Kamnoetvidya Science Academy
While there have been increased researches using deep learning techniques for
the extraction of vascular structure from the 2D en face OCTA, for such
approach, it is known that the data annotation process on the curvilinear
structure like the retinal vasculature is very costly and time consuming,
albeit few tried to address the annotation problem.
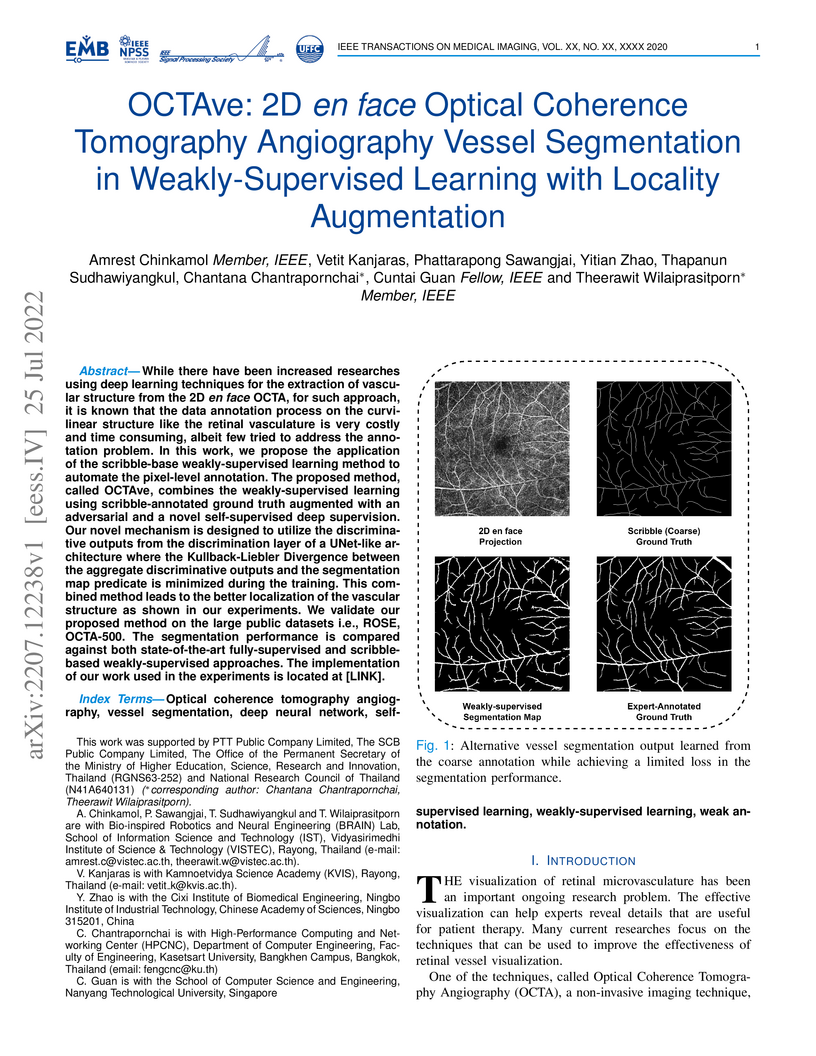
In this work, we propose the application of the scribble-base
weakly-supervised learning method to automate the pixel-level annotation. The
proposed method, called OCTAve, combines the weakly-supervised learning using
scribble-annotated ground truth augmented with an adversarial and a novel
self-supervised deep supervision. Our novel mechanism is designed to utilize
the discriminative outputs from the discrimination layer of a UNet-like
architecture where the Kullback-Liebler Divergence between the aggregate
discriminative outputs and the segmentation map predicate is minimized during
the training. This combined method leads to the better localization of the
vascular structure as shown in our experiments. We validate our proposed method
on the large public datasets i.e., ROSE, OCTA-500. The segmentation performance
is compared against both state-of-the-art fully-supervised and scribble-based
weakly-supervised approaches. The implementation of our work used in the
experiments is located at [LINK].
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.