Imperial-X
05 Dec 2025
Foundation machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) are trained on overlapping chemical spaces, yet their latent representations remain model-specific. Here, we show that independently developed MLIPs exhibit statistically consistent geometric organisation of atomic environments, which we term the Platonic representation. By projecting embeddings relative to a set of atomic anchors, we unify the latent spaces of seven MLIPs (spanning equivariant, non-equivariant, conservative, and non-conservative architectures) into a common metric space that preserves chemical periodicity and structural invariants. This unified framework enables direct cross-model optimal transport, interpretable embedding arithmetic, and the detection of representational biases. Furthermore, we demonstrate that geometric distortions in this space can indicate physical prediction failures, including symmetry breaking and incorrect phonon dispersions. Our results show that the latent spaces of diverse MLIPs present consistent statistical geometry shaped by shared physical and chemical constraints, suggesting that the Platonic representation offers a practical route toward interoperable, comparable, and interpretable foundation models for materials science.
Metadata-Driven Federated Learning of Connectional Brain Templates in Non-IID Multi-Domain Scenarios
Metadata-Driven Federated Learning of Connectional Brain Templates in Non-IID Multi-Domain Scenarios
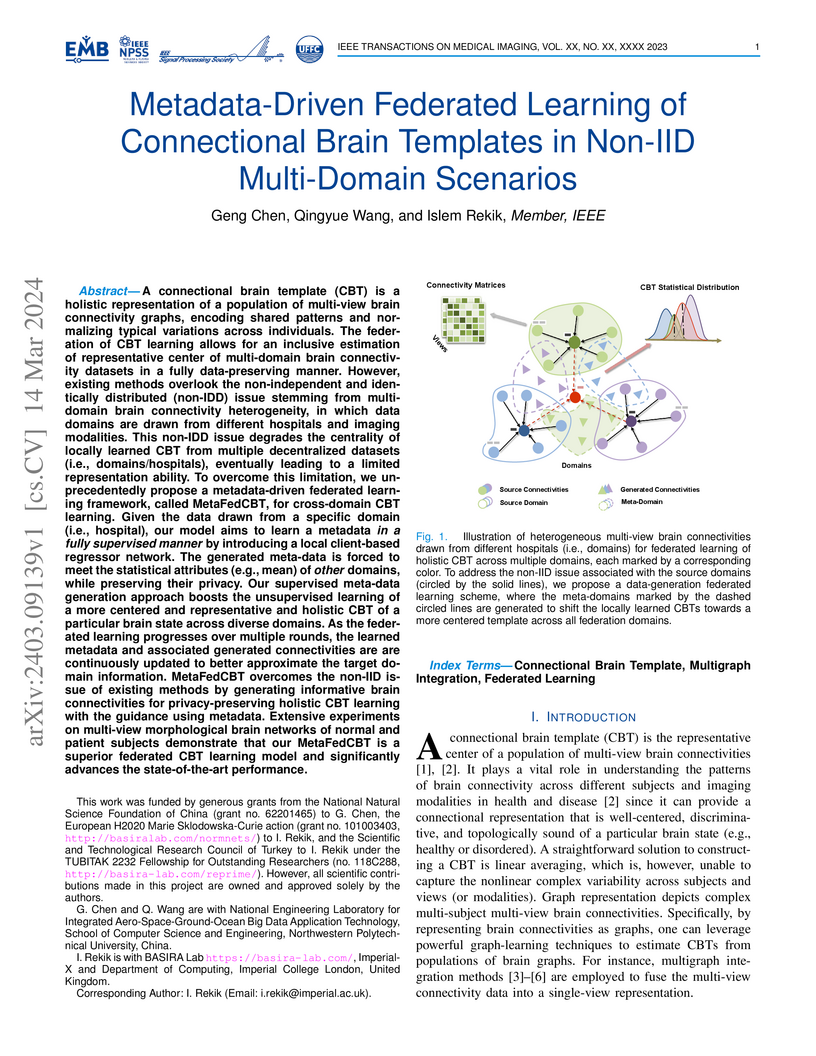
A connectional brain template (CBT) is a holistic representation of a
population of multi-view brain connectivity graphs, encoding shared patterns
and normalizing typical variations across individuals. The federation of CBT
learning allows for an inclusive estimation of the representative center of
multi-domain brain connectivity datasets in a fully data-preserving manner.
However, existing methods overlook the non-independent and identically
distributed (non-IDD) issue stemming from multidomain brain connectivity
heterogeneity, in which data domains are drawn from different hospitals and
imaging modalities. To overcome this limitation, we unprecedentedly propose a
metadata-driven federated learning framework, called MetaFedCBT, for
cross-domain CBT learning. Given the data drawn from a specific domain (i.e.,
hospital), our model aims to learn metadata in a fully supervised manner by
introducing a local client-based regressor network. The generated meta-data is
forced to meet the statistical attributes (e.g., mean) of other domains, while
preserving their privacy. Our supervised meta-data generation approach boosts
the unsupervised learning of a more centered, representative, and holistic CBT
of a particular brain state across diverse domains. As the federated learning
progresses over multiple rounds, the learned metadata and associated generated
connectivities are continuously updated to better approximate the target domain
information. MetaFedCBT overcomes the non-IID issue of existing methods by
generating informative brain connectivities for privacy-preserving holistic CBT
learning with guidance using metadata. Extensive experiments on multi-view
morphological brain networks of normal and patient subjects demonstrate that
our MetaFedCBT is a superior federated CBT learning model and significantly
advances the state-of-the-art performance.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.