IFISC (UIB-CSIC)
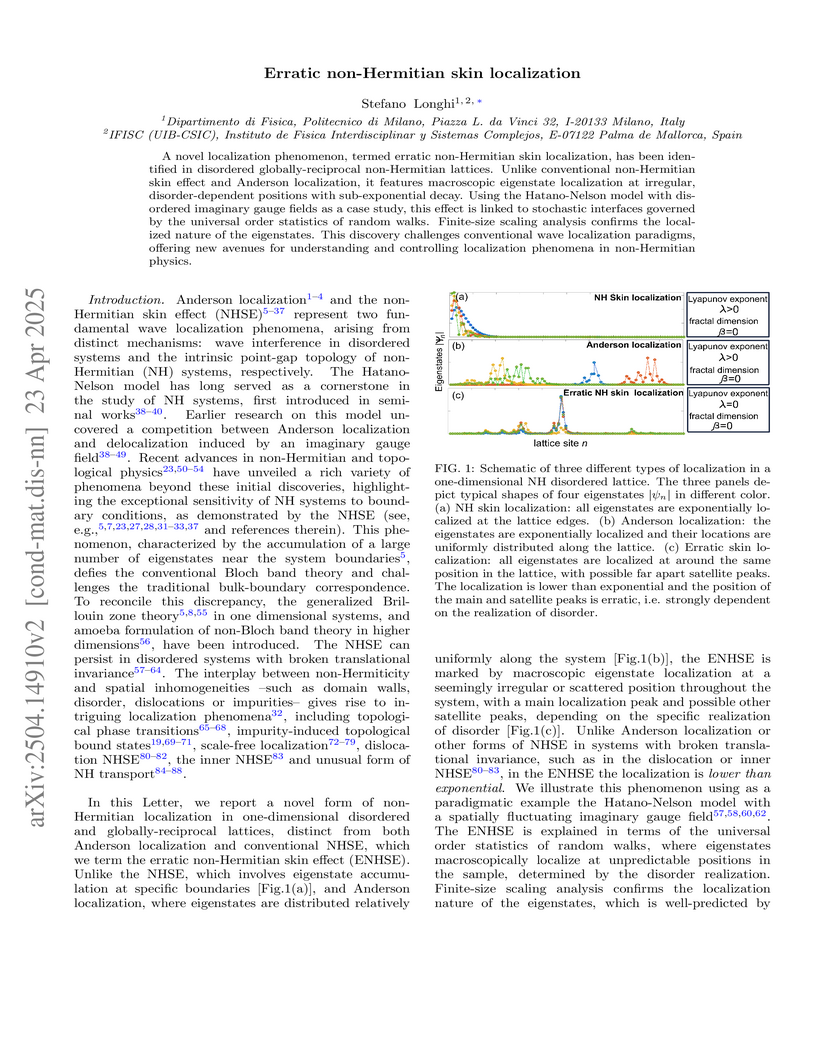
A novel localization phenomenon, termed erratic non-Hermitian skin
localization, has been identified in disordered globally-reciprocal
non-Hermitian lattices. Unlike conventional non-Hermitian skin effect and
Anderson localization, it features macroscopic eigenstate localization at
irregular, disorder-dependent positions with sub-exponential decay. Using the
Hatano-Nelson model with disordered imaginary gauge fields as a case study,
this effect is linked to stochastic interfaces governed by the universal order
statistics of random walks. Finite-size scaling analysis confirms the localized
nature of the eigenstates. This discovery challenges conventional wave
localization paradigms, offering new avenues for understanding and controlling
localization phenomena in non-Hermitian physics.
16 Nov 2016
We show the emergence of spontaneous synchronization between a pair of detuned quantum oscillators within a harmonic network. Our model does not involve any nonlinearity, driving, or external dissipation, thus providing the simplest scenario for the occurrence of local coherent dynamics in an extended harmonic system. A sufficient condition for synchronization is established by building upon the Rayleigh normal mode approach to vibrational systems. Our results show that mechanisms favoring synchronization, even between oscillators that are not directly coupled to each other, are transient energy depletion and crosstalk. We also address the possible buildup of quantum correlations during synchronization and show that indeed entanglement may be generated in detuned systems, starting from uncorrelated states and without any direct coupling between the two oscillators.
13 Oct 2025
Understanding the temporal dependence of precipitation is key to improving weather predictability and developing efficient stochastic rainfall models. We introduce an information-theoretic approach to quantify memory effects in discrete stochastic processes and apply it to daily precipitation records across the contiguous United States. The method is based on the predictability gain, a quantity derived from block entropy that measures the additional information provided by higher-order temporal dependencies. This statistic, combined with a bootstrap-based hypothesis testing and Fisher's method, enables a robust memory estimator from finite data. Tests with generated sequences show that this estimator outperforms other model-selection criteria such as AIC and BIC. Applied to precipitation data, the analysis reveals that daily rainfall occurrence is well described by low-order Markov chains, exhibiting regional and seasonal variations, with stronger correlations in winter along the West Coast and in summer in the Southeast, consistent with known climatological patterns. Overall, our findings establish a framework for building parsimonious stochastic descriptions, useful when addressing spatial heterogeneity in the memory structure of precipitation dynamics, and support further advances in real-time, data-driven forecasting schemes.
19 Dec 2021
Stefano Longhi's research investigates the bulk-edge correspondence and dynamical trapping at non-Hermitian topological interfaces where imaginary gauge fields induce directional transport in the same general direction. The work establishes that while localized interface states robustly exist under these conditions, dynamic light trapping is not guaranteed and critically depends on the relative strength of non-Hermiticity and the nature of the initial excitation, leading to phenomena like "self-healing" or "self-bending" of light.
The random walk of photons in a tight-binding lattice is known to exhibit diffusive motion similar to classical random walks under decoherence, clearly illustrating the quantum-to-classical transition. In this study, we reveal that the random walk of intense classical light under dephasing dynamics can disentangle quantum and ensemble averaging, making it possible to observe a subdiffusive walker dynamics, i.e. a behavior very distinct from both a classical and a quantum walker. These findings are demonstrated through proposing photonic random walks in synthetic temporal lattices, based on pulse dynamics in coupled fiber loops.
25 Mar 2022
A unique feature of non-Hermitian (NH) systems is the NH skin effect, i.e. the edge localization of an extensive number of bulk-band eigenstates in a lattice with open or semi-infinite boundaries. Unlike extended Bloch waves in Hermitian systems, the skin modes are normalizable eigenstates of the Hamiltonian that originate from the intrinsic non-Hermitian point-gap topology of the Bloch band energy spectra. Here we unravel a fascinating property of NH skin modes, namely self-healing, i.e. the ability to self-reconstruct their shape after being scattered off by a space-time potential.
In lattices with uncorrelated on-site potential disorder, Anderson
localization near the band edges can exhibit anomalously weak localization in
the form of Lifshitz tail states. These states correspond to clusters of
contiguous sites with nearly identical on-site energies, allowing excitations
to extend significantly beyond the characteristic localization length
determined by the inverse of Lyapunov exponent. Since Lifshitz tail states are
rare events, with an exponentially small density of states, they are typically
considered of limited practical importance. In this work, we demonstrate that
when Anderson localization is induced by disorder in an imaginary on-site
potential, Lifshitz tail states can dominate the system's dynamics and become
experimentally observable. This phenomenon is illustrated through the
Anderson-Bernoulli model in a non-Hermitian photonic lattice, shedding light on
the unique interplay between disorder and non-Hermiticity in such systems
15 May 2018
Network theory has played a dominant role in understanding the structure of
complex systems and their dynamics. Recently, quantum complex networks, i.e.
collections of quantum systems in a non-regular topology, have been explored
leading to significant progress in a multitude of diverse contexts including,
e.g., quantum transport, open quantum systems, quantum communication, extreme
violation of local realism, and quantum gravity geometries. However, the
question on how to produce and control general quantum complex networks in
experimental laboratory has remained open. Here we propose an all optical and
reconfigurable implementation of quantum complex networks. The experimental
proposal is based on optical frequency combs, parametric processes, pulse
shaping and multimode measurements allowing the arbitrary control of the number
of the nodes (optical modes) and topology of the links (interactions between
the modes) within the network. Moreover, we also show how to simulate quantum
dynamics within the network combined with the ability to address its individual
nodes. To demonstrate the versatility of these features, we discuss the
implementation of two recently proposed probing techniques for quantum complex
networks and structured environments. Overall, our general method for
implementing quantum complex networks with reconfigurable set-up has potential
to define an experimental playground for designing and controlling complex
networks -- and dynamics therein -- for several quantum physical frameworks.
22 Jun 2021
It has long been recognized that emission of radiation from atoms is not an
intrinsic property of individual atoms themselves, but it is largely affected
by the characteristics of the photonic environment and by the collective
interaction among the atoms. A general belief is that preventing full decay
and/or decoherence requires the existence of dark states, i.e., dressed
light-atom states that do not decay despite the dissipative environment. Here,
we show that, contrary to such a common wisdom, decoherence suppression can be
intermittently achieved on a limited time scale, without the need for any dark
state, when the atom is coupled to a chiral ring environment, leading to a
highly non-exponential staircase decay. This effect, that we refer to as
intermittent decoherence blockade, arises from periodic destructive
interference between light emitted in the present and light emitted in the
past, i.e., from delayed coherent quantum feedback.
Anderson localization, i.e. the suppression of diffusion in lattices with
random or incommensurate disorder, is a fragile interference phenomenon which
is spoiled out in the presence of dephasing effects or fluctuating disorder. As
a consequence, Anderson localization-delocalization phase transitions observed
in Hermitian systems, such as in one-dimensional quasicrystals when the
amplitude of the incommensurate potential is increased above a threshold, are
washed out when dephasing effects are included. Here we consider
localization-delocalization spectral phase transitions occurring in
non-Hermitian quasicrystals with local incommensurate gain and loss, and show
that, contrary to the Hermitian case, the non-Hermitian phase transition is
robust against dephasing effects. The results are illustrated by considering
synthetic quasicrystals in photonic mesh lattices.
06 Aug 2024
The Mpemba effect is the counterintuitive phenomenon in statistical physics for which a far-from-equilibrium state can relax toward equilibrium faster than a state closer to equilibrium. This effect has raised a great curiosity since long time and has been studied extensively in many classical and quantum systems. Here it is shown that the Mpemba effect can be observed in optics as well. Specifically, the process of light diffusion in finite-sized photonic lattices under incoherent (dephasing) dynamics is considered. Rather surprisingly, it is shown that certain highly-localized initial light distributions can diffuse faster than initial broadly delocalized distributions. The effect is illustrated by considering random walk of optical pulses in fiber-based temporal mesh lattices, which should provide an experimentally-accessible setup for the demonstration of the Mpemba effect in optics.
27 Oct 2024
The Mpemba effect refers to the surprising observation where, under certain conditions, a far-from-equilibrium state can relax toward equilibrium faster than a state closer to equilibrium. A paradigmatic example is provided by the curious fact that hot water can sometimes freeze faster than cold water. The Mpemba effect has intrigued scientists since long time and has been predicted and observed in a variety of classical and quantum systems. Recently, the search for Mpemba-like effects of purely quantum nature has raised a major interest. Here we predict the emergence of Mpemba effect in the quantum optics context exploiting non-classical states of light. By analyzing the decay dynamics of photon fields in a leaky optical resonator or waveguide, it is demonstrated that bosonic Mpemba effect emerges in the context of the quantum nature of light. Specifically, the relaxation dynamics is strongly influenced by the photon statistics of the initially trapped light field. The Mpemba effect is observed when comparing the decay dynamics of classical light fields (coherent states) with certain non-classical states, such as Fock states, squeezed states and Schrödinger cat states.
Mosaic lattice models have been recently introduced as a special class of disordered systems displaying resonance energies, multiple mobility edges and anomalous transport properties. In such systems on-site potential disorder, either uncorrelated or incommensurate, is introduced solely at every equally-spaced sites within the lattice, with a spacing M≥2. A remarkable property of disordered mosaic lattices is the persistence of extended states at some resonance frequencies that prevent complete Anderson localization, even in the strong disorder regime. Here we introduce a broader class of mosaic lattices and derive general expressions of mobility edges and localization length for incommensurate sinusoidal disorder, which generalize previous results [Y. Wang {\it et al.}, Phys. Rev. Lett. {\bf 125}, 196604 (2020)]. For both incommensurate and uncorrelated disorder, we prove that Anderson localization is protected by the open gaps of the disorder-free lattice, and derive some general criteria for complete Anderson localization. The results are illustrated by considering a few models, such as the mosaic Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model and the trimer mosaic lattice.
22 Mar 2025
The behavior of systems far from equilibrium is often complex and
unpredictable, challenging and sometimes overturning the physical intuition
derived from equilibrium scenarios. One striking example of this is the Mpemba
effect, which implies that non-equilibrium states can sometimes relax more
rapidly when they are further from equilibrium. Despite a rich historical
background, the precise conditions and mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain
unclear. Recently, there has been growing interest in investigating accelerated
relaxation and Mpemba-like effects within quantum systems. In this work, we
explore a quantum manifestation of the Mpemba effect in a simple and
paradigmatic model of open quantum systems: the damped quantum harmonic
oscillator, which describes the relaxation of a bosonic mode in contact with a
thermal bath at finite temperature T. By means of an exact analytical
analysis of the relaxation dynamics based on the method of moments in both
population and coherence subspaces, we demonstrate that any initial
distribution of populations with the first r moments exactly matching those
of the equilibrium distribution shows a super-accelerated relaxation to
equilibrium at a rate linearly increasing with r, leading to a pronounced
Mpemba effect. In particular, one can find a broad class of
far-from-equilibrium distributions that relax to equilibrium faster than any
other initial thermal state with a temperature T′ arbitrarily close to T.
The super-accelerated relaxation effect is shown to persist even for a broad
class of initial states with non-vanishing coherences, and a general criterion
for the observation of super-accelerated thermalization is presented.
The Hatano-Nelson model is a cornerstone of non-Hermitian physics, describing asymmetric hopping dynamics on a one-dimensional lattice, which gives rise to fascinating phenomena such as directional transport, non-Hermitian topology, and the non-Hermitian skin effect. It has been widely studied in both classical and quantum systems, with applications in condensed matter physics, photonics, and cold atomic gases. Recently, nonlinear extensions of the Hatano-Nelson model have opened a new avenue for exploring the interplay between nonlinearity and non-Hermitian effects. Particularly, in lattices with open boundary conditions, nonlinear skin modes and solitons, localized at the edge or within the bulk of the lattice, have been predicted. In this work, we examine the nonlinear extension of the Hatano-Nelson model with periodic boundary conditions and reveal a novel dynamical phenomenon arising from the modulational instability of nonlinear plane waves: growth blockade. This phenomenon is characterized by the abrupt halt of norm growth, as observed in the linear Hatano-Nelson model, and can be interpreted as a stopping of convective motion arising from self-induced disorder in the lattice.
13 Jan 2025
Echo chamber effects in social networks are generally attributed to the prevalence of interactions among like-minded peers. However, recent evidence has emphasized the role of hostile interactions between opposite-minded groups. We investigate the role of polarization, identified with structural balance, in the formation of echo chambers in signed networks. To do so, we generalize the Independent Cascade Model and the Linear Threshold Model to describe information propagation in presence of negative edges. Antagonistic connections do not disrupt the flow of information, but instead, alter the way information is framed. Our results show that echo chambers spontaneously emerge in balanced networks, but also in antibalanced ones for specific parameters. This highlights that structural polarization and echo chambers do not necessarily display a one-to-one correspondence, showing instead a complex and often counterintuitive interplay. The robustness of our results is confirmed with a complex contagion model and through simulations in different network topologies, including real-world datasets.
19 Mar 2025
This work explores the emergence of Mpemba-like effects within the quantum
theory of lasers. By examining the temporal dynamics of photon number
statistics in a single-mode laser above threshold, we reveal the curious and
counterintuitive possibility that a laser system, starting with photon
statistics far from equilibrium, may reach its stationary nearly-Poissonian
distribution faster than a system initially closer to equilibrium. Drawing
parallels to both classical and quantum Mpemba effects, we suggest that this
behavior results from the unique relaxation dynamics of photon states, which is
described by a non-integrable birth-death process. Our findings offer new
insights into the foundational aspects of quantum laser light and contribute to
the expanding body of research on non-equilibrium phenomena in quantum systems.
30 Apr 2025
In waveguide quantum electrodynamics systems, atomic radiation emission is
shaped by the photonic environment and collective atom interactions, offering
promising applications in quantum technologies. In particular, atom-photon
bound states, inhibiting complete spontaneous decay of the atom, can be
realized through waveguide dispersion engineering or by utilizing giant atoms.
While steady-state bound states are well understood, transient or virtual bound
states remain less explored. Here we investigate transient atom-photon bound
states, arising from initial atom-photon entanglement, and propose methods to
slow down spontaneous atomic decay.
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are a promising material for electronic
applications due to their easy fabrication and interesting semiconductor
properties. Further, CQDs exhibit quantum confinement and charging effects,
which may lead not only to improved performances but also to devices with novel
functionalities. Here, we investigate the electronic transport of CQDs embedded
on epoxy polymer. Our samples are coupled to interdigitated electrodes with
individually addressable microelectrodes. Remarkably, the current-voltage
characteristics show strongly nonlinear regimes at room temperature, ranging
from Schottky diode to Coulomb blockade and even negative differential
conductance behavior. We propose a master equation theoretical framework which
allows us to compute current curves that agree well with the observations. This
model emphasizes the importance of interacting dots and electron traps in
generating a cohesive picture that encompasses all transport regimes. Overall,
our results suggest that CQDs constitute a versatile materials platform for 3D
integrated electronic purposes.
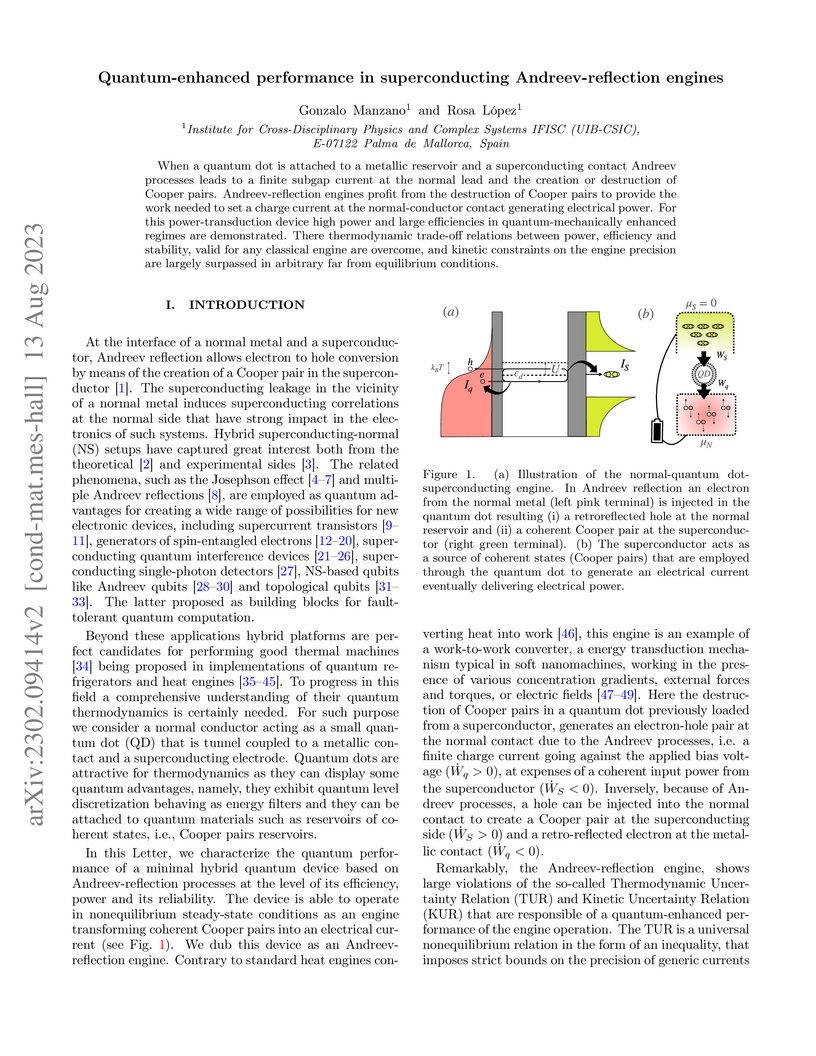
When a quantum dot is attached to a metallic reservoir and a superconducting contact Andreev processes leads to a finite subgap current at the normal lead and the creation or destruction of Cooper pairs. Andreev-reflection engines profit from the destruction of Cooper pairs to provide the work needed to set a charge current at the normal-conductor contact generating electrical power. For this power-transduction device high power and large efficiencies in quantum-mechanically enhanced regimes are demonstrated. There thermodynamic trade-off relations between power, efficiency and stability, valid for any classical engine are overcome, and kinetic constraints on the engine precision are largely surpassed in arbitrary far from equilibrium conditions.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.