University of Alaska Fairbanks
We give a non-technical introduction to convergence-divergence models, a new modeling approach for phylogenetic data that allows for the usual divergence of species post speciation but also allows for species to converge, i.e. become more similar over time. By examining the 3-taxon case in some detail we illustrate that phylogeneticists have been "spoiled" in the sense of not having to think about the structural parameters in their models by virtue of the strong assumption that evolution is treelike. We show that there are not always good statistical reasons to prefer the usual class of treelike models over more general convergence-divergence models. Specifically we show many 3-taxon datasets can be equally well explained by supposing violation of the molecular clock due to change in the rate of evolution along different edges, or by keeping the assumption of a constant rate of evolution but instead assuming that evolution is not a purely divergent process. Given the abundance of evidence that evolution is not strictly treelike, our discussion is an illustration that as phylogeneticists we often need to think clearly about the structural form of the models we use.
The inference of phylogenetic networks, which model complex evolutionary processes including hybridization and gene flow, remains a central challenge in evolutionary biology. Until now, statistically consistent inference methods have been limited to phylogenetic level-1 networks, which allow no interdependence between reticulate events. In this work, we establish the theoretical foundations for a statistically consistent inference method for a much broader class: semi-directed level-2 networks that are outer-labeled planar and galled. We precisely characterize the features of these networks that are distinguishable from the topologies of their displayed quartet trees. Moreover, we prove that an inter-taxon distance derived from these quartets is circular decomposable, enabling future robust inference of these networks from quartet data, such as concordance factors obtained from gene tree distributions under the Network Multispecies Coalescent model. Our results also have novel identifiability implications across different data types and evolutionary models, applying to any setting in which displayed quartets can be distinguished.
24 Aug 2020
We put forward a solution to the initial boundary value (IBV) problem for the nonlinear shallow water system in inclined channels of arbitrary cross-section by means of the generalized Carrier-Greenspan hodograph transform (Rybkin et al., 2014). Since the Carrier-Greenspan transform, while linearizing the shallow water system, seriously entangles the IBV in the hodograph plane, all previous solutions required some restrictive assumptions on the IBV conditions, e.g., zero initial velocity, smallness of boundary conditions. For arbitrary non-breaking initial conditions in the physical space, we present an explicit formula for equivalent IBV conditions in the hodograph plane, which can readily be treated by conventional methods. Our procedure, which we call the method of data projection, is based on the Taylor formula and allows us to reduce the transformed IBV data given on curves in the hodograph plane to the equivalent data on lines. Our method works equally well for any inclined bathymetry (not only plane beaches) and, moreover, is fully analytical for U-shaped bays. Numerical simulations show that our method is very robust and can be used to give express forecasting of tsunami wave inundation in narrow bays and fjords
16 Oct 2025
We discuss the following inverse problem: given the run-up data of a tsunami wave, can we recover its initial shape? We study this problem within the framework of the non-linear shallow water equations, a model widely used to study tsunami propagation and inundation. Previously, it has been demonstrated that in the case of infinite sloping bathymetry, it is possible to recover the initial water displacement and velocity from shoreline readings \cite{Rybkin23,Rybkin24,Rybkin25}.
We consider a finite sloping bathymerty. We show that it is possible to recover boundary conditions (water displacement and velocity) on a virtual buoy from the shoreline data. Further, we discuss stitching together the shallow water equations and the Boussinesq equation in a more complex piece-wise sloping bathymetry in order to recover the initial conditions, while incorporating the dispersion to our model.
30 Jul 2025
The radar interferometric absolute phase is essential for estimating topography and displacements. However, its conventional definition based on the range difference is idealized in that it cannot be applied to complex, dynamic targets. Here, a universal observational definition is proposed, which is easiest to describe for differential interferometry: The absolute phase is determined by temporally unwrapping the phase while continuously varying the intermediate acquisition time between primary and secondary acquisitions. This absolute phase is typically not directly observable because a continuous series of observations is required. The absolute phase of a point target is proportional to the range difference, matching the conventional definition. For general targets undergoing a cyclic change, the absolute phase may be nonzero and then cannot be interpreted as a range difference. When a phase singularity (vanishing coherence) occurs at an intermediate time, the absolute phase becomes undefined, a situation termed an absolute phase singularity. Absolute phase singularities complicate absolute phase reconstruction through multifrequency techniques and through unwrapping multidimensional interferograms. They leave no trace in an interferogram, but unwrapping paths need to avoid those across which the absolute phase jumps by nonzero integer multiples of 2π. Mathematical analyses identify conditions for unwrapping-based reconstruction up to a constant, accounting for absolute phase singularities, undersampling and noise. The general definition of the absolute phase and the mathematical analyses enable a comprehensive appraisal of InSAR processing chains and support the interpretation of observations whenever low coherence engenders phase and absolute phase singularities.
12 May 2019
The goal of the article is to explore what is the most probable type of simulation in which humanity lives (if any) and how this affects simulation termination risks. We firstly explore the question of what kind of simulation in which humanity is most likely located based on pure theoretical reasoning. We suggest a new patch to the classical simulation argument, showing that we are likely simulated not by our own descendants, but by alien civilizations. Based on this, we provide classification of different possible simulations and we find that simpler, less expensive and one-person-centered simulations, resurrectional simulations, or simulations of the first artificial general intelligence's (AGI's) origin (singularity simulations) should dominate. Also, simulations which simulate the 21st century and global catastrophic risks are probable. We then explore whether the simulation could collapse or be terminated. Most simulations must be terminated after they model the singularity or after they model a global catastrophe before the singularity. Undeniably observed glitches, but not philosophical speculations could result in simulation termination. The simulation could collapse if it is overwhelmed by glitches. The Doomsday Argument in simulations implies termination soon. We conclude that all types of the most probable simulations except resurrectional simulations are prone to termination risks in a relatively short time frame of hundreds of years or less from now.
11 Jun 2025
 University of WashingtonUniversity of CanterburyDESY
University of WashingtonUniversity of CanterburyDESY University of ChicagoGhent UniversityVictoria University of WellingtonSungkyunkwan University
University of ChicagoGhent UniversityVictoria University of WellingtonSungkyunkwan University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Nagoya UniversityTU Dortmund UniversityPennsylvania State University
Nagoya UniversityTU Dortmund UniversityPennsylvania State University Yale UniversityLouisiana State University
Yale UniversityLouisiana State University University of Maryland
University of Maryland Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University Stockholm University
Stockholm University Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Purdue University
Purdue University University of AlbertaUppsala UniversityGeorgia TechHumboldt University of BerlinUniversity of RochesterCase Western Reserve UniversityUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of Geneva
University of AlbertaUppsala UniversityGeorgia TechHumboldt University of BerlinUniversity of RochesterCase Western Reserve UniversityUniversity of SheffieldUniversity of Geneva Queen Mary University of London
Queen Mary University of London Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyNiels Bohr InstituteКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоLund UniversityChulalongkorn UniversityUniversity of AlabamaTechnical University of DortmundUniversity of AdelaideUniversite Libre de BruxellesUniversity of Minnesota Twin CitiesUniversity of KansasUniversity of WuppertalUniversity of Nebraska–LincolnErlangen-Nuremberg UniversityUniversity of Alaska FairbanksUniversity of MuensterMarquette UniversityUniversity of AntwerpenRWTH Aachen UniversityRuhr-University-Bochum
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyNiels Bohr InstituteКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоLund UniversityChulalongkorn UniversityUniversity of AlabamaTechnical University of DortmundUniversity of AdelaideUniversite Libre de BruxellesUniversity of Minnesota Twin CitiesUniversity of KansasUniversity of WuppertalUniversity of Nebraska–LincolnErlangen-Nuremberg UniversityUniversity of Alaska FairbanksUniversity of MuensterMarquette UniversityUniversity of AntwerpenRWTH Aachen UniversityRuhr-University-BochumWe report a study of the inelasticity distribution in the scattering of neutrinos of energy 80−560 GeV off nucleons. Using atmospheric muon neutrinos detected in IceCube's sub-array DeepCore during 2012-2021, we fit the observed inelasticity in the data to a parameterized expectation and extract the values that describe it best. Finally, we compare the results to predictions from various combinations of perturbative QCD calculations and atmospheric neutrino flux models.
19 Apr 2025
We present a catalog of Local Universe Near-Infrared Seyfert (LUNIS)
\textit{K-}band integral field unit (IFU) data of 88 nearby Active Galactic
Nuclei (AGN), curated from SINFONI/VLT and OSIRIS/Keck archival datasets. This
catalog includes both type 1 and 2 Seyfert AGN probed down to scales of tens of
parsecs with z < 0.02 and spanning over five orders of magnitude in
L14−195keV AGN luminosity. As part of this catalog we make publicly
available for all galaxies the processed datacubes, a central 200 pc integrated
spectrum, and two-dimensional maps of flux, velocity, and velocity dispersion
for H2 1-0 S(1) 2.1218 μm, [Si VI] 1.9641 μm, and Br-γ 2.1655
μm. The morphology and geometry of [Si VI], a tracer of AGN outflows, are
reported for the 66% of galaxies with extended emission. We utilize this
large sample to probe the behavior of molecular and ionized gas, identifying
trends in the properties of the circumnuclear gas (surface brightness and
velocity dispersion) with fundamental AGN properties (obscuration and X-ray
luminosity). While there is significant variation in circumnuclear gas
characteristics across the sample, we find molecular hydrogen to be less
centrally concentrated and exhibit lower velocity dispersion relative to
ionized gas. In addition, we find elevated molecular hydrogen surface
brightness and decreased [Si VI] velocity dispersion in obscured relative to
unobscured AGN. The [Si VI] and Br-γ emission scale with L14−195keV
X-ray luminosity, which, along with the elevated velocity dispersion compared
to the molecular gas, verifies an association with AGN outflow processes.
We investigate the launch of negative upward streamers from sprite glows.
This phenomenon is readily observed in high-speed observations of sprites and
underlies the classification of sprites into carrot or column types. First, we
describe how an attachment instability leads to a sharply defined region in the
upper part of the streamer channel. This region has an enhanced electric field,
low conductivity and strongly emits in the first positive system of molecular
nitrogen. We identify it as the sprite glow. We then show how, in the most
common configuration of a carrot sprite, several upward streamers emerge close
to the lower boundary of the glow, where negative charge gets trapped and the
lateral electric field is high enough. These streamers cut off the current
flowing towards the glow and lead to the optical deactivation of the glow
above. Finally, we discuss how our results naturally explain angel sprites.
08 Jun 2023
 CNRS
CNRS UCLA
UCLA Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of Chicago
University of Chicago Peking University
Peking University NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center University of Southampton
University of Southampton Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay University of Arizona
University of Arizona Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Iowa
Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Iowa Princeton University
Princeton University Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of Colorado BoulderObservatoire de ParisINAFPrinceton Plasma Physics LaboratoryUniversity of California BerkeleySwedish Institute of Space PhysicsUniversity of Maryland at College ParkUniversity of New HampshireSouthwest Research InstituteThe Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics LaboratoryUniversity of Hawai’iSmithsonian Astrophysical ObservatoryWest Virginia UniversityUniversity of New BrunswickEcole Polytechnique, Institut Polytechnique de ParisUniversity of Alaska FairbanksLPPIGEP, TU BraunschweigLATMOS - CNRS- IPSL-UVSQIRAP CNRS University of Toulouse CNES
Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of Colorado BoulderObservatoire de ParisINAFPrinceton Plasma Physics LaboratoryUniversity of California BerkeleySwedish Institute of Space PhysicsUniversity of Maryland at College ParkUniversity of New HampshireSouthwest Research InstituteThe Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics LaboratoryUniversity of Hawai’iSmithsonian Astrophysical ObservatoryWest Virginia UniversityUniversity of New BrunswickEcole Polytechnique, Institut Polytechnique de ParisUniversity of Alaska FairbanksLPPIGEP, TU BraunschweigLATMOS - CNRS- IPSL-UVSQIRAP CNRS University of Toulouse CNESCollisionless shocks are fundamental processes that are ubiquitous in space plasma physics throughout the Heliosphere and most astrophysical environments. Earth's bow shock and interplanetary shocks at 1 AU offer the most readily accessible opportunities to advance our understanding of the nature of collisionless shocks via fully-instrumented, in situ observations. One major outstanding question pertains to the energy budget of collisionless shocks, particularly how exactly collisionless shocks convert incident kinetic bulk flow energy into thermalization (heating), suprathermal particle acceleration, and a variety of plasma waves, including nonlinear structures. Furthermore, it remains unknown how those energy conversion processes change for different shock orientations (e.g., quasi-parallel vs. quasi-perpendicular) and driving conditions (upstream Alfvénic and fast Mach numbers, plasma beta, etc.). Required to address these questions are multipoint observations enabling direct measurement of the necessary plasmas, energetic particles, and electric and magnetic fields and waves, all simultaneously from upstream, downstream, and at the shock transition layer with observatory separations at ion to magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) scales. Such a configuration of spacecraft with specifically-designed instruments has never been available, and this white paper describes a conceptual mission design -- MAKOS -- to address these outstanding questions and advance our knowledge of the nature of collisionless shocks.
 CNRS
CNRS UCLA
UCLA Imperial College London
Imperial College London UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Michigan
University of Michigan Peking University
Peking University Boston UniversityHoward UniversityLancaster University
Boston UniversityHoward UniversityLancaster University University of MinnesotaUniversity of Colorado
University of MinnesotaUniversity of Colorado Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Iowa
Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Iowa Princeton UniversityJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics LaboratoryObservatoire de ParisKhalifa UniversityLudwig Maximilian University of MunichCNESMax Planck Institute for Solar System ResearchNew Mexico State UniversitySouthwest Research InstituteLESIANorthumbria UniversityUniversity of Alaska FairbanksNASALAMSpace Dynamics LaboratoryGSFCLASPSSLUniversit PSLAix-Marseille Universit",Universit
Paris Cit
Princeton UniversityJohns Hopkins University Applied Physics LaboratoryObservatoire de ParisKhalifa UniversityLudwig Maximilian University of MunichCNESMax Planck Institute for Solar System ResearchNew Mexico State UniversitySouthwest Research InstituteLESIANorthumbria UniversityUniversity of Alaska FairbanksNASALAMSpace Dynamics LaboratoryGSFCLASPSSLUniversit PSLAix-Marseille Universit",Universit
Paris CitHeliophysics is the field that "studies the nature of the Sun, and how it influences the very nature of space - and, in turn, the atmospheres of planetary bodies and the technology that exists there." However, NASA's Heliophysics Division tends to limit study of planetary magnetospheres and atmospheres to only those of Earth. This leaves exploration and understanding of space plasma physics at other worlds to the purview of the Planetary Science and Astrophysics Divisions. This is detrimental to the study of space plasma physics in general since, although some cross-divisional funding opportunities do exist, vital elements of space plasma physics can be best addressed by extending the expertise of Heliophysics scientists to other stellar and planetary magnetospheres. However, the diverse worlds within the solar system provide crucial environmental conditions that are not replicated at Earth but can provide deep insight into fundamental space plasma physics processes. Studying planetary systems with Heliophysics objectives, comprehensive instrumentation, and new grant opportunities for analysis and modeling would enable a novel understanding of fundamental and universal processes of space plasma physics. As such, the Heliophysics community should be prepared to consider, prioritize, and fund dedicated Heliophysics efforts to planetary targets to specifically study space physics and aeronomy objectives.
19 Sep 2024
The primary data which determine the evolution of glaciation are the bedrock
elevation and the surface mass balance. From this data, which we assume is
defined over a fixed land region, the glacier's geometry solves a free boundary
problem which balances the time derivative of the surface elevation, the
surface velocity from the Stokes flow, and the surface mass balance. A surface
elevation function for this problem is admissible if it is above the bedrock
topography, equivalently if the ice thickness is nonnegative. This free
boundary problem can be posed in weak form as a variational inequality. After
some preparatory theory for the glaciological Stokes problem, we conjecture
that the continuous space, implicit time step variational inequality problem
for the surface elevation is well-posed. This conjecture is supported both by
physical arguments and numerical evidence. We then prove a general theorem
which bounds the numerical error made by a finite element approximation of a
nonlinear variational inequality in a Banach space. The bound is a sum of error
terms of different types, essentially special to variational inequalities. In
the case of the implicit step glacier problem these terms are of three types:
errors from discretizing the bed elevation, errors from numerically solving for
the Stokes velocity, and finally an expected quasi-optimal finite element error
in the surface elevation itself.
08 Apr 2025
 University of WashingtonTechnical University of Munich (TUM)
University of WashingtonTechnical University of Munich (TUM) Columbia UniversityColorado School of MinesTexas Advanced Computing Center, The University of Texas at AustinUniversity of Alaska FairbanksUniversity of California at San DiegoUnited States Geological SurveyLudwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München
Columbia UniversityColorado School of MinesTexas Advanced Computing Center, The University of Texas at AustinUniversity of Alaska FairbanksUniversity of California at San DiegoUnited States Geological SurveyLudwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) MünchenWith the rise of data volume and computing power, seismological research requires more advanced skills in data processing, numerical methods, and parallel computing. We present the experience of conducting training workshops over various forms of delivery to support the adoption of large-scale High-Performance Computing and Cloud computing to advance seismological research. The seismological foci were on earthquake source parameter estimation in catalogs, forward and adjoint wavefield simulations in 2 and 3 dimensions at local, regional, and global scales, earthquake dynamics, ambient noise seismology, and machine learning. This contribution describes the series of workshops that were delivered as part of research projects, the learning outcomes of the participants, and lessons learned by the instructors. Our curriculum was grounded on open and reproducible science, large-scale scientific computing and data mining, and computing infrastructure (access and usage) for HPC and the cloud. We also describe the types of teaching materials that have proven beneficial to the instruction and the sustainability of the program. We propose guidelines to deliver future workshops on these topics.
21 Mar 2025
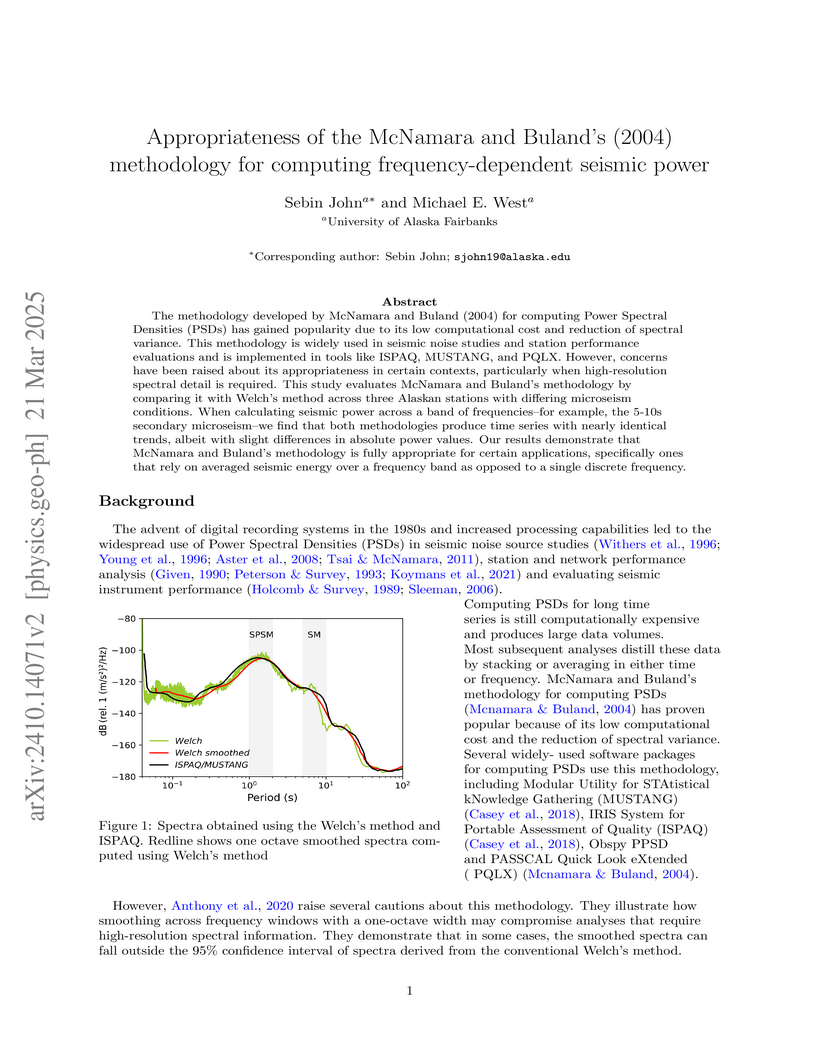
The methodology developed by McNamara and Buland (2004) for computing Power
Spectral Densities (PSDs) has gained popularity due to its low computational
cost and reduction of spectral variance. This methodology is widely used in
seismic noise studies and station performance evaluations and is implemented in
tools like ISPAQ, MUSTANG, and PQLX. However, concerns have been raised about
its appropriateness in certain contexts, particularly when high-resolution
spectral detail is required. This study evaluates McNamara and Buland's
methodology by comparing it with Welch's method across three Alaskan stations
with differing microseism conditions. When calculating seismic power across a
band of frequencies--for example, the 5-10s secondary microseism--we find that
both methodologies produce time series with nearly identical trends, albeit
with slight differences in absolute power values. Our results demonstrate that
McNamara and Buland's methodology is fully appropriate for certain
applications, specifically ones that rely on averaged seismic energy over a
frequency band as opposed to a single discrete frequency.
24 Oct 2024
Although conceptual assessment tests are frequently administered in a
pre/post-semester fashion, there are inherent issues with this paradigm.
Specifically, education researchers and instructors have limited ability to
observe the progression of student conceptual understanding throughout the
course. Furthermore, instructors are limited in the usefulness of the feedback
they can give to the students involved. To address these issues, we propose the
use of computerized adaptive testing (CAT) and increasing the frequency of
CAT-based assessments during the course, while reducing the test length per
administration, thus keeping or decreasing the total number of test items
administered throughout the course. The feasibility of this idea depends on how
far the test length per administration can be reduced without compromising the
test accuracy and precision. Specifically, the overall test length is desired
to be shorter than when the full assessment is administered as a pretest and
subsequent post-test. To achieve this goal, we developed a CAT algorithm that
we call Chain-CAT. This algorithm sequentially links the results of each CAT
administration using collateral information. We developed the Chain-CAT
algorithm using the items of the Force Concept Inventory (FCI) and analyzed the
efficiency by numerical simulations. We found that collateral information
significantly improved the test efficiency, and the overall test length could
be shorter than the pre-post method. Without constraints for item balancing and
exposure control, simulation results indicated that the efficiency of Chain-CAT
is comparable to that of the pre-post method even if the length of each CAT
administration is only 5 items and the CAT is administered 9 times throughout
the semester. (To continue, see text.)
In this paper we discuss the meaning of feedback parameter, greenhouse effect
and transient climate response usually related to the globally averaged energy
balance model of Schneider and Mass. After scrutinizing this model and the
corresponding planetary radiation balance we state that (a) the this globally
averaged energy balance model is flawed by unsuitable physical considerations,
(b) the planetary radiation balance for an Earth in the absence of an
atmosphere is fraught by the inappropriate assumption of a uniform surface
temperature, the so-called radiative equilibrium temperature of about 255 K,
and (c) the effect of the radiative anthropogenic forcing, considered as a
perturbation to the natural system, is much smaller than the uncertainty
involved in the solution of the model of Schneider and Mass. This uncertainty
is mainly related to the empirical constants suggested by various authors and
used for predicting the emission of infrared radiation by the Earth's skin.
Furthermore, after inserting the absorption of solar radiation by atmospheric
constituents and the exchange of sensible and latent heat between the Earth and
the atmosphere into the model of Schneider and Mass the surface temperatures
become appreciably lesser than the radiative equilibrium temperature. Moreover,
neither the model of Schneider and Mass nor the Dines-type two-layer energy
balance model for the Earth-atmosphere system, both contain the planetary
radiation balance for an Earth in the absence of an atmosphere as an asymptotic
solution, do not provide evidence for the existence of the so-called
atmospheric greenhouse effect if realistic empirical data are used.
20 Feb 2025
Variational inequalities play a pivotal role in a wide array of scientific
and engineering applications. This project presents two techniques for adaptive
mesh refinement (AMR) in the context of variational inequalities, with a
specific focus on the classical obstacle problem.
We propose two distinct AMR strategies: Variable Coefficient Elliptic
Smoothing (VCES) and Unstructured Dilation Operator (UDO). VCES uses a nodal
active set indicator function as the initial iterate to a time-dependent heat
equation problem. Solving a single step of this problem has the effect of
smoothing the indicator about the free boundary. We threshold this smoothed
indicator function to identify elements near the free boundary. Key parameters
such as timestep and threshold values significantly influence the efficacy of
this method.
The second strategy, UDO, focuses on the discrete identification of elements
adjacent to the free boundary, employing a graph-based approach to mark
neighboring elements for refinement. This technique resembles the dilation
morphological operation in image processing, but tailored for unstructured
meshes.
We also examine the theory of variational inequalities, the convergence
behavior of finite element solutions, and implementation in the Firedrake
finite element library. Convergence analysis reveals that accurate free
boundary estimation is pivotal for solver performance. Numerical experiments
demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods in dynamically enhancing
mesh resolution around free boundaries, thereby improving the convergence rates
and computational efficiency of variational inequality solvers. Our approach
integrates seamlessly with existing Firedrake numerical solvers, and it is
promising for solving more complex free boundary problems.
20 Feb 2025
The Gray configuration is a (27_3) configuration which typically is realized
as the points and lines of the 3 x 3 x 3 integer lattice. It occurs as a member
of an infinite family of configurations defined by Bouwer in 1972. Since their
discovery, both the Gray configuration and its Levi graph (i.e., its point-line
incidence graph) have been the subject of intensive study. Its automorphism
group contains cyclic subgroups isomorphic to Z_3 and Z_9, so it is natural to
ask whether the Gray configuration can be realized in the plane with any of the
corresponding rotational symmetry. In this paper, we show that there are two
distinct polycyclic realizations with Z_3 symmetry. In contrast, the only
geometric polycyclic realization with straight lines and Z_9 symmetry is only a
"weak" realization, with extra unwanted incidences (in particular, the
realization is actually a (27_4) configuration).
Inference of phylogenetic networks is of increasing interest in the genomic
era. However, the extent to which phylogenetic networks are identifiable from
various types of data remains poorly understood, despite its crucial role in
justifying methods. This work obtains strong identifiability results for large
sub-classes of galled tree-child semidirected networks. Some of the conditions
our proofs require, such as the identifiability of a network's tree of blobs or
the circular order of 4 taxa around a cycle in a level-1 network, are already
known to hold for many data types. We show that all these conditions hold for
quartet concordance factor data under various gene tree models, yielding the
strongest results from 2 or more samples per taxon. Although the network
classes we consider have topological restrictions, they include non-planar
networks of any level and are substantially more general than level-1 networks
-- the only class previously known to enjoy identifiability from many data
types. Our work establishes a route for proving future identifiability results
for tree-child galled networks from data types other than quartet concordance
factors, by checking that explicit conditions are met.
09 May 2025
We consider the dynamical system with boundary control for the vector
Schr\"odinger equation on the interval with a non-self-adjoint matrix
potential. For this system, we study the inverse problem of recovering the
matrix potential from the dynamical Dirichlet--to--Neumann operator. We first
provide a method to recover spectral data for an abstract system from dynamic
data and apply it to the Schr\"odinger equation. We then develop a strategy for
solving the inverse problem for the Schr\"odinger equation using this method
with other techniques of the Boundary control method.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.