Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPIDS)
15 Feb 2024
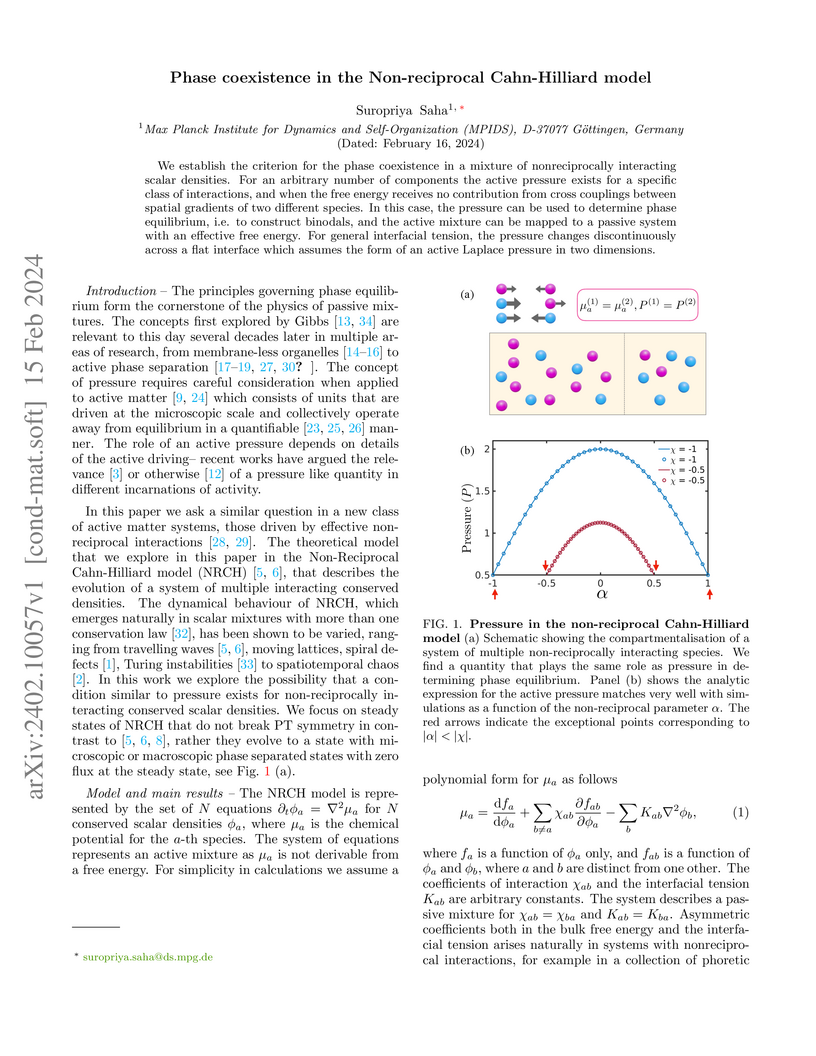
We establish the criterion for the phase coexistence in a mixture of nonreciprocally interacting scalar densities. For an arbitrary number of components the active pressure exists for a specific class of interactions, and when the free energy receives no contribution from cross couplings between spatial gradients of two different species. In this case, the pressure can be used to determine phase equilibrium, i.e. to construct binodals, and the active mixture can be mapped to a passive system with an effective free energy. For general interfacial tension, the pressure changes discontinuously across a flat interface which assumes the form of an active Laplace pressure in two dimensions.
Optimal percolation concerns the identification of the minimum-cost strategy
for the destruction of any extensive connected components in a network.
Solutions of such a dismantling problem are important for the design of optimal
strategies of disease containment based either on immunization or social
distancing. Depending on the specific variant of the problem considered,
network dismantling is performed via the removal of nodes or edges, and
different cost functions are associated to the removal of these microscopic
elements. In this paper, we show that network representations in geometric
space can be used to solve several variants of the network dismantling problem
in a coherent fashion. Once a network is embedded, dismantling is implemented
using intuitive geometric strategies. We demonstrate that the approach well
suits both Euclidean and hyperbolic network embeddings. Our systematic analysis
on synthetic and real networks demonstrates that the performance of
embedding-aided techniques is comparable to, if not better than, the one of the
best dismantling algorithms currently available on the market.
15 Oct 2014
Natural and man-made transport webs are frequently dominated by dense sets of
nested cycles. The architecture of these networks, as defined by the topology
and edge weights, determines how efficiently the networks perform their
function. Yet, the set of tools that can characterize such a weighted
cycle-rich architecture in a physically relevant, mathematically compact way is
sparse. In order to fill this void, we have developed a new algorithm that
rests on an abstraction of the physical `tiling' in the case of a two
dimensional network to an effective tiling of an abstract surface in space that
the network may be thought to sit in. Generically these abstract surfaces are
richer than the flat plane and as a result there are now two families of
fundamental units that may aggregate upon cutting weakest links -- the
plaquettes of the tiling and the longer `topological' cycles associated with
the abstract surface itself. Upon sequential removal of the weakest links, as
determined by the edge weight, neighboring plaquettes merge and a tree
characterizing this merging process results. The properties of this
characteristic tree can provide the physical and topological data required to
describe the architecture of the network and to build physical models. The new
algorithm can be used for automated phenotypic characterization of any weighted
network whose structure is dominated by cycles, such as mammalian vasculature
in the organs, the root networks of clonal colonies like quaking aspen, or the
force networks in jammed granular matter.
07 Apr 2020
We study the nonequilibrium interaction of two isotropic chemically-active particles taking into account the exact near-field chemical interactions as well as hydrodynamic interactions. We identify regions in the parameter space wherein the dynamical system describing the two particles can have a fixed-point---a phenomenon that cannot be captured under the far-field approximation. We find that due to near-field effects, the particles may reach a stable equilibrium at a nonzero gap size, or make a complex that can dissociate in the presence of sufficiently strong noise. We explicitly show that the near-field effects are originated from a self-generated neighbor-reflected chemical gradient, similar to interactions of a self-propelling phoretic particle and a flat substrate.
05 Mar 2014
Non-normal transient growth of disturbances is considered as an essential
prerequisite for subcritical transition in shear flows, i.e. transition to
turbulence despite linear stability of the laminar flow. In this work we
present numerical and analytical computations of linear transient growth
covering all linearly stable regimes of Taylor--Couette flow. Our numerical
experiments reveal comparable energy amplifications in the different regimes.
For high shear Reynolds numbers Re the optimal transient energy growth always
follows a 2/3-scaling with Re, which allows for large amplifications even in
regimes where the presence of turbulence remains debated. In co-rotating
Rayleigh-stable flows the optimal perturbations become increasingly columnar in
their structure, as the optimal axial wavenumber goes to zero. In this limit of
axially invariant perturbations we show that linear stability and transient
growth are independent of the cylinders' rotation-ratio and we derive a
universal 2/3-scaling of optimal energy growth with Re using WKB-theory. Based
on this, a semi-empirical formula for the estimation of linear transient growth
valid in all regimes is obtained.
Reliable functioning of infrastructure networks is essential for our modern society. Cascading failures are the cause of most large-scale network outages. Although cascading failures often exhibit dynamical transients, the modeling of cascades has so far mainly focused on the analysis of sequences of steady states. In this article, we focus on electrical transmission networks and introduce a framework that takes into account both the event-based nature of cascades and the essentials of the network dynamics. We find that transients of the order of seconds in the flows of a power grid play a crucial role in the emergence of collective behaviors. We finally propose a forecasting method to identify critical lines and components in advance or during operation. Overall, our work highlights the relevance of dynamically induced failures on the synchronization dynamics of national power grids of different European countries and provides methods to predict and model cascading failures.
Nonreciprocal interactions are commonplace in continuum-level descriptions of both biological and synthetic active matter, yet studies addressing their implications for time-reversibility have so far been limited to microscopic models. Here, we derive a general expression for the average rate of informational entropy production in the most generic mixture of conserved phase fields with nonreciprocal couplings and additive conservative noise. For the particular case of a binary system with Cahn-Hilliard dynamics augmented by nonreciprocal cross-diffusion terms, we observe a non-trivial scaling of the entropy production rate across a parity-time symmetry breaking phase transition. We derive a closed-form analytic expression in the weak-noise regime for the entropy production rate due to the emergence of a macroscopic dynamic phase, showing it can be written in terms of the global polar order parameter, a measure of parity-time symmetry breaking.
The mean compositions of individual components can be tuned to control phase behavior in number-conserving passive mixtures. In this work, we investigate the role of variable average density in a system of infinitely many non-reciprocally interacting scalar densities, within the framework of the multi-species non-reciprocal Cahn-Hilliard (NRCH) model. Rather than focusing on specific parameter choices, we study ensembles of systems where the inter-species interaction coefficients and average densities are sampled from probability distributions. We show that non-reciprocity stabilizes the homogeneous mixed state even in the presence of compositional disorder. Using random matrix theory, we derive a general condition for the onset of spinodal instability, which we verify through simulations. Finally, we illustrate the connection between the statistics of the most unstable eigenvalue and the emergent nonlinear dynamics.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.