Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
We give simple and unified proofs of weak holomorhpic Morse inequalities on complete manifolds, q-convex manifolds, pseudoconvex domains, weakly 1-complete manifolds and covering manifolds. This paper is essentially based on the asymptotic Bergman kernel functions and the Bochner-Kodaira-Nakano formulas.
07 Jan 2025
In any dimension N≥1, for given mass a>0, we look to critical points of the energy functional
I(u)=21∫RN∣∇u∣2dx+∫RNu2∣∇u∣2dx−p1∫RN∣u∣pdx constrained to the set
Sa={u∈X∣∫RN∣u∣2dx=a},
where X:=\left\{u \in H^1(\mathbb{R}^N)\Big| \int_{\mathbb{R}^N} u^2|\nabla u|^2 dx <\infty\right\}.
We focus on the mass super-critical case 4+\frac{4}{N}0when1\leq N\leq 4.ForN\geq 5,wefindanexplicitnumbera_0suchthattheexistenceofminimizeristrueifandonlyifa\in (0, a_0]$.
In the mass super-critical case, the existence of a minimizer to the problem Ma, or more generally the existence of a constrained critical point of I on Sa, had hitherto only been obtained by assuming that p≤2∗. In particular, the restriction N≤3 was necessary.
We also study the asymptotic behavior of the minimizers to Ma as the mass a↓0, as well as when a↑a∗, where a∗=+∞ for 1≤N≤4, while a∗=a0 for N≥5.
26 Feb 2025
Yui and Zagier made some fascinating conjectures on the factorization on the
norm of the difference of Weber class invariants $ f(\mathfrak a_1) -
f(\mathfrak a_2)basedontheircalculationin\citeYZ.Here\mathfrak a_i$
belong two diferent ideal classes of discrimants Di in imagainary quadratic
fields Q(Di). In \cite{LY}, we proved these conjectures and
their generalizations when (D1,D2)=1 using the so-called big CM value
formula of Borcherds lifting. In this sequel, we prove the conjectures when
Q(D1)=Q(D2) using the so-called small CM
value formula. In addition, we give a precise factorization formula for the
resultant of two different Weber class invariant polynomials for distinct
orders.
25 Oct 2024
In this work, we establish modular parameterizations for two general formulas for π1 that subsume conjectural Ramanujan type formulas due to Z.-W. Sun, which have remained open since 2011. As an application of this, in a conceptual way we interpret how Sun's conjectural formulas arise and can be verified, as well as recover other cases that were proved by Cooper, Wan and Zudilin.
22 Jul 2025
The signs of Fourier coefficients of certain eta quotients are determined by dissecting expansions for theta functions and by applying a general dissection formula for certain classes of quintuple products. A characterization is given for the coefficient sign patterns for (qp;qp)∞(qi;qi)∞ for integers i>1 and primes p>3. The sign analysis for this quotient addresses and extends a conjecture of Bringmann et al. for the coefficients of (q2;q2)∞(q5;q5)∞−1. The sign distribution for additional classes of eta quotients is considered. This addresses multiple conjectures posed by Bringmann et al.
20 Oct 2025
We use certain Morse functions to construct conformal metrics with negative sectional curvature on locally conformally flat manifolds with boundary. Moreover, without conformally flatness assumption, we also construct conformal metric of positive Einstein tensor.
03 Jun 2025
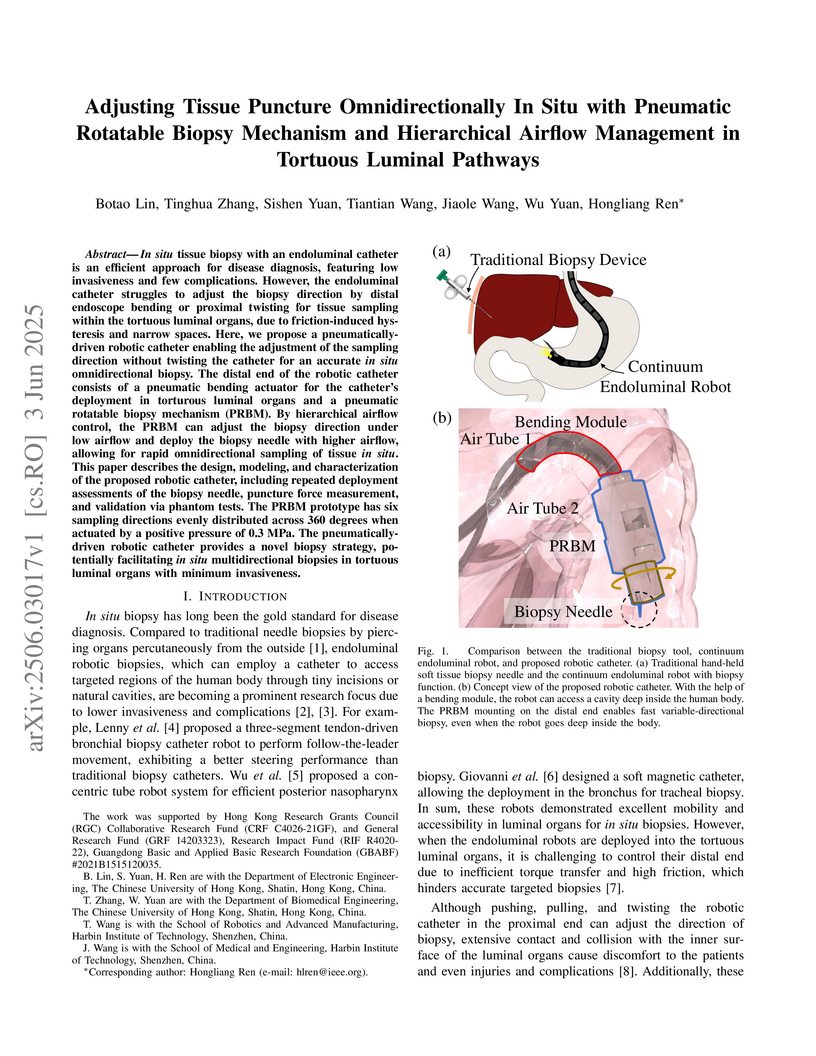
In situ tissue biopsy with an endoluminal catheter is an efficient approach
for disease diagnosis, featuring low invasiveness and few complications.
However, the endoluminal catheter struggles to adjust the biopsy direction by
distal endoscope bending or proximal twisting for tissue sampling within the
tortuous luminal organs, due to friction-induced hysteresis and narrow spaces.
Here, we propose a pneumatically-driven robotic catheter enabling the
adjustment of the sampling direction without twisting the catheter for an
accurate in situ omnidirectional biopsy. The distal end of the robotic catheter
consists of a pneumatic bending actuator for the catheter's deployment in
torturous luminal organs and a pneumatic rotatable biopsy mechanism (PRBM). By
hierarchical airflow control, the PRBM can adjust the biopsy direction under
low airflow and deploy the biopsy needle with higher airflow, allowing for
rapid omnidirectional sampling of tissue in situ. This paper describes the
design, modeling, and characterization of the proposed robotic catheter,
including repeated deployment assessments of the biopsy needle, puncture force
measurement, and validation via phantom tests. The PRBM prototype has six
sampling directions evenly distributed across 360 degrees when actuated by a
positive pressure of 0.3 MPa. The pneumatically-driven robotic catheter
provides a novel biopsy strategy, potentially facilitating in situ
multidirectional biopsies in tortuous luminal organs with minimum invasiveness.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.