Overview
MM-HELIX is a benchmark designed to evaluate the multimodal long-chain reflective reasoning capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). The benchmark addresses a critical gap in current MLLM evaluation: while these models show proficiency in direct reasoning tasks, their ability to perform iterative thinking, self-correction, and backtracking remains largely unexplored. MM-HELIX consists of 42 carefully designed tasks across four categories (Algorithms, Graphs, Puzzles, Games) that require models to comprehend complex rules, perform visual observation, and engage in multi-step thought processes.
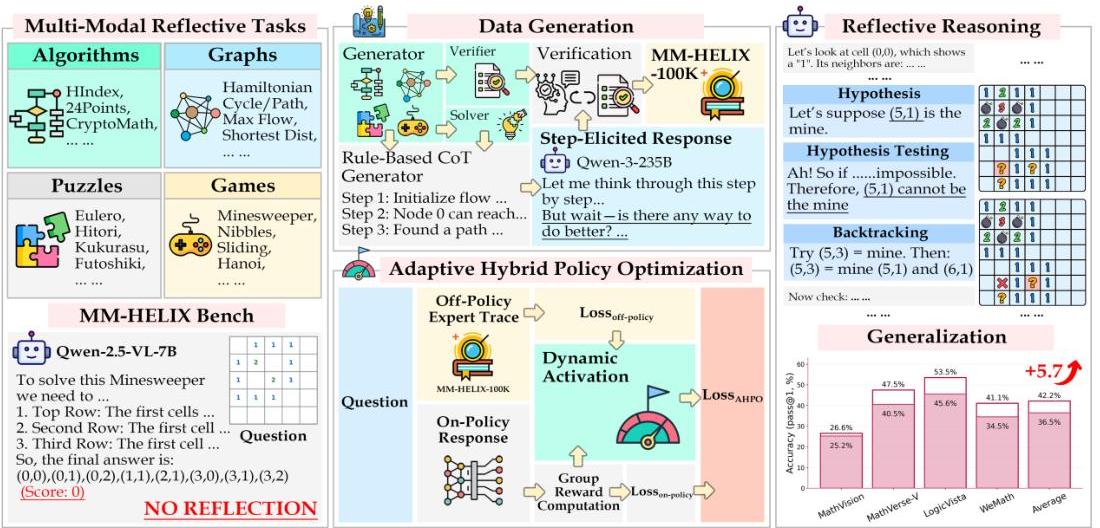 Figure 1: Overview of the MM-HELIX benchmark framework, showing the four task categories, data generation pipeline, and the proposed Adaptive Hybrid Policy Optimization (AHPO) training method.
Figure 1: Overview of the MM-HELIX benchmark framework, showing the four task categories, data generation pipeline, and the proposed Adaptive Hybrid Policy Optimization (AHPO) training method.
Key Specifications
Dataset Size: 1,260 evaluation instances (30 instances per task across 5 difficulty levels) and MM-HELIX-100K training dataset containing 100,000 high-quality reflective reasoning traces
Task Categories:
- Algorithms (9 tasks): Mathematical/computational challenges like "24 Points", "Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock", "Container With Most Water"
- Graphs (8 tasks): Graph analysis tasks including "Eulerian Cycle", "Max Flow", "Shortest Distance"
- Puzzles (19 tasks): Logic puzzles such as "Sudoku", "Nonogram", "Bridges", "Kakuro"
- Games (6 tasks): Strategic planning games like "Sokoban", "Minesweeper", "Tower of Hanoi"
Difficulty Levels: Five programmatically generated levels (1: very easy to 5: very hard) based on task-specific parameters like number of reasoning steps
Input Format: Multimodal inputs combining textual problem descriptions with visual representations (images of game boards, charts, puzzles, etc.)
Evaluation Metric: Accuracy, determined by exact-match comparison for simple answers or algorithmic verification through rule simulation for complex multi-step solutions
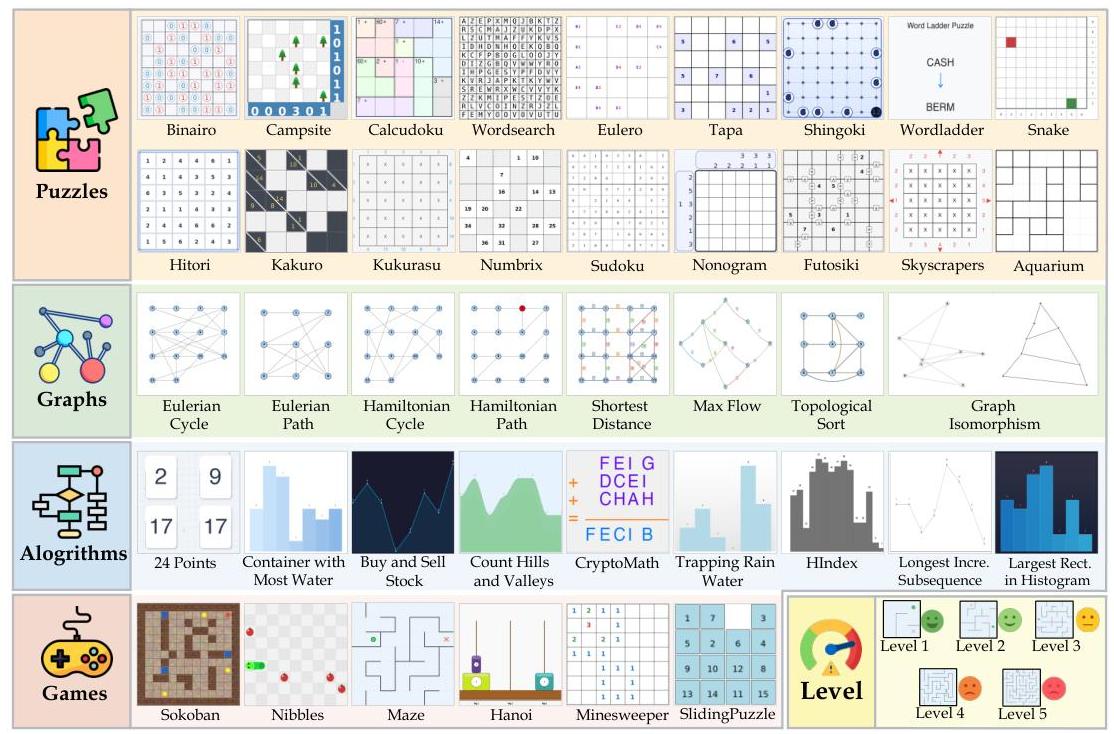 Figure 2: Examples of tasks across all four categories in MM-HELIX, showing the diversity of visual and reasoning challenges.
Figure 2: Examples of tasks across all four categories in MM-HELIX, showing the diversity of visual and reasoning challenges.
Data Examples
Example 1: Aquarium Puzzle (Level 1)
Image: 4x4 grid with numbers indicating water levels per row/column
Question: Determine which cells are filled with water based on rules:
1. Each region must be filled to uniform water level
2. Water cannot float - filled cells must have support below
3. Numbers indicate filled cells per row/column
4. Regions separated by thick black lines
Answer Format: List coordinates of filled cells
Reference Answer: [(2,1), (3,1), (0,2), (3,2), (0,3), (1,3)]
Example 2: Nibbles Game (Level 5)
Image: Grid showing a snake and multiple apples
Goal: Find sequence of moves to eat all apples
Game Rules:
1. Control snake with up/down/left/right commands
2. Snake must eat all apples on grid
3. Snake grows longer by one segment when eating
4. Snake cannot collide with walls or itself
5. Snake moves one cell at a time
Output Format: Sequence of moves
Example: "up right down left up"
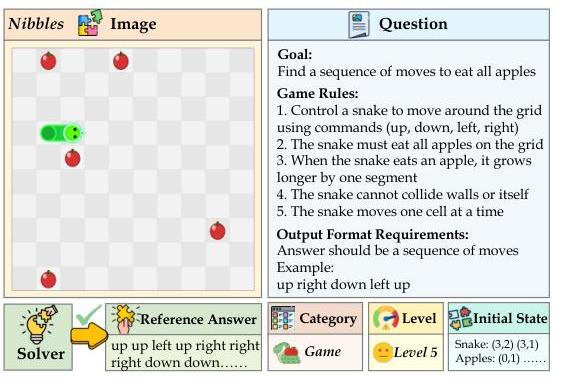 Figure 3: Detailed example of the Nibbles task showing the multimodal input format and expected reasoning process.
Figure 3: Detailed example of the Nibbles task showing the multimodal input format and expected reasoning process.
Significance
MM-HELIX reveals a profound deficit in current MLLMs' reflective reasoning capabilities. Even state-of-the-art models like GPT-5 achieve only 58.1% accuracy on multimodal inputs, while the best open-source model reaches 33.3%. The benchmark demonstrates a significant modality gap, with text-only performance substantially higher (e.g., GPT-5: 84.5% vs 58.1%), indicating that visual comprehension remains a major bottleneck for complex reasoning.
The benchmark introduces several key innovations:
- Programmatic Generation Framework: Automated instance generation with deterministic solvers and verifiers enables scalable evaluation
- Long-chain Reasoning Focus: Average chain-of-thought traces exceed 4,000 tokens, requiring sustained coherent reasoning
- Hierarchical Difficulty: Progressive complexity allows fine-grained analysis of model capabilities and failure modes
The work also contributes MM-HELIX-100K, a large-scale dataset of reflective reasoning traces generated through the Step-Elicited Response Generation (SERG) pipeline, which reduces generation time by 90% while achieving 99.8% success rate compared to 25% for unconstrained generation.
Usage
The MM-HELIX benchmark and related resources are available at: https://mm-helix.github.io/
Resources Available:
- Benchmark Dataset: MM-HELIX evaluation set with 1,260 instances
- Training Data: MM-HELIX-100K with high-quality reasoning traces
- Code Repository: Implementation of evaluation framework, data generation pipeline (SERG), and training methods
- Model Checkpoints: Pre-trained MM-HELIX-7B-Thinking model demonstrating +18.6% improvement over baseline
The benchmark uses standard evaluation protocols with temperature settings of 0.6 for thinking models and 0.0 for non-thinking models. The framework supports both multimodal and text-only evaluation modes, enabling comprehensive analysis of model capabilities across modalities.