Huzhou Institute of Zhejiang University
21 Apr 2025
Zhong et al. from Zhejiang University introduce a framework that automatically generates diverse, dynamically feasible, and collision-avoiding aerobatic flight trajectories for UAVs using conditional diffusion models combined with trajectory optimization. This approach allows non-expert operators to design complex aerial maneuvers in challenging environments with minimal human intervention.
16 Jul 2025
Optimization has been widely used to generate smooth trajectories for motion planning. However, existing trajectory optimization methods show weakness when dealing with large-scale long trajectories. Recent advances in parallel computing have accelerated optimization in some fields, but how to efficiently solve trajectory optimization via parallelism remains an open question. In this paper, we propose a novel trajectory optimization framework based on the Consensus Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (CADMM) algorithm, which decomposes the trajectory into multiple segments and solves the subproblems in parallel. The proposed framework reduces the time complexity to O(1) per iteration to the number of segments, compared to O(N) of the state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches. Furthermore, we introduce a closed-form solution that integrates convex linear and quadratic constraints to speed up the optimization, and we also present numerical solutions for general inequality constraints. A series of simulations and experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms the SOTA approach in terms of efficiency and smoothness. Especially for a large-scale trajectory, with one hundred segments, achieving over a tenfold speedup. To fully explore the potential of our algorithm on modern parallel computing architectures, we deploy our framework on a GPU and show high performance with thousands of segments.
29 May 2025
Differential drive robots are widely used in various scenarios thanks to their straightforward principle, from household service robots to disaster response field robots. There are several types of driving mechanisms for real-world applications, including two-wheeled, four-wheeled skid-steering, tracked robots, and so on. The differences in the driving mechanisms usually require specific kinematic modeling when precise control is desired. Furthermore, the nonholonomic dynamics and possible lateral slip lead to different degrees of difficulty in getting feasible and high-quality trajectories. Therefore, a comprehensive trajectory optimization framework to compute trajectories efficiently for various kinds of differential drive robots is highly desirable. In this paper, we propose a universal trajectory optimization framework that can be applied to differential drive robots, enabling the generation of high-quality trajectories within a restricted computational timeframe. We introduce a novel trajectory representation based on polynomial parameterization of motion states or their integrals, such as angular and linear velocities, which inherently matches the robots' motion to the control principle. The trajectory optimization problem is formulated to minimize complexity while prioritizing safety and operational efficiency. We then build a full-stack autonomous planning and control system to demonstrate its feasibility and robustness. We conduct extensive simulations and real-world testing in crowded environments with three kinds of differential drive robots to validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Terrain analysis is critical for the practical ap- plication of ground mobile robots in real-world tasks, espe- cially in outdoor unstructured environments. In this paper, we propose a novel spatial-temporal traversability assessment method, which aims to enable autonomous robots to effectively navigate through complex terrains. Our approach utilizes sparse Gaussian processes (SGP) to extract geometric features (curvature, gradient, elevation, etc.) directly from point cloud scans. These features are then used to construct a high- resolution local traversability map. Then, we design a spatial- temporal Bayesian Gaussian kernel (BGK) inference method to dynamically evaluate traversability scores, integrating historical and real-time data while considering factors such as slope, flatness, gradient, and uncertainty metrics. GPU acceleration is applied in the feature extraction step, and the system achieves real-time performance. Extensive simulation experiments across diverse terrain scenarios demonstrate that our method outper- forms SOTA approaches in both accuracy and computational efficiency. Additionally, we develop an autonomous navigation framework integrated with the traversability map and validate it with a differential driven vehicle in complex outdoor envi- ronments. Our code will be open-source for further research and development by the community, this https URL.
26 Jun 2023
In recent years, there is a noteworthy advancement in autonomous drone racing. However, the primary focus is on attaining execution times, while scant attention is given to the challenges of dynamic environments. The high-speed nature of racing scenarios, coupled with the potential for unforeseeable environmental alterations, present stringent requirements for online replanning and its timeliness. For racing in dynamic environments, we propose an online replanning framework with an efficient polynomial trajectory representation. We trade off between aggressive speed and flexible obstacle avoidance based on an optimization approach. Additionally, to ensure safety and precision when crossing intermediate racing waypoints, we formulate the demand as hard constraints during planning. For dynamic obstacles, parallel multi-topology trajectory planning is designed based on engineering considerations to prevent racing time loss due to local optimums. The framework is integrated into a quadrotor system and successfully demonstrated at the DJI Robomaster Intelligent UAV Championship, where it successfully complete the racing track and placed first, finishing in less than half the time of the second-place.
17 Nov 2025
Differential drive mobile manipulators combine the mobility of wheeled bases with the manipulation capability of multi-joint arms, enabling versatile applications but posing considerable challenges for trajectory planning due to their high-dimensional state space and nonholonomic constraints. This paper introduces TopAY, an optimization-based planning framework designed for efficient and safe trajectory generation for differential drive mobile manipulators. The framework employs a hierarchical initial value acquisition strategy, including topological paths search for the base and parallel sampling for the manipulator. A polynomial trajectory representation with arc length-yaw parameterization is also proposed to reduce optimization complexity while preserving dynamic feasibility. Extensive simulation and real-world experiments validate that TopAY achieves higher planning efficiency and success rates than state-of-the-art method in dense and complex scenarios. The source code is released at this https URL .
05 Mar 2025
Autonomous navigation of car-like robots on uneven terrain poses unique
challenges compared to flat terrain, particularly in traversability assessment
and terrain-associated kinematic modelling for motion planning. This paper
introduces SEB-Naver, a novel SE(2)-based local navigation framework designed
to overcome these challenges. First, we propose an efficient traversability
assessment method for SE(2) grids, leveraging GPU parallel computing to enable
real-time updates and maintenance of local maps. Second, inspired by
differential flatness, we present an optimization-based trajectory planning
method that integrates terrain-associated kinematic models, significantly
improving both planning efficiency and trajectory quality. Finally, we unify
these components into SEB-Naver, achieving real-time terrain assessment and
trajectory optimization. Extensive simulations and real-world experiments
demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach. The code is at
this https URL
11 Mar 2021
The development of aerial autonomy has enabled aerial robots to fly agilely
in complex environments. However, dodging fast-moving objects in flight remains
a challenge, limiting the further application of unmanned aerial vehicles
(UAVs). The bottleneck of solving this problem is the accurate perception of
rapid dynamic objects. Recently, event cameras have shown great potential in
solving this problem. This paper presents a complete perception system
including ego-motion compensation, object detection, and trajectory prediction
for fast-moving dynamic objects with low latency and high precision. Firstly,
we propose an accurate ego-motion compensation algorithm by considering both
rotational and translational motion for more robust object detection. Then, for
dynamic object detection, an event camera-based efficient regression algorithm
is designed. Finally, we propose an optimizationbased approach that
asynchronously fuses event and depth cameras for trajectory prediction.
Extensive real-world experiments and benchmarks are performed to validate our
framework. Moreover, our code will be released to benefit related researches.
07 Sep 2021
With the autonomy of aerial robots advances in recent years, autonomous drone racing has drawn increasing attention. In a professional pilot competition, a skilled operator always controls the drone to agilely avoid obstacles in aggressive attitudes, for reaching the destination as fast as possible. Autonomous flight like elite pilots requires planning in SE(3), whose non-triviality and complexity hindering a convincing solution in our community by now. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes an open-source baseline, which includes a high-performance SE(3) planner and a challenging simulation platform tailored for drone racing. We specify the SE(3) trajectory generation as a soft-penalty optimization problem, and speed up the solving process utilizing its underlying parallel structure. Moreover, to provide a testbed for challenging the planner, we develop delicate drone racing tracks which mimic real-world set-up and necessities planning in SE(3). Besides, we provide necessary system components such as common map interfaces and a baseline controller, to make our work plug-in-and-use. With our baseline, we hope to future foster the research of SE(3) planning and the competition of autonomous drone racing.
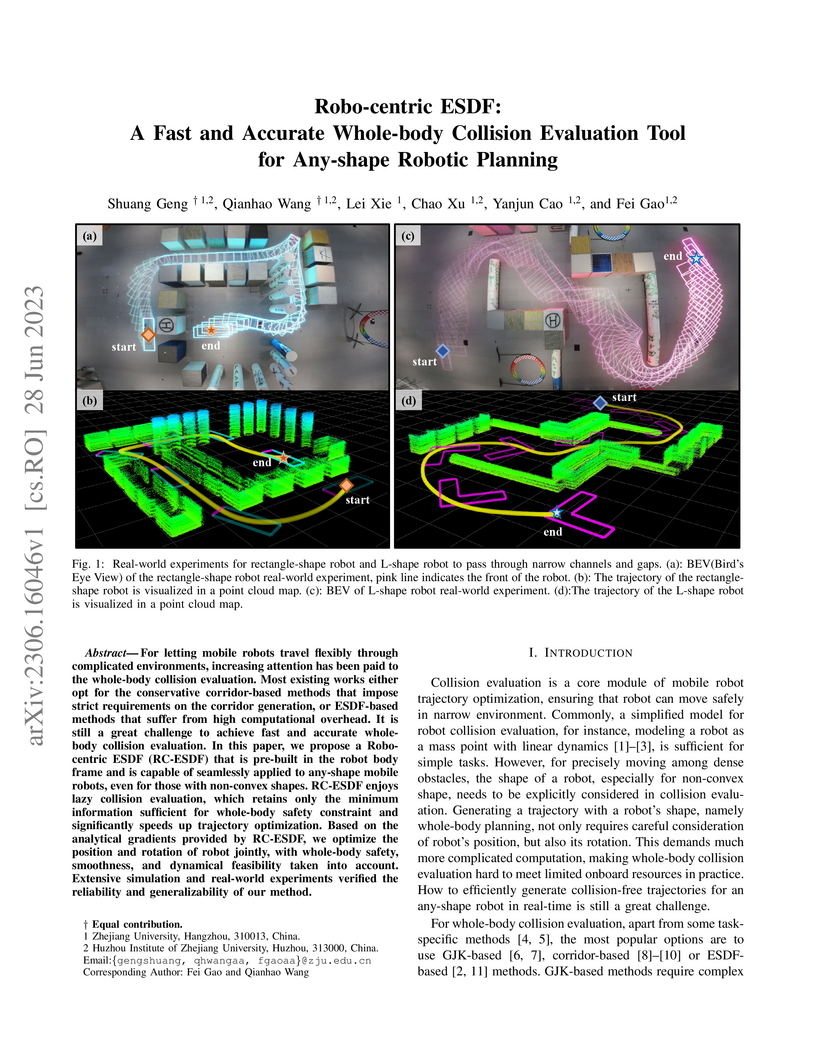
28 Jun 2023
Researchers from Zhejiang University introduced Robo-centric Euclidean Signed Distance Field (RC-ESDF) to redefine collision detection in trajectory planning by pre-computing a distance field relative to the robot. This approach facilitates real-time trajectory optimization with accurate whole-body collision checking for arbitrary robot shapes, demonstrating a 17x speedup over environment-based ESDF methods.
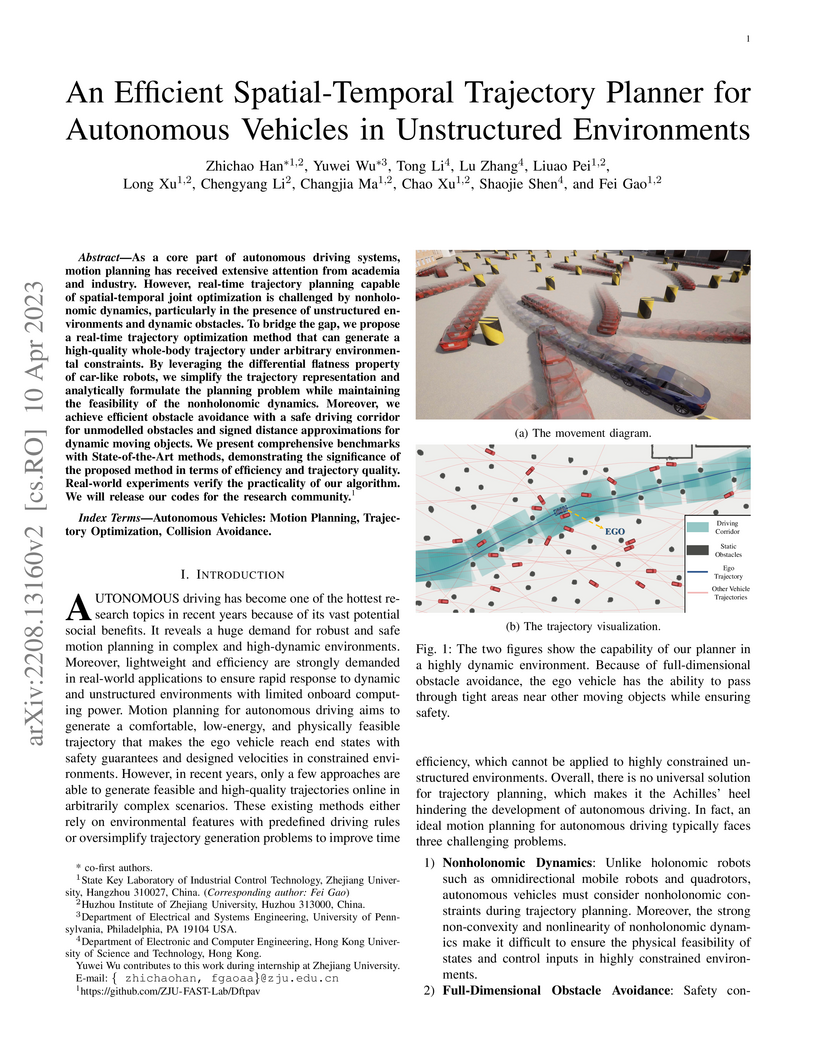
10 Apr 2023
As a core part of autonomous driving systems, motion planning has received extensive attention from academia and industry. However, real-time trajectory planning capable of spatial-temporal joint optimization is challenged by nonholonomic dynamics, particularly in the presence of unstructured environments and dynamic obstacles. To bridge the gap, we propose a real-time trajectory optimization method that can generate a high-quality whole-body trajectory under arbitrary environmental constraints. By leveraging the differential flatness property of car-like robots, we simplify the trajectory representation and analytically formulate the planning problem while maintaining the feasibility of the nonholonomic dynamics. Moreover, we achieve efficient obstacle avoidance with a safe driving corridor for unmodelled obstacles and signed distance approximations for dynamic moving objects. We present comprehensive benchmarks with State-of-the-Art methods, demonstrating the significance of the proposed method in terms of efficiency and trajectory quality. Real-world experiments verify the practicality of our algorithm. We will release our codes for the research community
14 Sep 2025
The tractor-trailer robot consists of a drivable tractor and one or more non-drivable trailers connected via hitches. Compared to typical car-like robots, the addition of trailers provides greater transportation capability. However, this also complicates motion planning due to the robot's complex kinematics, high-dimensional state space, and deformable structure. To efficiently plan safe, time-optimal trajectories that adhere to the kinematic constraints of the robot and address the challenges posed by its unique features, this paper introduces a lightweight, compact, and high-order smooth trajectory representation for tractor-trailer robots. Based on it, we design an efficiently solvable spatial-temporal trajectory optimization problem. To deal with deformable structures, which leads to difficulties in collision avoidance, we fully leverage the collisionfree regions of the environment, directly applying deformations to trajectories in continuous space. This approach not requires constructing safe regions from the environment using convex approximations through collision-free seed points before each optimization, avoiding the loss of the solution space, thus reducing the dependency of the optimization on initial values. Moreover, a multi-terminal fast path search algorithm is proposed to generate the initial values for optimization. Extensive simulation experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves severalfold improvements in efficiency compared to existing algorithms, while also ensuring lower curvature and trajectory duration. Real-world experiments involving the transportation, loading and unloading of goods in both indoor and outdoor scenarios further validate the effectiveness of our method. The source code is accessible at this https URL.
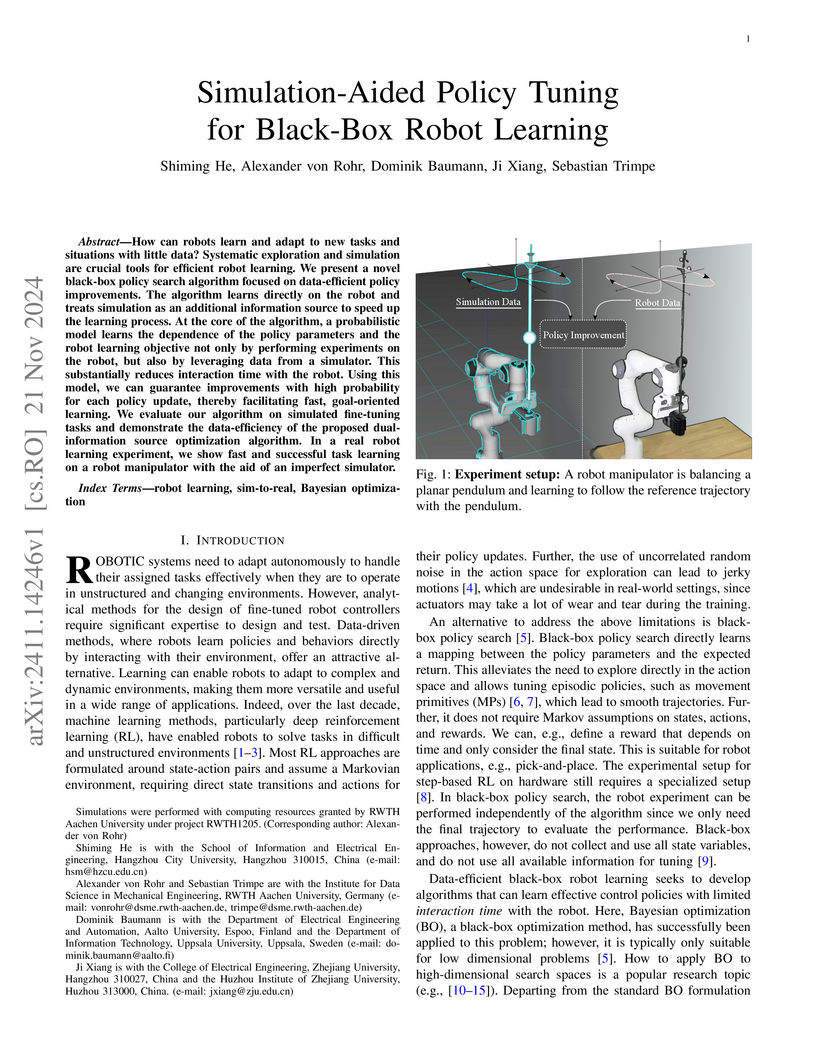
21 Nov 2024
This research from RWTH Aachen University and collaborators introduces High-Confidence Improvement GIBO (HCI-GIBO) and its extension, Simulation-Aided HCI-GIBO (S-HCI-GIBO), as data-efficient black-box optimization algorithms for robot policy tuning. S-HCI-GIBO notably reduced real robot evaluations by over 50% in a trajectory tracking task while maintaining performance, by intelligently switching between simulator and real-world queries during the learning process.
06 May 2022
Accurate and reliable sensor calibration is essential to fuse LiDAR and inertial measurements, which are usually available in robotic applications. In this paper, we propose a novel LiDAR-IMU calibration method within the continuous-time batch-optimization framework, where the intrinsics of both sensors and the spatial-temporal extrinsics between sensors are calibrated without using calibration infrastructure such as fiducial tags. Compared to discrete-time approaches, the continuous-time formulation has natural advantages for fusing high rate measurements from LiDAR and IMU sensors. To improve efficiency and address degenerate motions, two observability-aware modules are leveraged: (i) The information-theoretic data selection policy selects only the most informative segments for calibration during data collection, which significantly improves the calibration efficiency by processing only the selected informative segments. (ii) The observability-aware state update mechanism in nonlinear least-squares optimization updates only the identifiable directions in the state space with truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD), which enables accurate calibration results even under degenerate cases where informative data segments are not available. The proposed LiDAR-IMU calibration approach has been validated extensively in both simulated and real-world experiments with different robot platforms, demonstrating its high accuracy and repeatability in commonly-seen human-made environments. We also open source our codebase to benefit the research community: {\url{this https URL}}.
10 Mar 2021
In this paper, we introduce a complete system for autonomous flight of
quadrotors in dynamic environments with onboard sensing. Extended from existing
work, we develop an occlusion-aware dynamic perception method based on depth
images, which classifies obstacles as dynamic and static. For representing
generic dynamic environment, we model dynamic objects with moving ellipsoids
and fuse static ones into an occupancy grid map. To achieve dynamic avoidance,
we design a planning method composed of modified kinodynamic path searching and
gradient-based optimization. The method leverages manually constructed
gradients without maintaining a signed distance field (SDF), making the
planning procedure finished in milliseconds. We integrate the above methods
into a customized quadrotor system and thoroughly test it in realworld
experiments, verifying its effective collision avoidance in dynamic
environments.
20 Jul 2022
This letter presents a complete framework Meeting-Merging-Mission for multi-robot exploration under communication restriction. Considering communication is limited in both bandwidth and range in the real world, we propose a lightweight environment presentation method and an efficient cooperative exploration strategy. For lower bandwidth, each robot utilizes specific polytopes to maintains free space and super frontier information (SFI) as the source for exploration decision-making. To reduce repeated exploration, we develop a mission-based protocol that drives robots to share collected information in stable rendezvous. We also design a complete path planning scheme for both centralized and decentralized cases. To validate that our framework is practical and generic, we present an extensive benchmark and deploy our system into multi-UGV and multi-UAV platforms.
15 Feb 2023
Localization and mapping with heterogeneous multi-sensor fusion have been
prevalent in recent years. To adequately fuse multi-modal sensor measurements
received at different time instants and different frequencies, we estimate the
continuous-time trajectory by fixed-lag smoothing within a factor-graph
optimization framework. With the continuous-time formulation, we can query
poses at any time instants corresponding to the sensor measurements. To bound
the computation complexity of the continuous-time fixed-lag smoother, we
maintain temporal and keyframe sliding windows with constant size, and
probabilistically marginalize out control points of the trajectory and other
states, which allows preserving prior information for future sliding-window
optimization. Based on continuous-time fixed-lag smoothing, we design
tightly-coupled multi-modal SLAM algorithms with a variety of sensor
combinations, like the LiDAR-inertial and LiDAR-inertial-camera SLAM systems,
in which online timeoffset calibration is also naturally supported. More
importantly, benefiting from the marginalization and our derived analytical
Jacobians for optimization, the proposed continuous-time SLAM systems can
achieve real-time performance regardless of the high complexity of
continuous-time formulation. The proposed multi-modal SLAM systems have been
widely evaluated on three public datasets and self-collect datasets. The
results demonstrate that the proposed continuous-time SLAM systems can achieve
high-accuracy pose estimations and outperform existing state-of-the-art
methods. To benefit the research community, we will open source our code at
~\url{this https URL}.
07 Feb 2023
With the development of robotics, ground robots are no longer limited to
planar motion. Passive height variation due to complex terrain and active
height control provided by special structures on robots require a more general
navigation planning framework beyond 2D. Existing methods rarely considers both
simultaneously, limiting the capabilities and applications of ground robots. In
this paper, we proposed an optimization-based planning framework for ground
robots considering both active and passive height changes on the z-axis. The
proposed planner first constructs a penalty field for chassis motion
constraints defined in R3 such that the optimal solution space of the
trajectory is continuous, resulting in a high-quality smooth chassis
trajectory. Also, by constructing custom constraints in the z-axis direction,
it is possible to plan trajectories for different types of ground robots which
have z-axis degree of freedom. We performed simulations and realworld
experiments to verify the efficiency and trajectory quality of our algorithm.
10 Oct 2024
In recent times, an increasing number of researchers have been devoted to utilizing deep neural networks for end-to-end flight navigation. This approach has gained traction due to its ability to bridge the gap between perception and planning that exists in traditional methods, thereby eliminating delays between modules. However, the practice of replacing original modules with neural networks in a black-box manner diminishes the overall system's robustness and stability. It lacks principled explanations and often fails to consistently generate high-quality motion trajectories. Furthermore, such methods often struggle to rigorously account for the robot's kinematic constraints, resulting in the generation of trajectories that cannot be executed satisfactorily. In this work, we combine the advantages of traditional methods and neural networks by proposing an optimization-embedded neural network. This network can learn high-quality trajectories directly from visual inputs without the need of mapping, while ensuring dynamic feasibility. Here, the deep neural network is employed to directly extract environment safety regions from depth images. Subsequently, we employ a model-based approach to represent these regions as safety constraints in trajectory optimization. Leveraging the availability of highly efficient optimization algorithms, our method robustly converges to feasible and optimal solutions that satisfy various user-defined constraints. Moreover, we differentiate the optimization process, allowing it to be trained as a layer within the neural network. This approach facilitates the direct interaction between perception and planning, enabling the network to focus more on the spatial regions where optimal solutions exist. As a result, it further enhances the quality and stability of the generated trajectories.
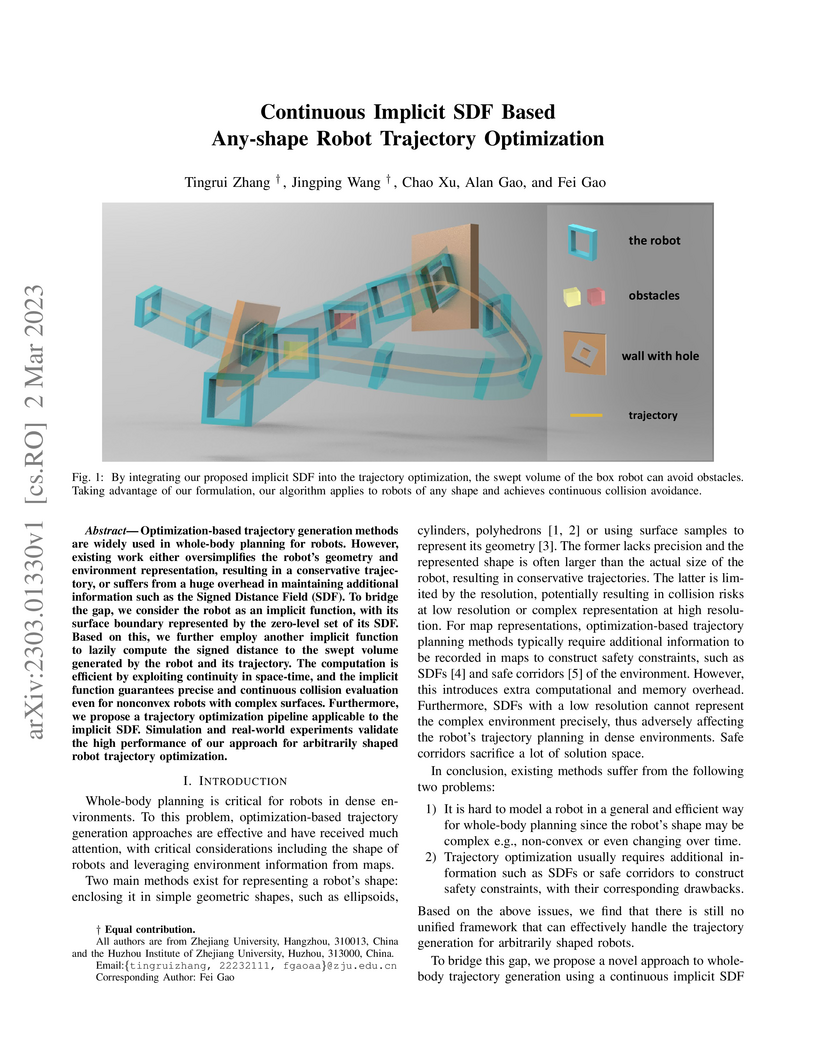
02 Mar 2023
Optimization-based trajectory generation methods are widely used in whole-body planning for robots. However, existing work either oversimplifies the robot's geometry and environment representation, resulting in a conservative trajectory, or suffers from a huge overhead in maintaining additional information such as the Signed Distance Field (SDF). To bridge the gap, we consider the robot as an implicit function, with its surface boundary represented by the zero-level set of its SDF. Based on this, we further employ another implicit function to lazily compute the signed distance to the swept volume generated by the robot and its trajectory. The computation is efficient by exploiting continuity in space-time, and the implicit function guarantees precise and continuous collision evaluation even for nonconvex robots with complex surfaces. Furthermore, we propose a trajectory optimization pipeline applicable to the implicit SDF. Simulation and real-world experiments validate the high performance of our approach for arbitrarily shaped robot trajectory optimization.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.