Ask or search anything...
AWS Bedrock Science
AIDE: Attribute-Guided MultI-Hop Data Expansion for Data Scarcity in Task-Specific Fine-tuning
14 Jul 2025
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) for specific tasks requires diverse, high-quality training data. However, obtaining sufficient relevant data remains a significant challenge. Existing data synthesis methods either depend on extensive seed datasets or struggle to balance task relevance and data diversity. To address these challenges, we propose Attribute-guided multI-hop Data Expansion (AIDE), a novel data synthesis framework that uses a multi-hop process to expand very few seed data points while ensuring data diversity and task relevance. AIDE extracts the main topic and key knowledge attributes from the seeds to guide the synthesis steps. The process repeats for K hops, using the generated data as seeds. To prevent irrelevant data generation as the hop depth increases, AIDE incorporates a residual connection mechanism. Our empirical results show that AIDE enables fine-tuning of Mistral-7B, Llama-3.1-8B and Llama-3.2-3B from 10 seeds, surpassing the models fine-tuned on human curated data. Furthermore, AIDE outperforms state-of-the-art data synthesis methods, such as Evol-Instruct, by over 30% in task-specific fine-tuning. Code is available at this https URL.
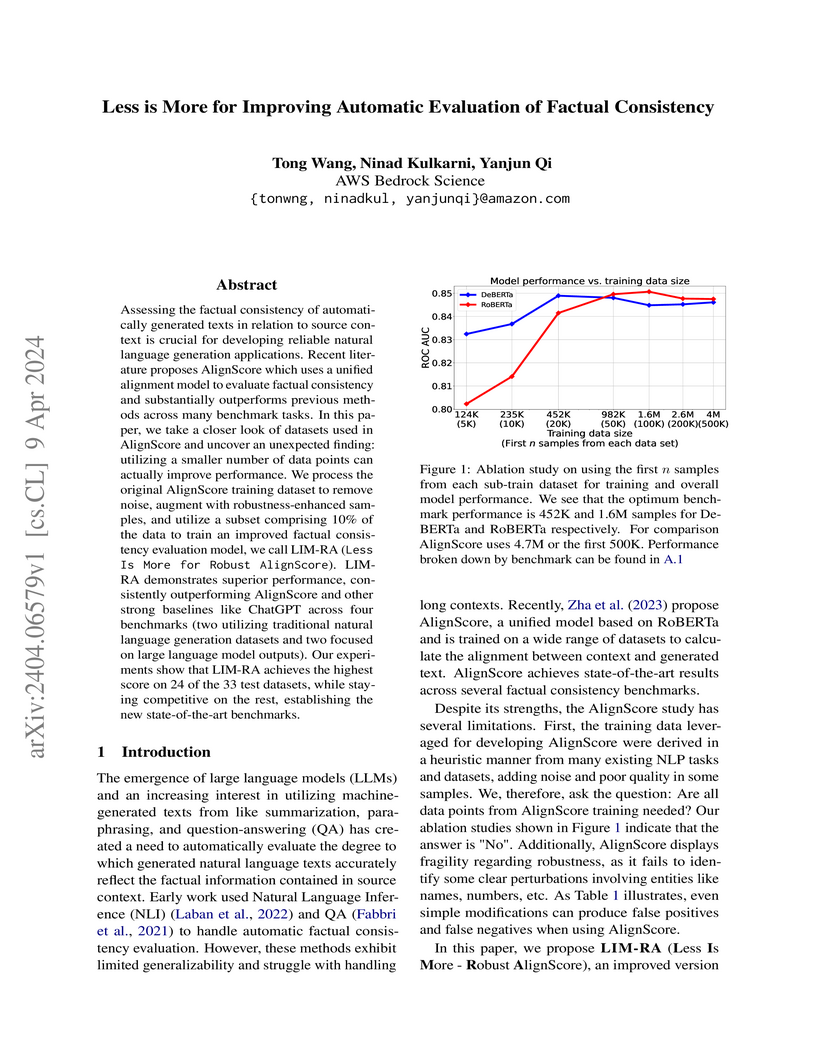
Less is More for Improving Automatic Evaluation of Factual Consistency
09 Apr 2024
LIM-RA is an advanced model for the automatic evaluation of factual consistency, achieving a 4.4% relative improvement in average AUC-ROC over previous state-of-the-art methods on a diverse set of benchmarks, including a new LLM-specific benchmark. It leverages a meticulously curated, smaller training dataset and demonstrates enhanced robustness to specific entity perturbations.
View blogTaeBench: Improving Quality of Toxic Adversarial Examples
01 May 2025
Toxicity text detectors can be vulnerable to adversarial examples - small
perturbations to input text that fool the systems into wrong detection.
Existing attack algorithms are time-consuming and often produce invalid or
ambiguous adversarial examples, making them less useful for evaluating or
improving real-world toxicity content moderators. This paper proposes an
annotation pipeline for quality control of generated toxic adversarial examples
(TAE). We design model-based automated annotation and human-based quality
verification to assess the quality requirements of TAE. Successful TAE should
fool a target toxicity model into making benign predictions, be grammatically
reasonable, appear natural like human-generated text, and exhibit semantic
toxicity. When applying these requirements to more than 20 state-of-the-art
(SOTA) TAE attack recipes, we find many invalid samples from a total of 940k
raw TAE attack generations. We then utilize the proposed pipeline to filter and
curate a high-quality TAE dataset we call TaeBench (of size 264k). Empirically,
we demonstrate that TaeBench can effectively transfer-attack SOTA toxicity
content moderation models and services. Our experiments also show that TaeBench
with adversarial training achieve significant improvements of the robustness of
two toxicity detectors.
Towards Improved Preference Optimization Pipeline: from Data Generation to Budget-Controlled Regularization
07 Nov 2024 Wanyu Du
Wanyu Du
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and its variants have become the de facto standards for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences or specific goals. However, DPO requires high-quality preference data and suffers from unstable preference optimization. In this work, we aim to improve the preference optimization pipeline by taking a closer look at preference data generation and training regularization techniques. For preference data generation, we demonstrate that existing scoring-based reward models produce unsatisfactory preference data and perform poorly on out-of-distribution tasks. This significantly impacts the LLM alignment performance when using these data for preference tuning. To ensure high-quality preference data generation, we propose an iterative pairwise ranking mechanism that derives preference ranking of completions using pairwise comparison signals. For training regularization, we observe that preference optimization tends to achieve better convergence when the LLM predicted likelihood of preferred samples gets slightly reduced. However, the widely used supervised next-word prediction regularization strictly prevents any likelihood reduction of preferred samples. This observation motivates our design of a budget-controlled regularization formulation. Empirically we show that combining the two designs leads to aligned models that surpass existing SOTA across two popular benchmarks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.