Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint Laboratory for Emotional Intelligence and Pervasive Computing
Researchers at institutions including South China University of Technology and City University of Hong Kong developed SCD-MLLM, a unified framework leveraging a Multimodal Large Language Model for automatic depression detection. The system maintains stable and accurate performance across diverse real-world scenarios and effectively handles situations with partially missing input modalities.
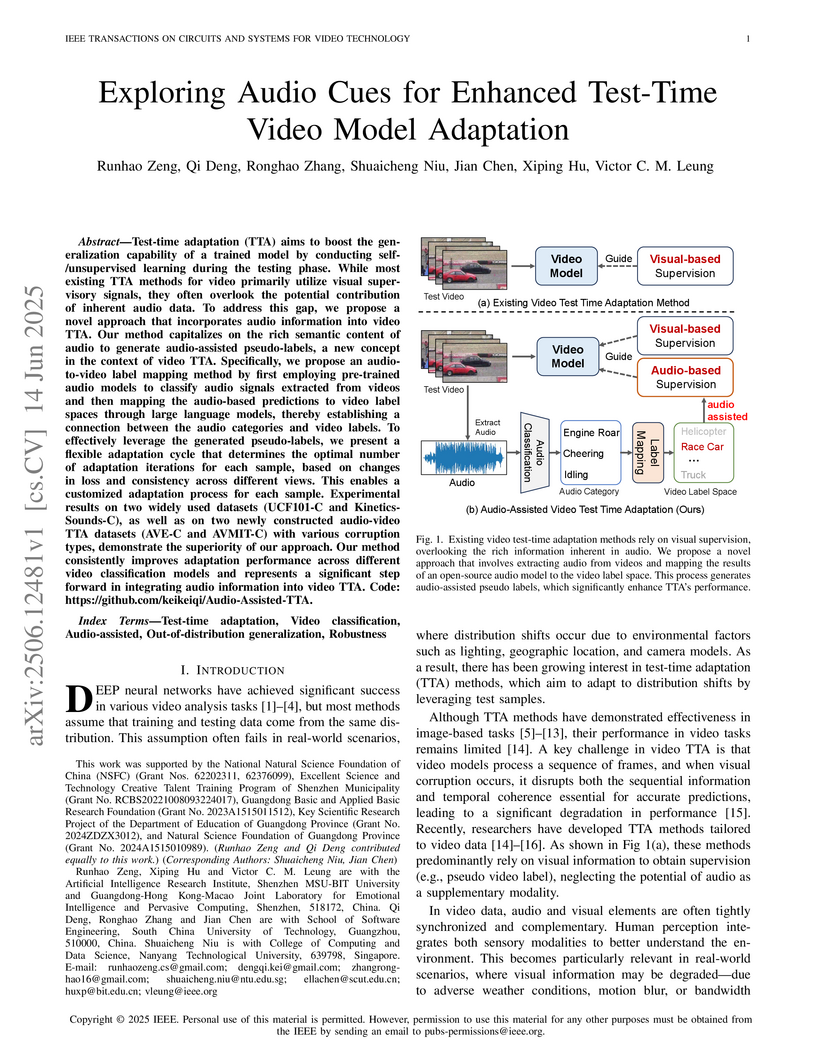
Test-time adaptation (TTA) aims to boost the generalization capability of a
trained model by conducting self-/unsupervised learning during the testing
phase. While most existing TTA methods for video primarily utilize visual
supervisory signals, they often overlook the potential contribution of inherent
audio data. To address this gap, we propose a novel approach that incorporates
audio information into video TTA. Our method capitalizes on the rich semantic
content of audio to generate audio-assisted pseudo-labels, a new concept in the
context of video TTA. Specifically, we propose an audio-to-video label mapping
method by first employing pre-trained audio models to classify audio signals
extracted from videos and then mapping the audio-based predictions to video
label spaces through large language models, thereby establishing a connection
between the audio categories and video labels. To effectively leverage the
generated pseudo-labels, we present a flexible adaptation cycle that determines
the optimal number of adaptation iterations for each sample, based on changes
in loss and consistency across different views. This enables a customized
adaptation process for each sample. Experimental results on two widely used
datasets (UCF101-C and Kinetics-Sounds-C), as well as on two newly constructed
audio-video TTA datasets (AVE-C and AVMIT-C) with various corruption types,
demonstrate the superiority of our approach. Our method consistently improves
adaptation performance across different video classification models and
represents a significant step forward in integrating audio information into
video TTA. Code: this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.