International Research Centre MagTop
We study the magnetic and electronic properties of Ni-intercalated NbSe2.We calculate the magnetic exchanges of NixNbSe2 (x=1/3,1/4, and 1) and find that the out-of-plane magnetic coupling depends on the Ni connectivity: it is ferromagnetic when Ni atoms stack on top of each other, and antiferromagnetic otherwise. Focusing on Ni0.25NbSe2, we identify a ground-state transition from a stripe antiferromagnetic phase with Kramers degeneracy to a ferromagnetic phase above a critical Coulomb interaction UC. Spin--orbit coupling lowers UC, aligns the easy axis along z, and stabilizes collinear AFM and FM states over the competing 120∘ phase. Ni intercalation also strongly modifies the electronic structure, replacing the Γ-point hole pocket of pristine NbSe2 with an electron pocket and shifting the Van Hove singularity away from the Fermi level, thereby suppressing potential instabilities. Finally, we investigate the altermagnetic phase in the broader class T0.25MX2, finding that spin--orbit effects induce orbital antiferromagnetism with weak ferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the Néel vector orientation. Our results demonstrate that Ni-intercalated NbSe2 provides a versatile platform to explore and tune multiple competing magnetic phases that lie close in energy.
 CNRS
CNRS Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay Sorbonne UniversitéInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTop
Sorbonne UniversitéInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTop CEAChungnam National UniversityEcole Normale SupérieureLaboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques IntensesINSA ToulouseJohannes Kepler UniversitätInstitut de physique théoriqueNational Technical University ”KhPI”Universit PSLUniversit
Grenoble AlpesLaboratoire de Physique de l extquoterightEcole normale supérieureUniversit
Toulouse 3
CEAChungnam National UniversityEcole Normale SupérieureLaboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques IntensesINSA ToulouseJohannes Kepler UniversitätInstitut de physique théoriqueNational Technical University ”KhPI”Universit PSLUniversit
Grenoble AlpesLaboratoire de Physique de l extquoterightEcole normale supérieureUniversit
Toulouse 3Two-dimensional quantum materials can host original electronic phases that arise from the interplay of electronic correlations, symmetry and topology. In particular, the spontaneous breaking of internal symmetry that acts simultaneously on the pseudospin and the spatial degree of freedom realizes a nematic ordering. We report evidence of a quantum Hall valley nematic phase with an underlying SU(3) order parameter space obtained by a spontaneous polarization between the threefold degenerate valley pseudospins in Pb1-xSnxSe quantum wells. In the presence of a Zeeman field, we demonstrate a further control of the nematic ordering with an explicit symmetry breaking. Evidence of both spontaneous and explicit SU(3) symmetry breaking, reminiscent of the quark flavor paradigm, is of fundamental interest to shape the many body physics in a SU(3) system.
13 Nov 2025
We investigate the single crystals of Ni0.19NbSe2, revealing that Ni intercalation profoundly alters the physical properties of NbSe2. Magnetic measurements clearly show that the system is magnetically frustrated with antiferromagnetic ordering below 23.5\,K, with an irreversibility temperature near 10\,K, and a magnetic hysteresis with a small net magnetic moment. Overall, the system can be described as an inhomogeneous antiferromagnetic phase with magnetic disorder and magnetic frustration. We found two Curie-Weiss temperatures of -80\,K for the field in the {\it ab}-plane and -137\,K for the field out of plane, which are a consequence of anisotropic interactions in spin space and favor an orientation of the spin along the {\it c}-axis. Temperature-dependent resistivity shows a complete suppression of both charge density waves and superconducting order down to 300\,mK. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy at 84\,K reveals a Γ-centered electron pocket in Ni0.19NbSe2, which is absent in pristine NbSe2. The electronic structure results show a shift of the van Hove singularity (VHS), which is the main cause of the suppression of the electronic orders. These results align with recent theoretical predictions that Ni intercalation with cationic disorder favors frustrated antiferromagnetic stripe states, shifts the VHS and reconstructs the Fermi surface in NbSe2. Our findings position Ni0.19NbSe2 within a magnetically frustrated, non-superconducting regime, highlighting how partial intercalation and disorder drive complex magnetic order and the Fermi surface reconstruction in low-dimensional quantum materials.
01 Aug 2025
Chiral crystals, due to the lack of inversion and mirror symmetries, exhibit unique spin responses to external fields, enabling physical effects rarely observed in high-symmetry systems. Here, we show that materials from the chiral dichalcogenide family TM3X6 (T = 3d, M = 4d/5d, X = S) exhibit persistent spin texture (PST) - unidirectional spin polarization of states across large regions of the reciprocal space - in their nonmagnetic metallic phase. Using the example of NiTa3S6 and NiNb3S6, we show that PSTs cover the full Fermi surface, a rare and desirable feature that enables efficient charge-to-spin conversion and suggests long spin lifetimes and coherent spin transport above magnetic ordering temperatures. At low temperatures, the materials that order antiferromagnetically become chiral altermagnets, where spin textures originating from spin-orbit coupling and altermagnetism combine in a way that sensitively depends on the orientation of the Neel vector. Using symmetry analysis and first-principles calculations, we classify magnetic ground states across the family, identify cases with weak ferromagnetism, and track the evolution of spin textures and charge-to-spin conversion across magnetic phases and different Neel vector orientations, revealing spin transport signatures that allow one to distinguish Neel vector directions. These findings establish TM3X6 as a tunable platform for efficient charge-to-spin conversion and spin transport, combining structural chirality, persistent spin textures, and altermagnetism.
16 Sep 2025
Transport measurements of hybrid nanowires often rely on the observation of a zero-bias conductance peak as a hallmark of Majorana bound states (MBSs). However, such signatures can also be produced by trivial zero-energy Andreev bound states (ABSs) or by quasi-Majorana bound states (QMBSs), complicating their unambiguous identification. Here we propose microwave absorption visibility, extracted from parity-dependent cavity-nanowire susceptibility measurements, as a complementary probe of MBSs nonlocality. We study a Rashba spin-orbit nanowire consisting of a proximitized superconducting segment and an uncovered quantum-dot region, capacitively coupled to a single-mode microwave cavity. We show that true MBSs yield finite visibility only when both MBSs are simultaneously coupled to the cavity, reflecting their intrinsic nonlocality. In contrast, ABSs and QMBSs exhibit visibility extrema even when the cavity couples only locally to part of the nanowire. We further demonstrate that this distinction persists in the presence of Gaussian disorder, which may otherwise generate trivial subgap states. Motivated by recent experiments, we also analyze ``poor man's" Majoranas in double-quantum-dot setups, where analytical results confirm the same nonlocal visibility criterion. Finally, we discuss a cavity-driven scheme for initializing the electronic system in a given parity state. Our results establish cavity-based visibility as a robust and versatile probe of MBSs, providing a clear route to distinguish them from trivial zero-energy states in hybrid superconducting platforms.
27 Jul 2019
Point-contact spectroscopy of several non-superconducting topological materials reveals a low temperature phase transition that is characterized by a Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer-type of criticality. We find such a behavior of differential conductance for topological surfaces of non-magnetic and magnetic Pb1−y−xSnyMnxTe. We examine a possible contribution from superconducting nanoparticles, and show to what extent our data are consistent with Brzezicki's et al. theory [arXiv:1812.02168], assigning the observations to a collective state adjacent to atomic steps at topological surfaces.
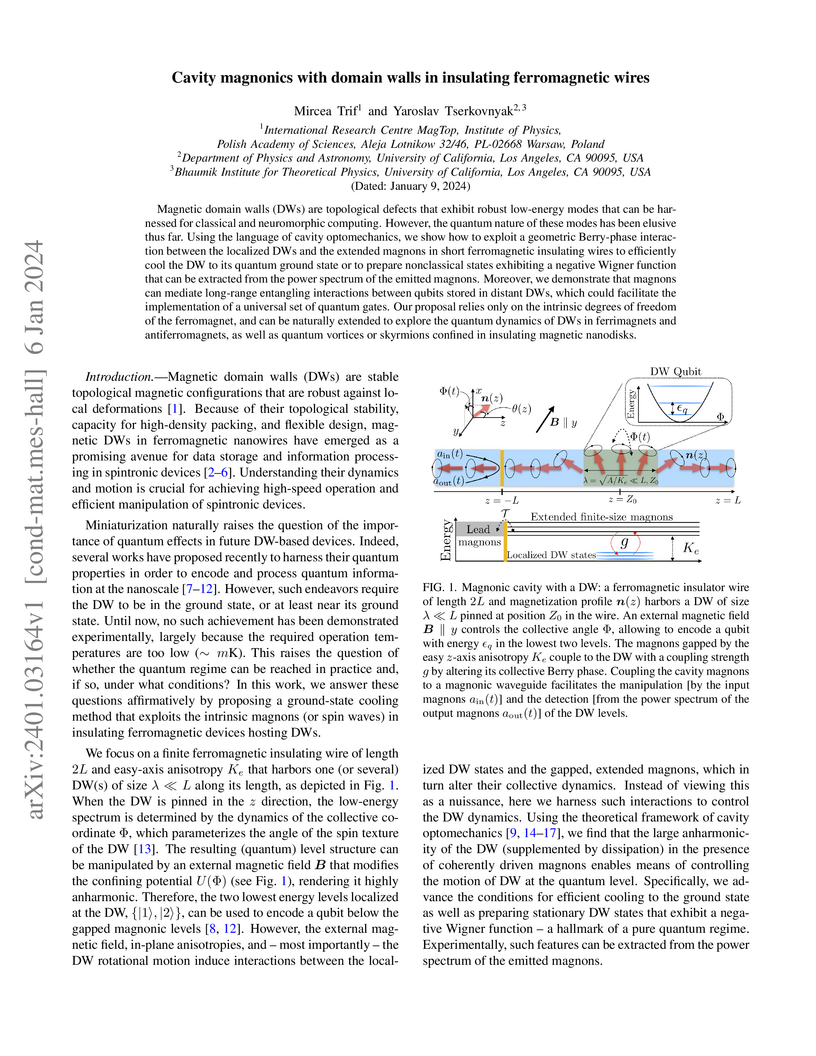
Magnetic domain walls (DWs) are topological defects that exhibit robust low-energy modes that can be harnessed for classical and neuromorphic computing. However, the quantum nature of these modes has been elusive thus far. Using the language of cavity optomechanics, we show how to exploit a geometric Berry-phase interaction between the localized DWs and the extended magnons in short ferromagnetic insulating wires to efficiently cool the DW to its quantum ground state or to prepare nonclassical states exhibiting a negative Wigner function that can be extracted from the power spectrum of the emitted magnons. Moreover, we demonstrate that magnons can mediate long-range entangling interactions between qubits stored in distant DWs, which could facilitate the implementation of a universal set of quantum gates. Our proposal relies only on the intrinsic degrees of freedom of the ferromagnet, and can be naturally extended to explore the quantum dynamics of DWs in ferrimagnets and antiferromagnets, as well as quantum vortices or skyrmions confined in insulating magnetic nanodisks.
06 Apr 2019
We report a combined theoretical and experimental investigation of magnetic proximity and Hall transport in Pt/Cr bilayers. Density functional theory indicates that an interfacial magnetization can be induced in the Pt layer and a strong magnetocrystalline anisotropy with an easy axis out of plane arises in the antiferromagnet. A signal ascribed to the anomalous Hall effect is detected and associated to the interface between Pt and Cr layers. We show that this effect originates from the combination of proximity-induced magnetization and a nontrivial topology of the band structure at the interface.
28 Feb 2023
We report the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) and the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE) data for the non-collinear Weyl semimetal CeAlSi. The anomalous Hall conductivity ({\sigma}_ij^A) was measured for two different orientations of the magnetic field (B), namely {\sigma}_yz^A for B II a and {\sigma}_xy^A for B II c, where a and c denote the crystallographic axes. We find that {\sigma}_xy^A and {\sigma}_yz^A are of opposite sign and both are large below the Curie temperature (T_C). In the paramagnetic phase, {\sigma}_xy^A raises even more and goes through a maximum at T ~ 170 K, whereas the absolute value of {\sigma}_yz^A decreases with increasing temperature. The origin of the sign difference between {\sigma}_xy^A and {\sigma}_yz^A was attributed to the reconstruction of the band structure under the variation of the spin orientation. Further, in a system where humps in the AHE are present and scalar spin chirality is zero, we show that the k-space topology plays an important role to determine the transport properties at both low and high temperatures. We also observed the anomalous contribution in the Nernst conductivity ({\alpha}_xy^A) measured for B II c. {\alpha}_xy^A/T turns out to be sizeable in the magnetic phase and above T_C slowly decreases with temperature. We were able to recreate the temperature dependences of {\sigma}_xy^A and {\alpha}_xy^A/T in the paramagnetic phase using a single band toy-model assuming a non-zero Berry curvature in the vicinity of the Weyl node. A decisive factor appears to be a small energy distance between the Fermi level and a Weyl point.
26 Feb 2025
University of Oslo Monash UniversityConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche
Monash UniversityConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara University of CopenhagenUniversity of WarsawAarhus University
University of CopenhagenUniversity of WarsawAarhus University Université Paris-SaclayPolitecnico di MilanoUniversity of BolognaInternational Research Centre MagTopFondazione Bruno KesslerSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversità di ParmaCNRUniversity of WürzburgEuropean Spallation Source ERICUniversit`a degli Studi di TriesteFritz Haber Institut der Max Planck GesellshaftUniversit
di SalernoUniv-Rennes
Université Paris-SaclayPolitecnico di MilanoUniversity of BolognaInternational Research Centre MagTopFondazione Bruno KesslerSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversità di ParmaCNRUniversity of WürzburgEuropean Spallation Source ERICUniversit`a degli Studi di TriesteFritz Haber Institut der Max Planck GesellshaftUniversit
di SalernoUniv-Rennes
 Monash UniversityConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche
Monash UniversityConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara University of CopenhagenUniversity of WarsawAarhus University
University of CopenhagenUniversity of WarsawAarhus University Université Paris-SaclayPolitecnico di MilanoUniversity of BolognaInternational Research Centre MagTopFondazione Bruno KesslerSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversità di ParmaCNRUniversity of WürzburgEuropean Spallation Source ERICUniversit`a degli Studi di TriesteFritz Haber Institut der Max Planck GesellshaftUniversit
di SalernoUniv-Rennes
Université Paris-SaclayPolitecnico di MilanoUniversity of BolognaInternational Research Centre MagTopFondazione Bruno KesslerSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversità di ParmaCNRUniversity of WürzburgEuropean Spallation Source ERICUniversit`a degli Studi di TriesteFritz Haber Institut der Max Planck GesellshaftUniversit
di SalernoUniv-RennesThe kagome lattice stands as a rich platform for hosting a wide array of
correlated quantum phenomena, ranging from charge density waves and
superconductivity to electron nematicity and loop current states. Direct
detection of loop currents in kagome systems has remained a formidable
challenge due to their intricate spatial arrangements and the weak magnetic
field signatures they produce. This has left their existence and underlying
mechanisms a topic of intense debate. In this work, we uncover a hallmark
reconcilable with loop currents: spin handedness-selective signals that surpass
conventional dichroic, spin, and spin-dichroic responses. We observe this
phenomenon in the kagome metal CsTi3Bi5 and we call it the anomalous
spin-optical helical effect. This effect arises from the coupling of light' s
helicity with spin-orbital electron correlations, providing a groundbreaking
method to visualize loop currents in quantum materials. Our discovery not only
enriches the debate surrounding loop currents but also paves the way for new
strategies to exploit the electronic phases of quantum materials via
light-matter interaction.
06 Dec 2019
By tuning the angle between graphene layers to specific "magic angles" the lowest energy bands of twisted bilayer graphene (TBLG) can be made flat. The flat nature of the bands favors the formation of collective ground states and, in particular, TBLG has been shown to support superconductivity. When the energy bands participating in the superconductivity are well-isolated, the superfluid weight scales inversely with the effective mass of such bands. For flat-band systems one would therefore conclude that even if superconducting pairing is present most of the signatures of the superconducting state should be absent. This conclusion is at odds with the experimental observations for TBLG. We calculate the superfluid weight for TBLG taking into account both the conventional contribution and the contribution arising from the quantum geometry of the bands. We find that both contributions are larger than one would expect treating the bands as well-isolated, that at the magic angle the geometric contribution is larger than the conventional one, and that for small deviations away from the magic angle the conventional contribution is larger than the geometric one. Our results show that, despite the flatness of the bands the superfluid weight in TBLG is finite and consistent with experimental observations. We also show how the superfluid weight can be tuned by varying the chemical potential and the twist angle opening the possibility to tune the nature of the superconducting transition between the standard BCS transition and the Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition.
11 Aug 2025
Understanding the electronic structure of transition-metal dopants in IV-VI semiconductors is critical for tuning their band structure. We analyze properties of Cr dopant in Pb1−xSnxTe and PbSe by magnetic and transport measurements, which are interpreted based on density functional calculations. We demonstrate that the pinning of the Fermi energy to the chromium resonant level occurs for both n-type and p-type Pb1−xSnxTe in the whole composition range. This enables us to determine the valence band and conduction band offsets at the PbTe/SnTe/PbSe heterointerfaces, which is important for designing high-prformance 2D transistors. Furthermore, the magnetic measurements reveal the presence of Cr ions in three charge states, Cr3+, Cr2+, and Cr1+. The last one corresponds to the Cr dopants incorporated at the interstitial, and not the substitutional, sites. The measured concentrations of the interstitial and substitutional Cr are comparable.
Chiral symmetry is a fundamental property with profound implications for the properties of elementary particles, that implies a spectral symmetry (i.e. E => -E ) in their dispersion relation. In condensed matter physics, chiral symmetry is frequently associated with superconductors or materials hosting Dirac fermions such as graphene or topological insulators. There, chiral symmetry is an emergent low-energy property, accompanied by an emergent spectral symmetry. While the chiral symmetry can be broken by crystal distortion or external perturbations, the spectral symmetry frequently survives. As the presence of spectral symmetry does not necessarily imply chiral symmetry, the question arises how these two properties can be experimentally differentiated. Here, we demonstrate how a system with preserved spectral symmetry can reveal underlying broken chiral symmetry using topological defects. Our study shows that these defects induce a spectral imbalance in the Landau level spectrum, providing direct evidence of symmetry alteration at topological domain walls. Using high-resolution STM/STS we demonstrate the intricate interplay between chiral and translational symmetry which is broken at step edges in topological crystalline insulator Pb1−xSnxSe. The chiral symmetry breaking leads to a shift in the guiding center coordinates of the Landau orbitals near the step edge, thus resulting in a distinct chiral flow of the spectral density of Landau levels. This study underscores the pivotal role of topological defects as sensitive probes for detecting hidden symmetries, offering profound insights into emergent phenomena with implications for fundamental physics.
Using first principle calculations we examine properties of (Cd,V)Te, (Cd,Cr)Te, (Hg,V)Te, and (Hg,Cr)Te relevant to the quantum anomalous Hall effect (QAHE), such as the position of V- and Cr- derived energy levels and the exchange interactions between magnetic ions. We consider CdTe and HgTe, containing 12.5% of cation-substitutional V or Cr ions in comparison to the well-known case of (Cd,Mn)Te and (Hg,Mn)Te, and examine their suitability for the fabrication of ferromagnetic barriers or ferromagnetic topological quantum wells, respectively. To account for the strong correlation of transition metal d electrons we employ hybrid functionals with different mixing parameters aHSE focusing on aHSE = 0.32, which better reproduces the experimental band gaps in HgTe, CdTe, Hg0.875Mn0.125Te, and Cd0.875Mn0.125Te. We find that Cr, like Mn, acts as an isoelectronic dopant but V can be an in-gap donor in CdTe and a resonant donor in HgTe, similar to the case of Fe in HgSe. From the magnetic point of view, Cr-doping results in a ferromagnetic phase within the general gradient approximation (GGA) but interactions become antiferromagnetic within hybrid functionals. However, (Hg,V)Te is a ferromagnet within both exchange-correlation functionals in a stark contrast to (Hg,Mn)Te for which robust antiferromagnetic coupling is found theoretically and experimentally. Furthermore, we establish that the Jahn-Teller effect is relevant only in the case of Cr-doping. Considering lower defect concentrations in HgTe-based quantum wells compared to (Bi,Sb)3Te2 layers, our results imply that HgTe quantum wells or (Cd,Hg)Te barriers containing either V or Cr show advantages over (Bi,Sb,Cr,V)3Te2-based QAHE systems but whether (i) ferromagnetic coupling will dominate in the Cr case and (ii) V will not introduce too many electrons to the quantum well is to be checked experimentally
Consiglio Nazionale delle RicercheAarhus University Seoul National UniversityPolitecnico di MilanoInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoCNR-SPINUniversit‘a di SalernoIstituto Officina dei MaterialiCa
Foscari University of VeniceCa
M
Foscari University of VeniceUniversit
`
a di SalernoUniversit
`
a degli studi di Milano
Seoul National UniversityPolitecnico di MilanoInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoCNR-SPINUniversit‘a di SalernoIstituto Officina dei MaterialiCa
Foscari University of VeniceCa
M
Foscari University of VeniceUniversit
`
a di SalernoUniversit
`
a degli studi di Milano
 Seoul National UniversityPolitecnico di MilanoInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoCNR-SPINUniversit‘a di SalernoIstituto Officina dei MaterialiCa
Foscari University of VeniceCa
M
Foscari University of VeniceUniversit
`
a di SalernoUniversit
`
a degli studi di Milano
Seoul National UniversityPolitecnico di MilanoInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopSynchrotron SOLEILJagiellonian UniversityPolish Academy of SciencesUniversit`a degli Studi di MilanoCNR-SPINUniversit‘a di SalernoIstituto Officina dei MaterialiCa
Foscari University of VeniceCa
M
Foscari University of VeniceUniversit
`
a di SalernoUniversit
`
a degli studi di MilanoThe relation between crystal symmetries, electron correlations, and electronic structure steers the formation of a large array of unconventional phases of matter, including magneto-electric loop currents and chiral magnetism. Detection of such hidden orders is a major goal in condensed matter physics. However, to date, nonstandard forms of magnetism with chiral electronic ordering have been experimentally elusive. Here, we develop a theory for symmetry-broken chiral ground states and propose a methodology based on circularly polarized spin-selective angular-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy to probe them. We exploit the archetypal quantum material Sr2RuO4 and reveal spectroscopic signatures which, even though subtle, may be reconciled with the formation of spin-orbital chiral currents at the material surface. As we shed light on these chiral regimes, our findings pave the way for a deeper understanding of ordering phenomena and unconventional magnetism.
We formulate the tight-binding model for cubic α-Sn based on the DFT calculations. In the model, we incorporate a variable bond angle, which allows us to simulate the effect of the in-plane strain. In the bulk, we demonstrate the presence of the Z2 topological invariant and a non-zero mirror Chern number, making α-Sn one of the rare cases where dual topology can be observed. We calculate the topological phase diagram of multi-layer α-Sn as a function of strain and number of layers. We find that a non-trivial quantum spin Hall state appears only for compressive strain above five layers of thickness. Quite surprisingly, both in the trivial and non-trivial phases, we find a plethora of edge-states with energies inside the bulk gap of the system. Some of these states are localized at the side surfaces of the slab, some of them prefer top/bottom surfaces and some are localized in the hinges. We trace the microscopic origin of these states back to a minimal model that supports chiral symmetry and multiple one-dimensional winding numbers that take different values in different directions in the Brillouin zone.
31 May 2024
The interplay between topology, dissipation and nonlinearities can give rise to a wealth of new phenomena and pave the way for novel topological lasers, sensors and other quantum devices. Along these lines, we propose here an optomechanical setup in which the concomitant presence of a spatially modulated external drive and dissipation gives rise to a topologically nontrivial state for mechanical and optical excitations. We are able to show that the one-dimensional system considered here exhibits topologically protected end states for which mechanical and optical degrees of freedom are entangled. We show such entanglement to be robust with respect to the presence of nonzero-temperature baths and we propose a protocol for experimental observation of the entanglement.
10 Jan 2022
We have performed electron transport and ARPES measurements on single crystals of transition metal dipnictide TaAs2 cleaved along the (2 0 1) surface which has the lowest cleavage energy. A Fourier transform of the Shubnikov-de Haas oscillations shows four different peaks whose angular dependence was studied with respect to the angle between the magnetic field and the [2 0 1] direction. The results indicate the elliptical shape of the Fermi surface cross-sections. Additionally, a mobility spectrum analysis was carried out, which also reveals at least four types of carriers contributing to the conductance (two kinds of electrons and two kinds of holes). ARPES spectra were taken on freshly cleaved (2 0 1) surface and it was found that bulk states pockets at the constant energy surface are elliptical, which confirms the magnetotransport angle dependent studies. First-principles calculations support the interpretation of the experimental results. The theoretical calculations better reproduce the ARPES data if the theoretical Fermi level is increased, which is due to a small n-doping of the samples. This shifts the Fermi level closer to the Dirac point, allowing to investigate the physics of the Dirac and Weyl points, making this compound a platform for the investigation of the Dirac and Weyl points in three-dimensional materials.
24 May 2022
The electrical and thermo-electrical transport effects of the TaAs2 semimetal were measured in a magnetic field applied along [-2 0 1] direction. The resulting field dependences of the resistivity as well as the Hall, Seebeck and Nernst coefficient below T ~ 100 K can be satisfactory described within the two-band model consisting of the electron and hole pockets. At low temperature all the measured effects exhibit significant contribution from quantum oscillations. The fast Fourier transform (FFT) of the oscillatory Nernst signal shows two fundamental frequencies, Fa = 105 T and Fb = 221 T, and the second harmonic of the latter (F2b = 442 T). The ratio between FFT amplitudes of Fb and F2b changes with temperature in an unusual way, indicating that we observe the spin-zero effect caused by temperature change. This is likely related to substantial temperature dependence of the Lande g-factor, which in turn can result from non-parabolic energy dispersion or temperature evolution of the spin-orbit coupling.
11 Oct 2023
 CNRS
CNRS Tohoku UniversityCharles University
Tohoku UniversityCharles University Brookhaven National LaboratoryUniversity of ZagrebInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopUniversity of GenevaÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)TU WienUniversity of FribourgNational Synchrotron Light Source IILNCMIWPI Advanced Institute for Materials ResearchLausanne Centre for Ultrafast Science (LACUS)
Brookhaven National LaboratoryUniversity of ZagrebInstitute of Physics, Polish Academy of SciencesInternational Research Centre MagTopUniversity of GenevaÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)TU WienUniversity of FribourgNational Synchrotron Light Source IILNCMIWPI Advanced Institute for Materials ResearchLausanne Centre for Ultrafast Science (LACUS)EuCd2As2 is now widely accepted as a topological semimetal in which a
Weyl phase is induced by an external magnetic field. We challenge this view
through firm experimental evidence using a combination of electronic transport,
optical spectroscopy and excited-state photoemission spectroscopy. We show that
the EuCd2As2 is in fact a semiconductor with a gap of 0.77 eV. We show
that the externally applied magnetic field has a profound impact on the
electronic band structure of this system. This is manifested by a huge decrease
of the observed band gap, as large as 125~meV at 2~T, and consequently, by a
giant redshift of the interband absorption edge. However, the semiconductor
nature of the material remains preserved. EuCd2As2 is therefore a
magnetic semiconductor rather than a Dirac or Weyl semimetal, as suggested by
{\em ab initio} computations carried out within the local spin-density
approximation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.