Universidade de Minas Gerais
In a world of hardening borders, nations may deprive themselves of enjoying the benefits of cooperative immigrants. Here, we analyze the effect of efficient cooperative immigrants on a population playing public goods games. We considered a population structured on a square lattice with individuals playing public goods games with their neighbors. The demographics are determined by stochastic birth, death, and migration. The strategies spread through imitation dynamics. Our model shows that cooperation among natives can emerge due to social contagion of good role-model agents that can provide better quality public goods. Only a small fraction of efficient cooperators, among immigrants, is enough to trigger cooperation across the native population. We see that native cooperation achieves its peak at moderate values of immigration rate. Such efficient immigrant cooperators act as nucleation centers for the growth of cooperative clusters, that eventually dominate defection.
Cooperation is one of the foundations of human society. Many solutions to
cooperation problems have been developed and culturally transmitted across
generations. Because immigration can play a role in nourishing or disrupting
cooperation in societies, we must understand how the newcomers' culture
interacts with the hosting culture. Here, we investigate the effect of
different acculturation settings on the evolution of cooperation in spatial
public goods games with the immigration of defectors and efficient cooperators.
Here, immigrants may be socially influenced, or not, by the native culture
according to four acculturation settings: integration, where immigrants imitate
both immigrants and natives; marginalization, where immigrants do not imitate
either natives or other immigrants; assimilation, where immigrants only imitate
natives; and separation, where immigrants only imitate other immigrants. We
found that cooperation is greatly facilitated and reaches a peak for moderate
values of the migration rate under any acculturation setting. Most
interestingly, we found that the main acculturation factor driving the highest
levels of cooperation is that immigrants do not avoid social influence from
their fellow immigrants. We also show that integration may not promote the
highest level of native cooperation if the benefit of cooperation is low.
The Stag-hunt game is a prototype for social contracts. Adopting a new and better social contract is usually challenging because the current one is already widely adopted and stable due to deviants' sanctions. Thus, how does a population shift from the current social contract to a better one? In other words, how can a social system leave a local social optimum configuration to achieve an optimum global state? Here, we investigate the effect of promoting diversity on the evolution of social contracts. We considered group-structured populations where individuals play the Stag-hunt game in all groups. We model the diversity incentive as a Snow-drift game played in a single focus group where the individual is more prone to adopt a deviant norm. We show that moderate diversity incentives can change the system dynamics, leading the whole population to move from the locally optimal social normal to the globally optimal one. Thus, an initial fraction of adopters of the new norm can drive the system toward the new social optimum norm. After the new social contract becomes the new equilibrium, it remains stable even without the incentive. The results are obtained using Monte Carlo simulations and analytical approximation methods.
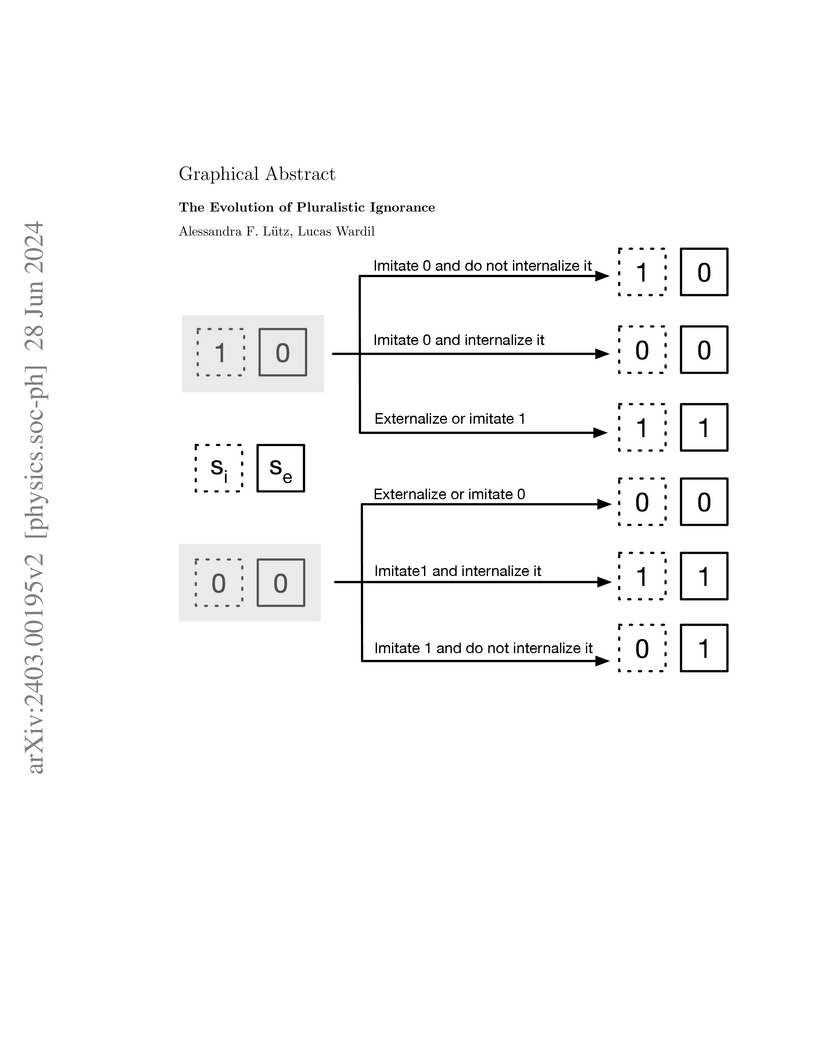
Pluralistic ignorance is a social-psychological phenomenon that occurs when
individuals privately hold beliefs that differ from perceived group norms.
Traditional models, based on opinion dynamics with private and public states,
fail to account for a key aspect: when nonexpression aligns with normative
behavior, initial social pressure can induce pluralistic ignorance. We show
that pluralistic ignorance persists under infrequent imitation and strong
initial minority influence. Although individuals can overcome this ignorance by
the end of interactions, it reemerges in subsequent meetings. However,
excessive imitation erases pluralistic ignorance, leading to a uniform state in
which internal and external states align. Furthermore, incorporating memory
into the internalization process shows that pluralistic ignorance peaks at
moderate imitation levels.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.