machine-learning
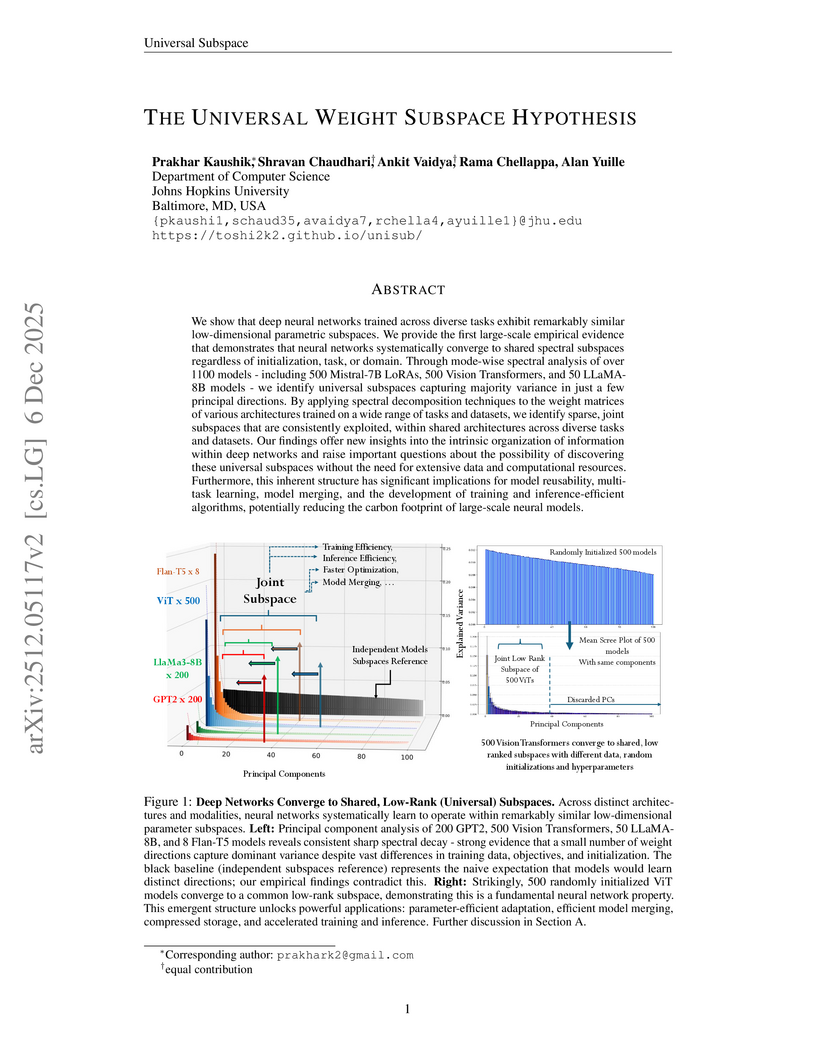
This paper presents the Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis, demonstrating empirically that deep neural networks trained across diverse tasks and modalities converge to shared low-dimensional parametric subspaces. This convergence enables significant memory savings, such as up to 100x for Vision Transformers and LLaMA models, and 19x for LoRA adapters, while preserving model performance and enhancing efficiency in model merging and adaptation.
Researchers from University of Wisconsin-Madison, UCLA, and Adobe Research introduce a computational framework for "relational visual similarity," which identifies image commonalities based on abstract logic rather than surface features. Their `relsim` model, trained on a novel dataset of images paired with anonymous group-derived captions, aligns significantly with human perception of relational similarity and outperforms existing attribute-based metrics in retrieval tasks.
Recent advances in diffusion transformers have empowered video generation models to generate high-quality video clips from texts or images. However, world models with the ability to predict long-horizon futures from past observations and actions remain underexplored, especially for general-purpose scenarios and various forms of actions. To bridge this gap, we introduce Astra, an interactive general world model that generates real-world futures for diverse scenarios (e.g., autonomous driving, robot grasping) with precise action interactions (e.g., camera motion, robot action). We propose an autoregressive denoising architecture and use temporal causal attention to aggregate past observations and support streaming outputs. We use a noise-augmented history memory to avoid over-reliance on past frames to balance responsiveness with temporal coherence. For precise action control, we introduce an action-aware adapter that directly injects action signals into the denoising process. We further develop a mixture of action experts that dynamically route heterogeneous action modalities, enhancing versatility across diverse real-world tasks such as exploration, manipulation, and camera control. Astra achieves interactive, consistent, and general long-term video prediction and supports various forms of interactions. Experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate the improvements of Astra in fidelity, long-range prediction, and action alignment over existing state-of-the-art world models.
08 Dec 2025
Researchers from Harvard University and Perplexity conducted a large-scale field study on the real-world adoption and usage of general-purpose AI agents, leveraging hundreds of millions of user interactions with Perplexity's Comet AI-powered browser and its integrated Comet Assistant. The study provides foundational evidence on who uses these agents, their usage intensity, and a detailed breakdown of use cases via a novel hierarchical taxonomy.
Researchers at ShanghaiTech University and Ant Group developed FlashMHF, an efficient multi-head Feed-Forward Network (FFN) for Transformer architectures that integrates a multi-head design with an I/O-aware fused kernel. This approach consistently improves language modeling perplexity and downstream task accuracy while reducing peak memory usage by 3-5x and accelerating inference up to 1.08x compared to standard FFNs.
The paper introduces Group Representational Position Encoding (GRAPE), a unified group-theoretic framework that re-conceptualizes and unifies existing positional encoding mechanisms like RoPE and ALiBi. It provides a principled design space for new encodings, demonstrating improved training stability and superior zero-shot performance in large language models.
Reinforcement learning (RL) post-training is crucial for aligning generative models with human preferences, but its prohibitive computational cost remains a major barrier to widespread adoption. We introduce \textbf{TreeGRPO}, a novel RL framework that dramatically improves training efficiency by recasting the denoising process as a search tree. From shared initial noise samples, TreeGRPO strategically branches to generate multiple candidate trajectories while efficiently reusing their common prefixes. This tree-structured approach delivers three key advantages: (1) \emph{High sample efficiency}, achieving better performance under same training samples (2) \emph{Fine-grained credit assignment} via reward backpropagation that computes step-specific advantages, overcoming the uniform credit assignment limitation of trajectory-based methods, and (3) \emph{Amortized computation} where multi-child branching enables multiple policy updates per forward pass. Extensive experiments on both diffusion and flow-based models demonstrate that TreeGRPO achieves \textbf{2.4× faster training} while establishing a superior Pareto frontier in the efficiency-reward trade-off space. Our method consistently outperforms GRPO baselines across multiple benchmarks and reward models, providing a scalable and effective pathway for RL-based visual generative model alignment. The project website is available at this http URL.
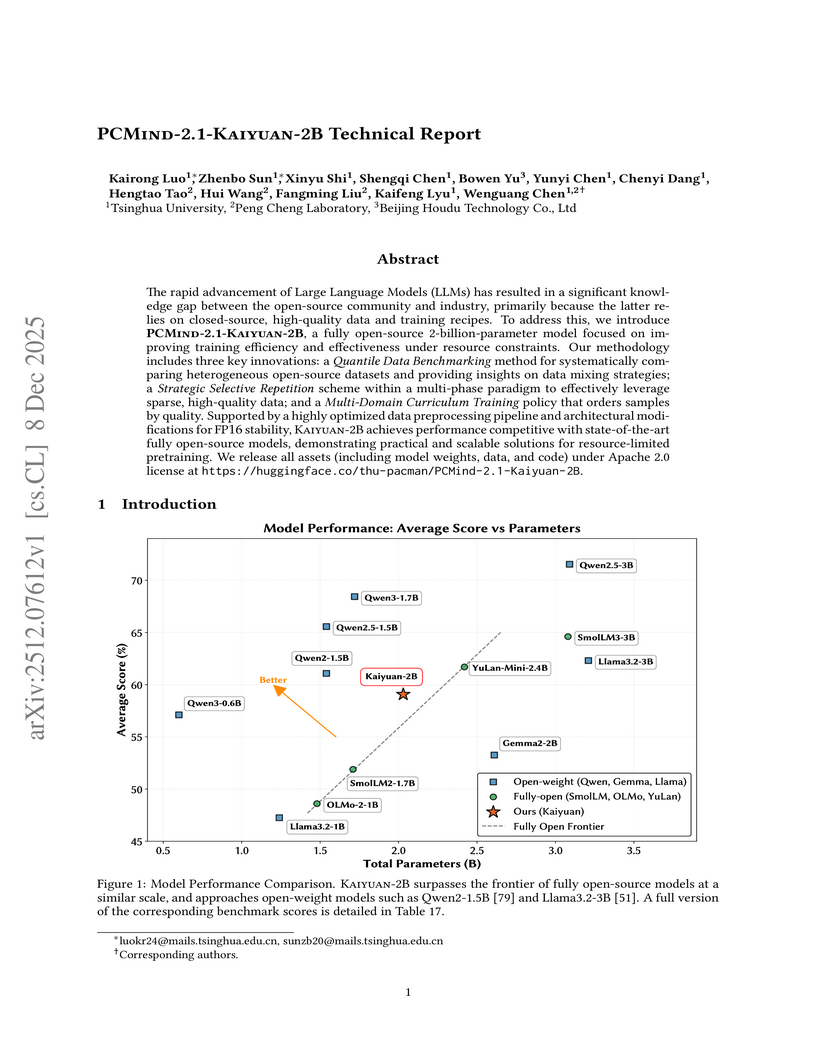
Researchers from Tsinghua University and Peng Cheng Laboratory developed PCMind-2.1-Kaiyuan-2B, a fully open-source 2-billion-parameter language model. It achieves competitive performance in Chinese language understanding, mathematical reasoning, and code generation by employing a multi-phase curriculum training with strategic data repetition and architectural modifications for FP16 stability, attaining an overall average score of 59.07% across evaluated benchmarks and outperforming several existing open-source models in its class.
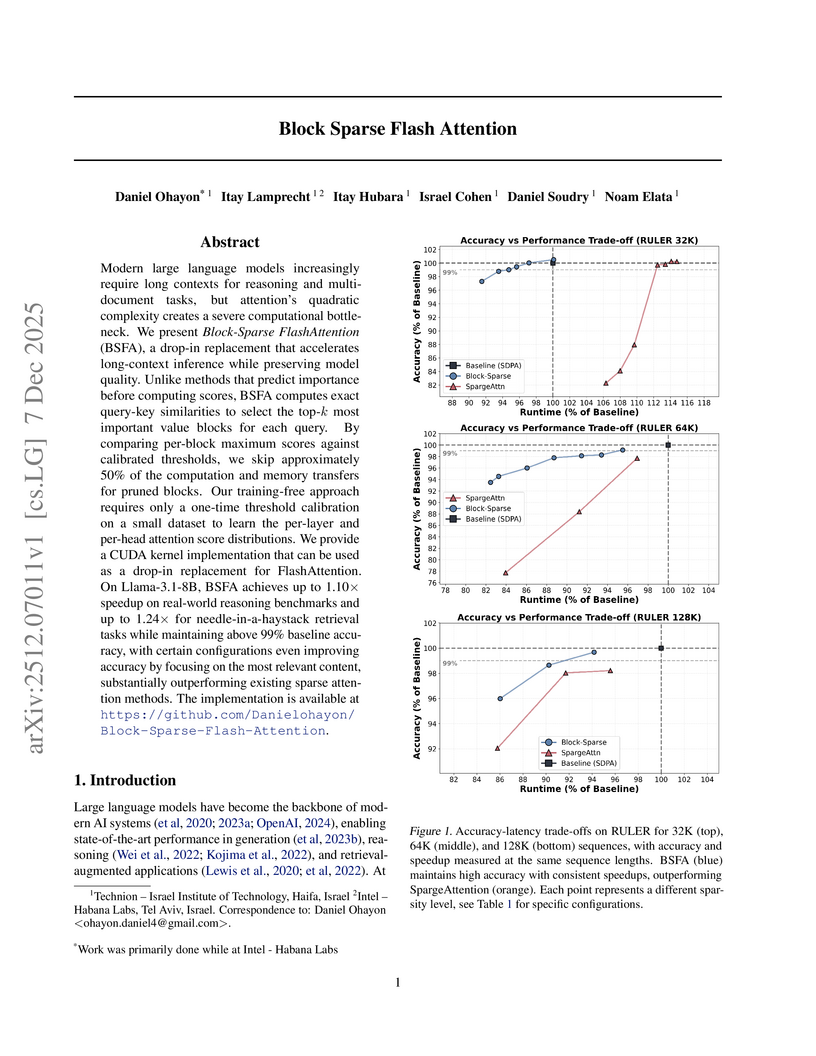
Modern large language models increasingly require long contexts for reasoning and multi-document tasks, but attention's quadratic complexity creates a severe computational bottleneck. We present Block-Sparse FlashAttention (BSFA), a drop-in replacement that accelerates long-context inference while preserving model quality. Unlike methods that predict importance before computing scores, BSFA computes exact query-key similarities to select the top-k most important value blocks for each query. By comparing per-block maximum scores against calibrated thresholds, we skip approximately 50% of the computation and memory transfers for pruned blocks. Our training-free approach requires only a one-time threshold calibration on a small dataset to learn the per-layer and per-head attention score distributions. We provide a CUDA kernel implementation that can be used as a drop-in replacement for FlashAttention. On Llama-3.1-8B, BSFA achieves up to 1.10x speedup on real-world reasoning benchmarks and up to 1.24x for needle-in-a-haystack retrieval tasks while maintaining above 99% baseline accuracy, with certain configurations even improving accuracy by focusing on the most relevant content, substantially outperforming existing sparse attention methods. The implementation is available at this https URL
Researchers from Alibaba Group and Wuhan University developed MUSE, a multimodal search-based framework for lifelong user interest modeling that integrates rich semantic information across both retrieval and fine-grained modeling stages. Deployed in Taobao's display advertising system, MUSE achieved a +12.6% CTR, +5.1% RPM, and +11.4% ROI in online A/B tests.
Researchers at Anthropic introduced Selective GradienT Masking (SGTM), a pre-training method designed to localize and remove specific capabilities from large language models to address dual-use risks. This technique achieves an improved trade-off between retaining general knowledge and forgetting targeted information, resists adversarial fine-tuning up to 7 times better than prior unlearning methods, and demonstrates reduced information leakage in larger models.
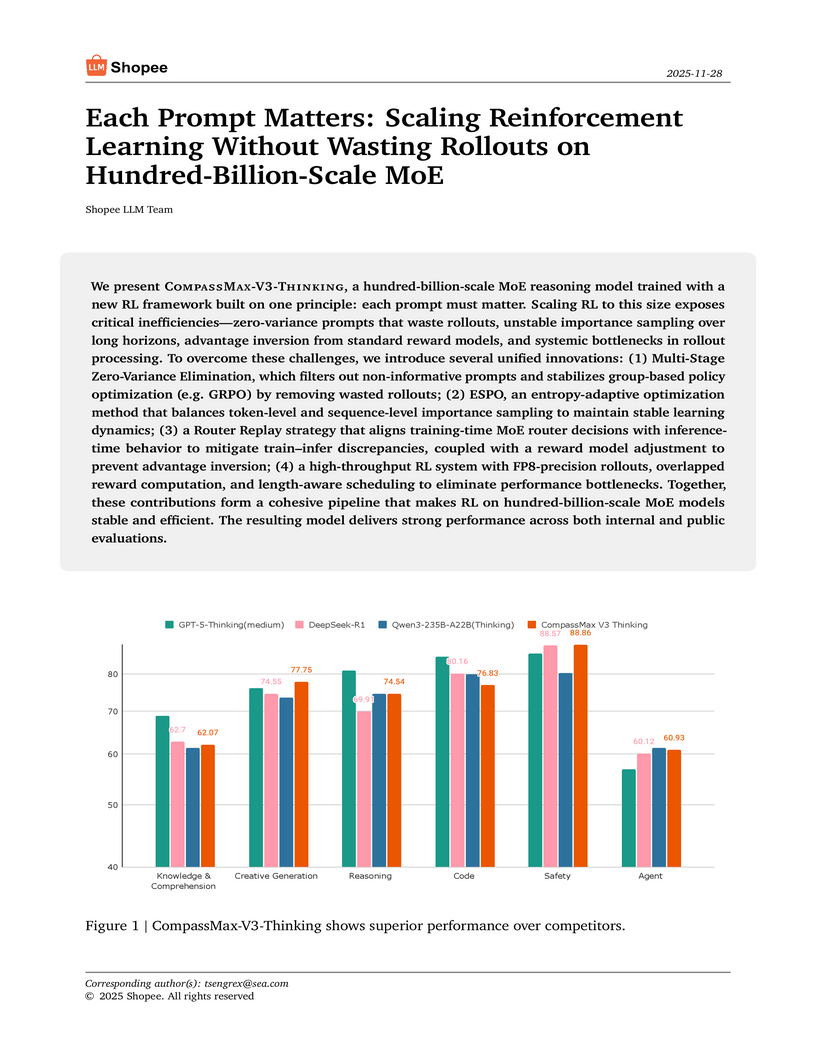
The Shopee LLM Team developed an integrated Reinforcement Learning framework for stable and efficient training of hundred-billion-scale Mixture-of-Experts models, culminating in CompassMax-V3-Thinking. This framework mitigates critical inefficiencies and instabilities in large-scale RL, leading to state-of-the-art performance across diverse reasoning and domain-specific e-commerce tasks.
An independent research team secured 1st place in the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge, achieving a 26% q-score by enhancing a Vision-Language-Action model (Pi0.5) with innovations like correlated noise for flow matching, "System 2" stage tracking, and practical inference-time heuristics. The approach demonstrated emergent recovery behaviors and addressed challenges in long-horizon, complex manipulation tasks.
Edward Y. Chang from Stanford University proposes a "Substrate plus Coordination" framework for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that Large Language Models (LLMs) provide a necessary System-1 pattern-matching substrate that requires a System-2 coordination layer to achieve reliable, goal-directed reasoning. This work formalizes semantic anchoring through the Unified Contextual Control Theory (UCCT) and introduces the Multi-Agent Collaborative Intelligence (MACI) architecture to implement this missing layer.
Researchers at Southern Methodist University systematically compared various memory encoding and injection methods for transformer-based world models, finding that State-Space Models (SSMs) combined with attention-based injection offer a scalable approach for enhancing long-term recall. This hybrid strategy significantly improved consistency over extended imagination horizons compared to a vanilla Vision Transformer, effectively mitigating perceptual drift.
A two-stage self-supervised framework integrates the Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) with Density Adaptive Attention Mechanisms (DAAM) to learn robust speech representations. This approach generates efficient, reversible discrete speech tokens at an ultra-low rate of 47.5 tokens/sec, designed for seamless integration with large language models.
02 Dec 2025
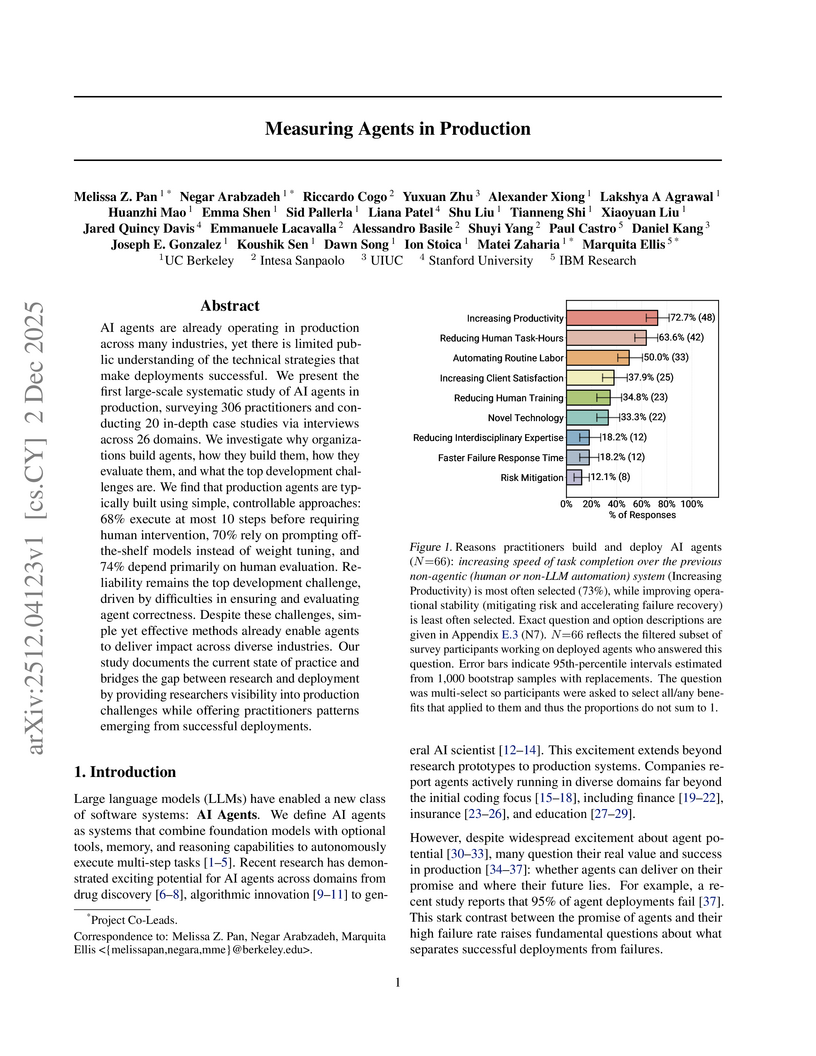
An empirical study surveyed 306 AI agent practitioners and conducted 20 in-depth case studies to analyze the technical strategies, architectural patterns, and challenges of successfully deployed AI agents. The research reveals how real-world production agents prioritize reliability and controlled autonomy to achieve productivity gains across diverse industries.
KAIST researchers developed TabPFN-GN, a method that reformulates graph node classification as a tabular learning problem, enabling a pre-trained tabular foundation model to achieve competitive or superior performance compared to Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) without graph-specific training. The method outperforms baseline GNNs on 5 out of 6 heterophilous datasets and ranks first on 3 homophilous datasets.
Conventional wisdom in the age of LLMs dictates that solving IQ-test-like visual puzzles from the ARC-AGI-1 benchmark requires capabilities derived from massive pretraining. To counter this, we introduce CompressARC, a 76K parameter model without any pretraining that solves 20% of evaluation puzzles by minimizing the description length (MDL) of the target puzzle purely during inference time. The MDL endows CompressARC with extreme generalization abilities typically unheard of in deep learning. To our knowledge, CompressARC is the only deep learning method for ARC-AGI where training happens only on a single sample: the target inference puzzle itself, with the final solution information removed. Moreover, CompressARC does not train on the pre-provided ARC-AGI "training set". Under these extremely data-limited conditions, we do not ordinarily expect any puzzles to be solvable at all. Yet CompressARC still solves a diverse distribution of creative ARC-AGI puzzles, suggesting MDL to be an alternative feasible way to produce intelligence, besides conventional pretraining.
08 Dec 2025
The ReLaX framework improves reasoning capabilities in Large Reasoning Models by addressing premature policy convergence through latent exploration, employing Koopman operator theory and Dynamic Spectral Dispersion. This approach enables sustained performance gains, achieving state-of-the-art results in both multimodal and mathematical reasoning benchmarks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.