Overview
MC-Bench is a benchmark for multi-context visual grounding that evaluates multimodal large language models' (MLLMs) ability to localize instances across multiple images based on open-ended text prompts. The benchmark addresses a critical gap by combining multi-image inputs with instance-level visual grounding tasks, moving beyond existing benchmarks that focus on either single-image grounding or multi-image understanding without precise localization.
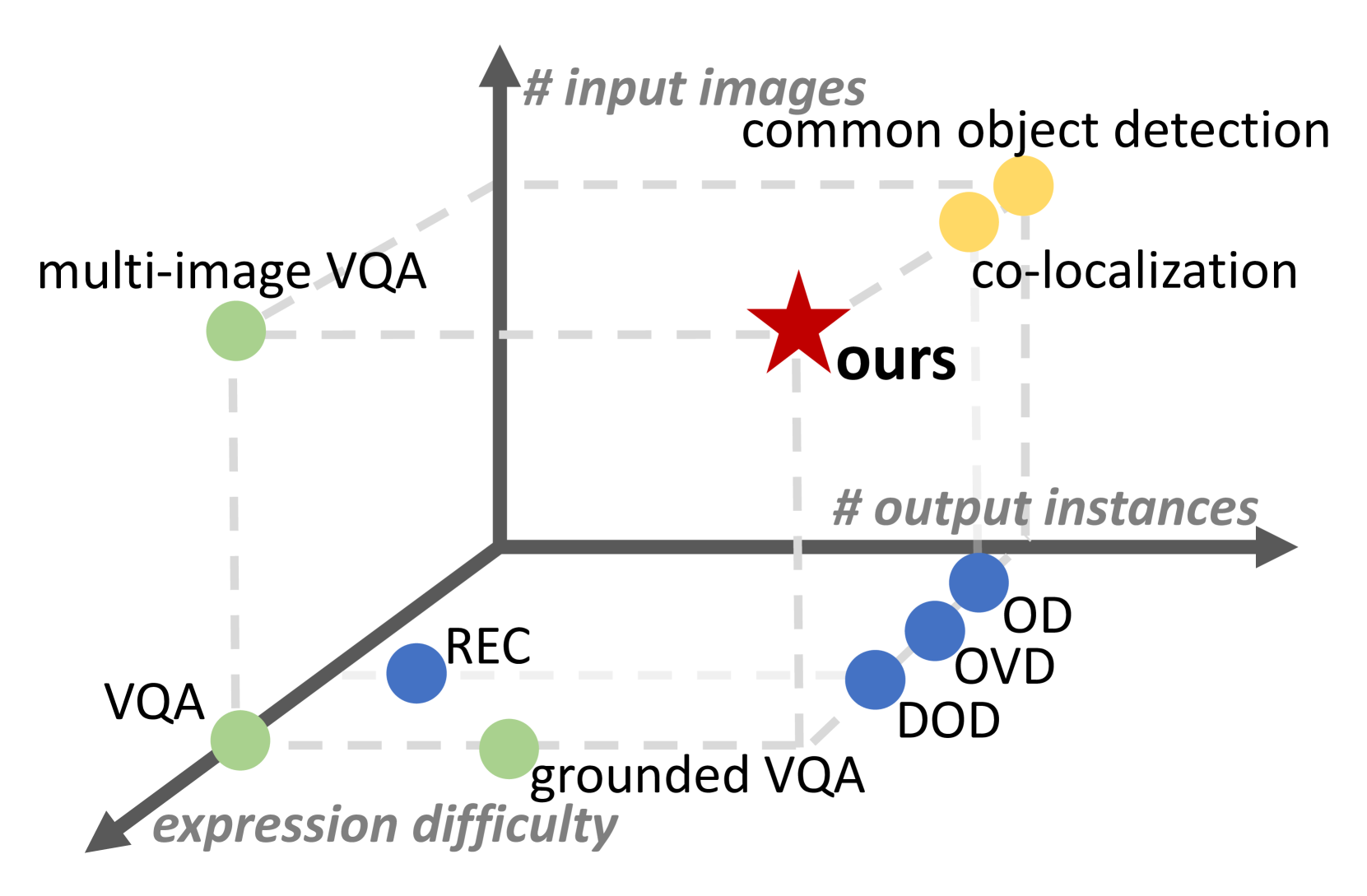 Figure showing MC-Bench's unique position combining multi-image input with instance-level grounding tasks
Figure showing MC-Bench's unique position combining multi-image input with instance-level grounding tasks
Key Specifications
MC-Bench contains 2,000 multi-context samples with 3,200 language-grounded bounding boxes spanning diverse domains including natural images, document photos, webpage screenshots, scientific diagrams, and artwork. The dataset features three text prompt styles:
- Referring (17.3%): Direct identification using category, attribute, or positional information
- Comparison (40.5%): Cross-image comparisons of visual content like object quantity or attributes
- Reasoning (42.2%): Complex descriptions requiring external knowledge and multi-hop reasoning
The benchmark covers 20 practical skills from document photo comprehension to forensic detection, with text prompts averaging 7.2 words. Each sample consists of image pairs with instance-level bounding box annotations.
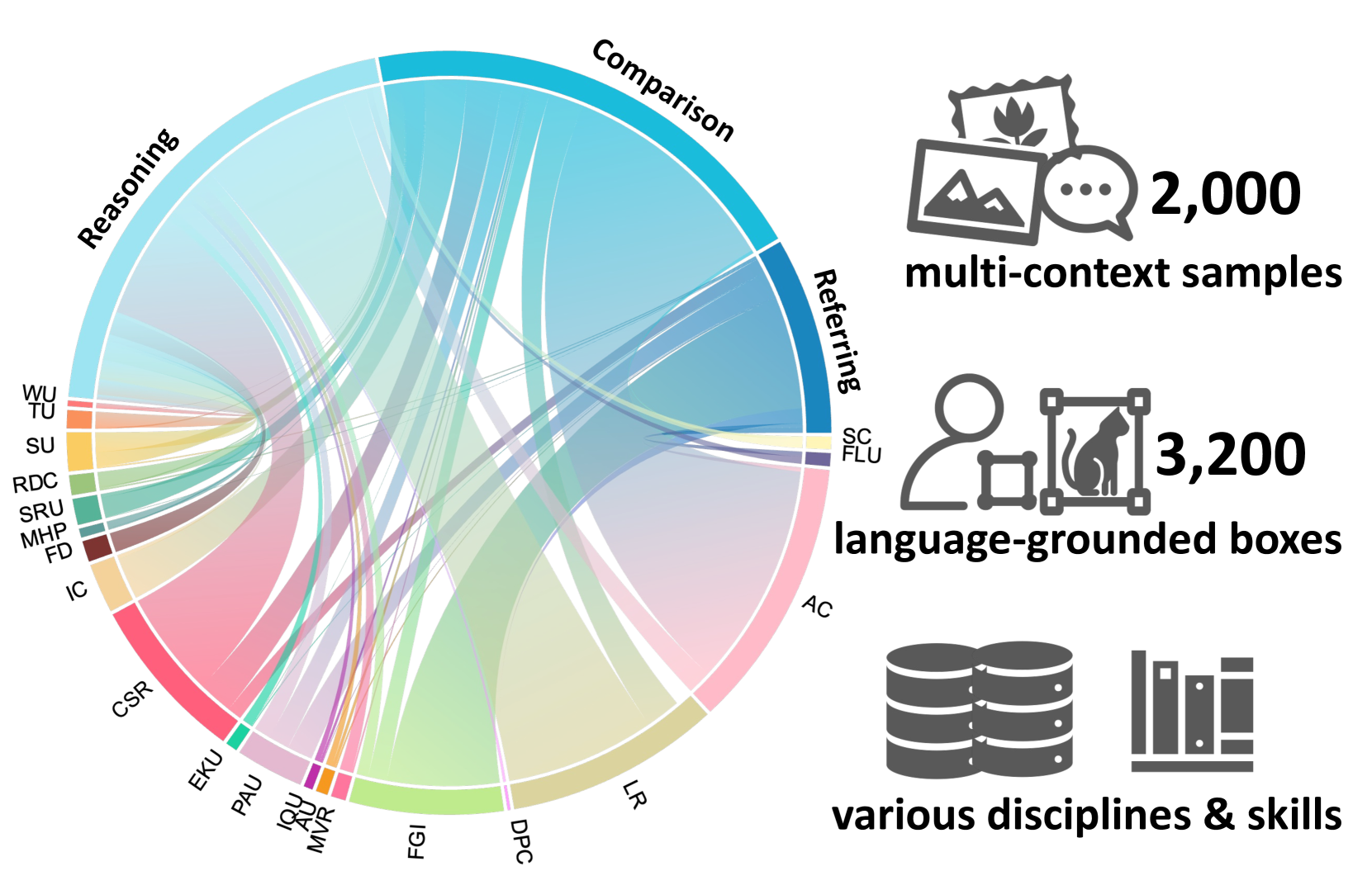 Comprehensive overview of MC-Bench's 2,000 multi-context samples across various skills and domains
Comprehensive overview of MC-Bench's 2,000 multi-context samples across various skills and domains
Data Examples
Example 1 - Referring Style:
Images: Two golf course photos
Text prompt: "People with flags in their hands"
Task: Locate all people holding flags across both images
Expected output: Bounding boxes for flag-holding individuals in both images
Example 2 - Reasoning Style:
Images: Two interview scenarios (TV studio setup, historical photos)
Text prompt: "People with the same role in the interview"
Task: Group people by their roles (interviewer, cameraman, interviewee) across contexts
Expected output: Grouped bounding boxes identifying role-based matches
 Examples showing successful grounding (left) and common failure modes (right) for different prompt styles
Examples showing successful grounding (left) and common failure modes (right) for different prompt styles
Significance
MC-Bench reveals substantial limitations in current MLLMs for multi-context visual grounding. The benchmark's comprehensive evaluation of over 20 models shows that even the best-performing systems significantly lag behind human performance (89.5% vs 69.7% accuracy). Key findings include:
- Agentic approaches (GPT-4o + G-DINO) outperform end-to-end MLLMs, achieving 66.8% accuracy and 36.2% AP50
- Scale benefits: Larger models like Qwen2-VL-72B show marked improvement over smaller variants
- Critical weaknesses: Models struggle with instance grouping, small object detection, and negative sample rejection
The benchmark highlights that current MLLMs predominantly excel at image-level understanding but fail at precise instance localization in multi-image contexts, indicating fundamental architectural limitations.
Usage
MC-Bench is publicly available at https://xuyunqiu.github.io/MC-Bench with planned leaderboard updates. The benchmark uses standard evaluation metrics including Accuracy for image-level performance and AP50 (Average Precision at IoU 0.5) for instance-level localization. Models are evaluated on their ability to identify relevant images and precisely localize target instances with bounding boxes in [x, y, w, h] format. The benchmark serves as an evaluation-only dataset with all 2,000 samples designated for testing.