Ask or search anything...
CloneBO proposes a method for efficiently optimizing antibody sequences by integrating a generative language model trained on natural clonal family evolution with Bayesian optimization. This approach yields antibodies with superior binding affinity and thermostability in wet lab experiments while requiring fewer experimental cycles compared to existing methods.
View blogResearchers developed UnmaskingTrees, an autoregressive framework using gradient-boosted decision trees and a novel probabilistic prediction method called BaltoBot, for tabular data imputation and generation. This method achieved leading performance in imputation and state-of-the-art results for generation with missingness, offering efficient sampling and closed-form density estimation for continuous and mixed-type data.
View blog New York University
New York University
 University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania
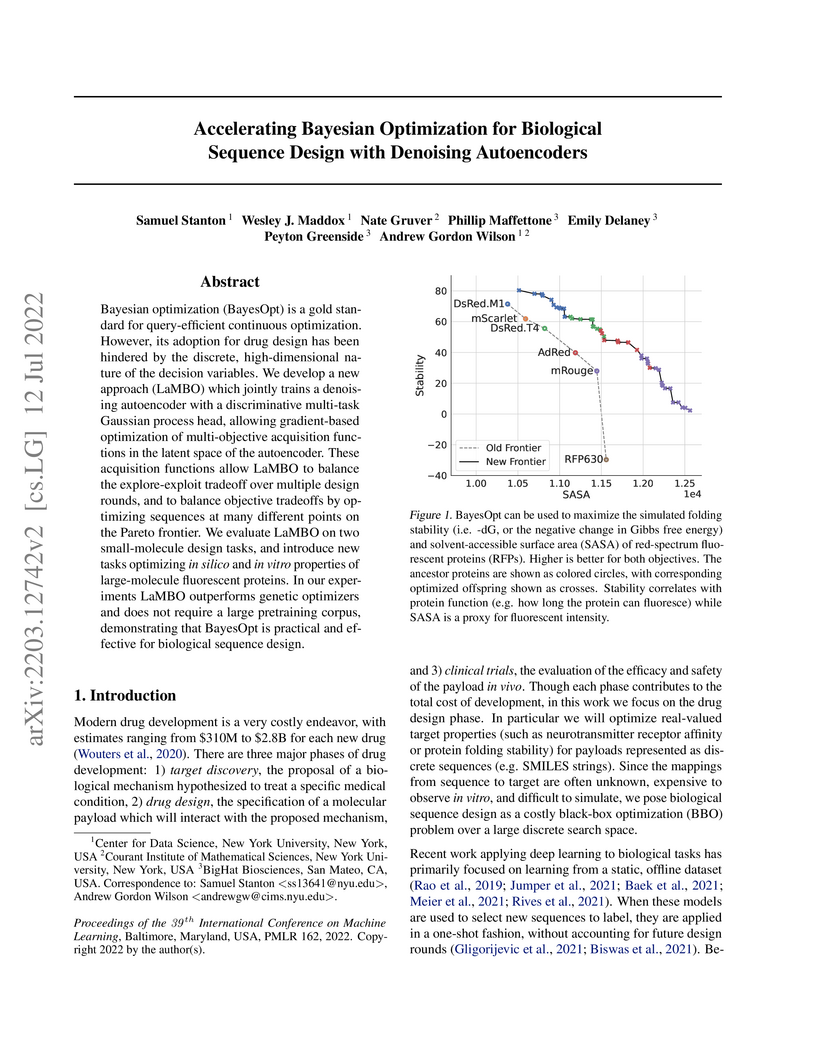


 University of Washington
University of Washington

 University of Chicago
University of Chicago