The Key Laboratory for Computer Systems of State Ethnic Affairs Commission
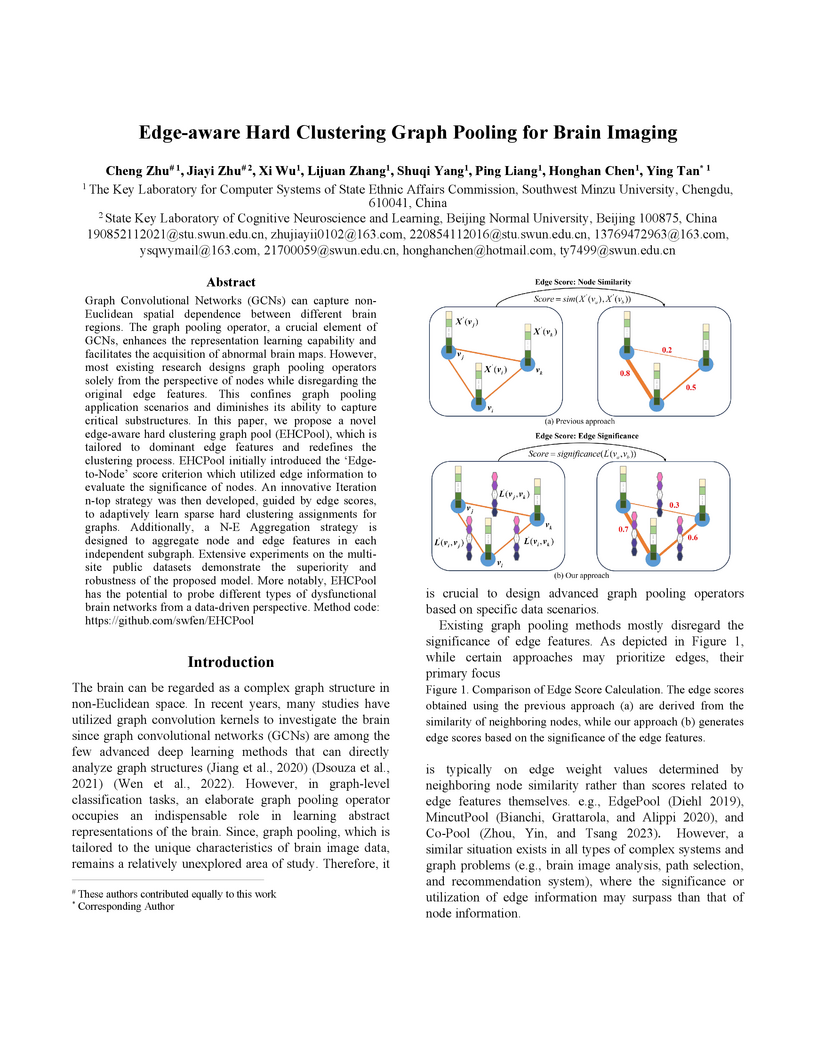
Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) can capture non-Euclidean spatial dependence between different brain regions. The graph pooling operator, a crucial element of GCNs, enhances the representation learning capability and facilitates the acquisition of abnormal brain maps. However, most existing research designs graph pooling operators solely from the perspective of nodes while disregarding the original edge features. This confines graph pooling application scenarios and diminishes its ability to capture critical substructures. In this paper, we propose a novel edge-aware hard clustering graph pool (EHCPool), which is tailored to dominant edge features and redefines the clustering process. EHCPool initially introduced the 'Edge-to-Node' score criterion which utilized edge information to evaluate the significance of nodes. An innovative Iteration n-top strategy was then developed, guided by edge scores, to adaptively learn sparse hard clustering assignments for graphs. Additionally, a N-E Aggregation strategy is designed to aggregate node and edge features in each independent subgraph. Extensive experiments on the multi-site public datasets demonstrate the superiority and robustness of the proposed model. More notably, EHCPool has the potential to probe different types of dysfunctional brain networks from a data-driven perspective. Method code: this https URL
Disaster monitoring is challenging due to the lake of infrastructures in monitoring areas. Based on the theory of Game-With-A-Purpose (GWAP), this paper contributes to a novel large-scale crowdsourcing disaster monitoring system. The system analyzes tagged satellite pictures from anonymous players, and then reports aggregated and evaluated monitoring results to its stakeholders. An algorithm based on directed graph centralities is presented to address the core issues of malicious user detection and disaster level calculation. Our method can be easily applied in other human computation systems. In the end, some issues with possible solutions are discussed for our future work.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.