for open-source models
- Cross-lingual evaluation (input/output language combinations)
Data Examples
Example 1: English Image-Text Pair
- Image: Safari scene with Sibebe Premium Lager beer bottle and glass on wooden railing, with African landscape and elephants in background
- Text: "Eswatini Beverages Ltd (EBL) was a subsidiary of SABMiller until 10 October 2016 when it was acquired by Anheuser-Busch InBev... The company was formed in 1995 by the merger of Eswatini Breweries, Ngwane Breweries, and Eswatini Bottlers. EBL produces and markets soft drinks, beer, and other alcoholic drinks..."
- Task Example (Object Recognition): "Question. Analyze this image and list all objects present. Categorize each object into groups such as furniture, electronics, devices, clothing, etc. Be thorough and specific."
Example 2: Cross-lingual Evaluation The benchmark supports evaluation where input text language differs from output response language, enabling assessment of cross-lingual transfer capabilities in VLMs across all four supported languages.
Significance
VLURes addresses critical gaps in VLM evaluation by:
- Low-resource language inclusion: First benchmark to systematically evaluate VLMs on Swahili and Urdu alongside high-resource languages
- Rich contextual evaluation: Article-length prose provides detailed background information, unlike existing benchmarks with short captions
- Novel unrelatedness task: Introduces the challenge of identifying irrelevant textual information, testing robustness in noisy data scenarios
- Comprehensive multilingual analysis: Enables cross-lingual performance comparison and language bias detection in VLMs
The benchmark reveals significant performance gaps between proprietary models (GPT-4o achieving 90%+ accuracy) and open-source models, with particularly severe limitations for low-resource languages where many open-source models achieve 0% accuracy on Swahili tasks.
Usage
The benchmark is available for research use and supports standard evaluation protocols. Models are evaluated using both automatic LLM-based judges (Gemini 1.5 Pro) and human evaluation from native speakers. The benchmark includes fine-tuning capabilities for open-source models and comprehensive cross-lingual analysis tools for understanding language transfer effects in VLMs.