computation-and-language
This research disentangles the causal effects of pre-training, mid-training, and reinforcement learning (RL) on language model reasoning using a controlled synthetic task framework. It establishes that RL extends reasoning capabilities only under specific conditions of pre-training exposure and data calibration, with mid-training playing a crucial role in bridging training stages and improving generalization.
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai Innovation Institute introduced RoPE++, an extension of Rotary Position Embeddings that re-incorporates the previously discarded imaginary component of attention scores to improve long-context modeling in Large Language Models. This method consistently outperforms standard RoPE on various benchmarks and offers significant KV-cache and parameter efficiency.
The Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) framework allows Large Language Models to autonomously acquire and deploy genuine parallel reasoning capabilities, without relying on external teacher models. Experiments show NPR improves accuracy by up to 24.5% over baselines and delivers up to 4.6 times faster inference, maintaining 100% parallel execution across various benchmarks.
Researchers at ShanghaiTech University and Ant Group developed FlashMHF, an efficient multi-head Feed-Forward Network (FFN) for Transformer architectures that integrates a multi-head design with an I/O-aware fused kernel. This approach consistently improves language modeling perplexity and downstream task accuracy while reducing peak memory usage by 3-5x and accelerating inference up to 1.08x compared to standard FFNs.
The paper introduces Group Representational Position Encoding (GRAPE), a unified group-theoretic framework that re-conceptualizes and unifies existing positional encoding mechanisms like RoPE and ALiBi. It provides a principled design space for new encodings, demonstrating improved training stability and superior zero-shot performance in large language models.
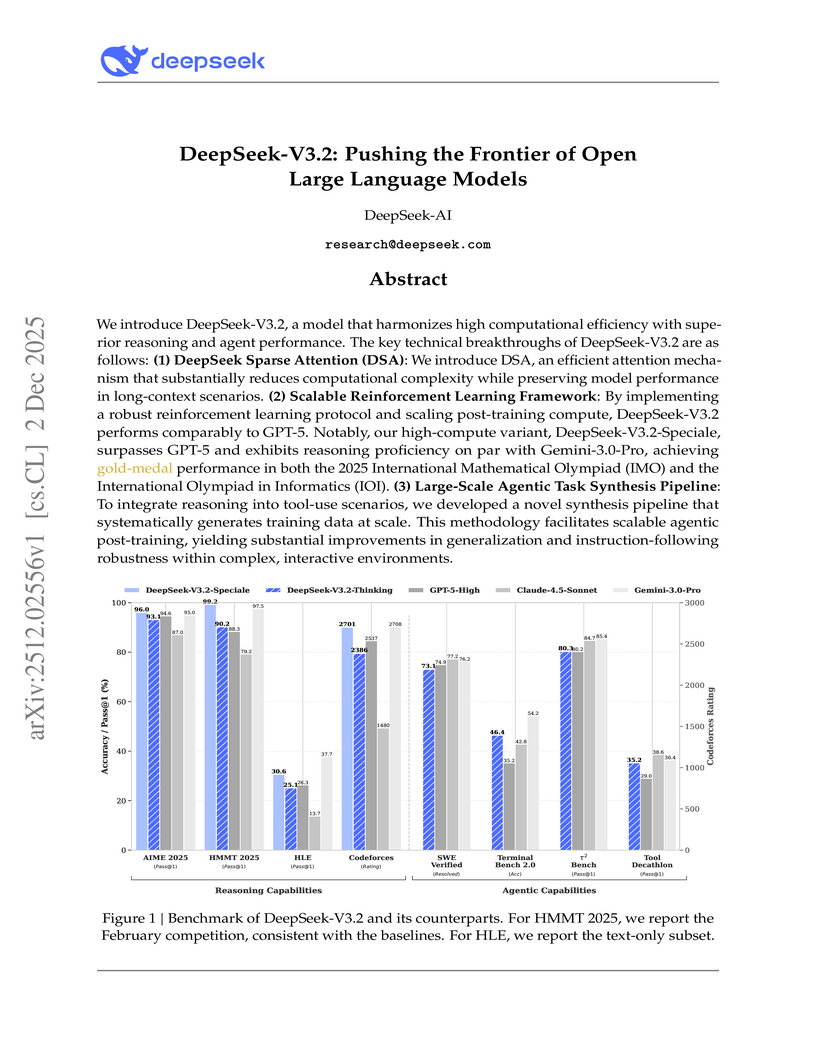
DeepSeek-AI developed DeepSeek-V3.2, an open large language model featuring DeepSeek Sparse Attention for improved efficiency and a scalable reinforcement learning framework, aiming to bridge the performance gap with proprietary models. The model, particularly its 'Speciale' variant, achieves gold-medal performance in elite competitions like the International Mathematical Olympiad and International Olympiad in Informatics, while also advancing agentic capabilities on various benchmarks.
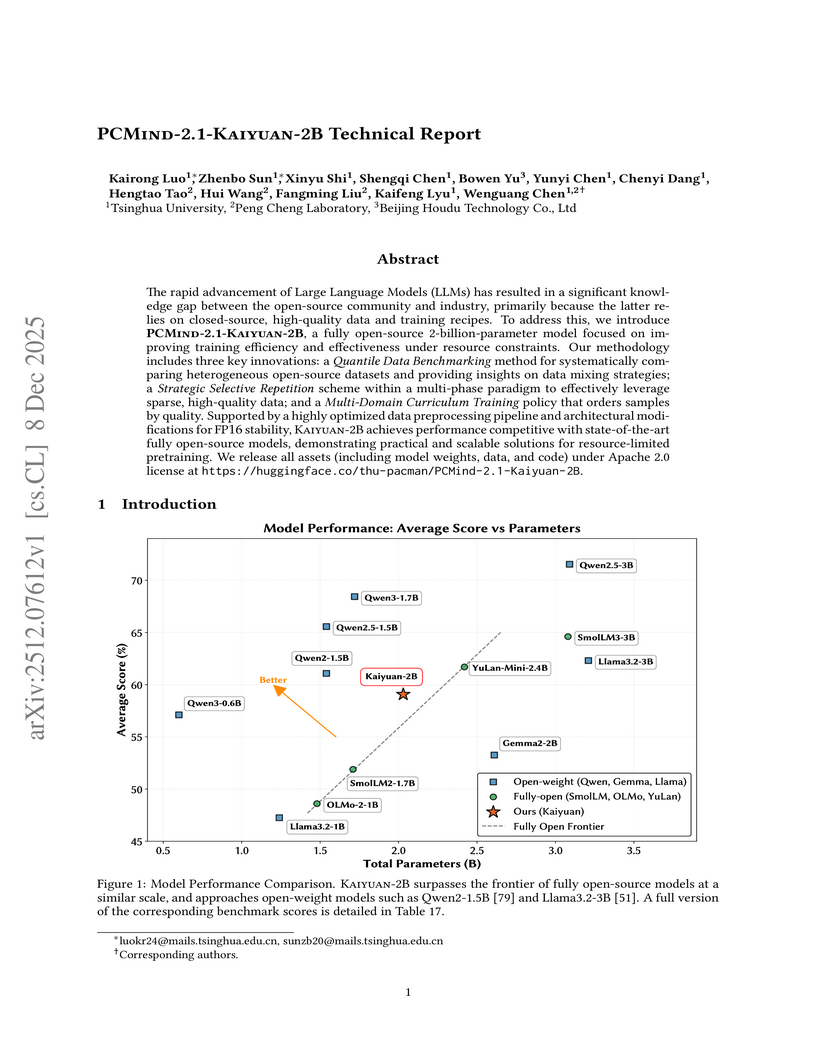
Researchers from Tsinghua University and Peng Cheng Laboratory developed PCMind-2.1-Kaiyuan-2B, a fully open-source 2-billion-parameter language model. It achieves competitive performance in Chinese language understanding, mathematical reasoning, and code generation by employing a multi-phase curriculum training with strategic data repetition and architectural modifications for FP16 stability, attaining an overall average score of 59.07% across evaluated benchmarks and outperforming several existing open-source models in its class.
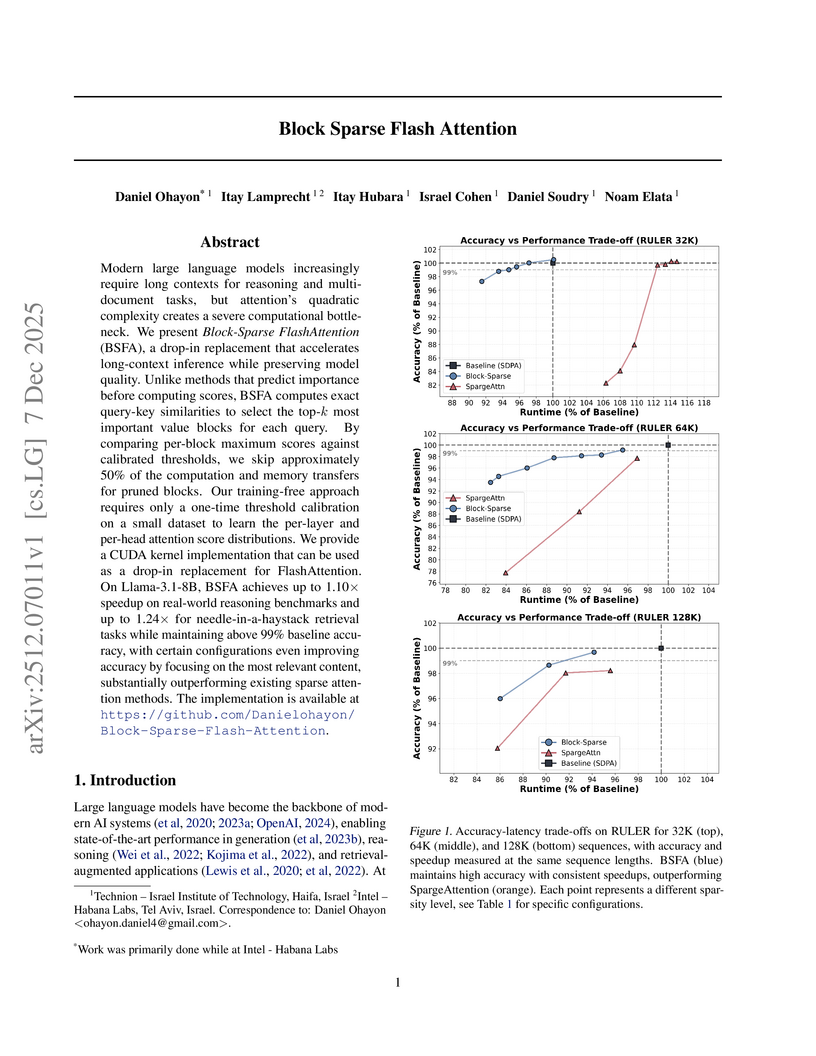
Modern large language models increasingly require long contexts for reasoning and multi-document tasks, but attention's quadratic complexity creates a severe computational bottleneck. We present Block-Sparse FlashAttention (BSFA), a drop-in replacement that accelerates long-context inference while preserving model quality. Unlike methods that predict importance before computing scores, BSFA computes exact query-key similarities to select the top-k most important value blocks for each query. By comparing per-block maximum scores against calibrated thresholds, we skip approximately 50% of the computation and memory transfers for pruned blocks. Our training-free approach requires only a one-time threshold calibration on a small dataset to learn the per-layer and per-head attention score distributions. We provide a CUDA kernel implementation that can be used as a drop-in replacement for FlashAttention. On Llama-3.1-8B, BSFA achieves up to 1.10x speedup on real-world reasoning benchmarks and up to 1.24x for needle-in-a-haystack retrieval tasks while maintaining above 99% baseline accuracy, with certain configurations even improving accuracy by focusing on the most relevant content, substantially outperforming existing sparse attention methods. The implementation is available at this https URL
Researchers from Google, NYU, ETH Zurich, and Stanford present a theoretical framework to formalize how large language models perform complex, iterative reasoning. The framework characterizes reasoning "oracles" and algorithms, proving that branching and genetic algorithms can achieve optimal success probabilities for models where oracle accuracy can decay with context size, and explains phenomena like "overthinking."
Researchers from Zhejiang University and ByteDance introduced CodeVision, a "code-as-tool" framework that equips Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to programmatically interact with images. The approach significantly improves MLLM robustness by correcting common image corruptions and enables state-of-the-art multi-tool reasoning through emergent tool use and error recovery.
This research introduces PersonaMem-v2, a dataset designed for implicit user persona learning, and an agentic memory framework, enabling smaller LLMs to achieve state-of-the-art personalization performance. The agentic memory system processes long conversational histories into a compact 2k-token memory, resulting in a 16x efficiency improvement while outperforming frontier models like GPT-5 variants.
The Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc. developed a theoretical formulation that justifies token-level optimization for sequence-level rewards in Large Language Model (LLM) reinforcement learning, identifying training–inference discrepancy and policy staleness as key instability factors. Their work also provides empirically validated strategies, including Routing Replay and clipping, to achieve stable and high-performing RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLMs.
Interleaved Latent Visual Reasoning (ILVR) introduces a framework for Multimodal Large Language Models to perform efficient and precise reasoning by dynamically generating latent visual representations within a unified text-latent sequence. This approach, developed by researchers from USC, Fudan University, and China University of Geosciences, achieves new state-of-the-art results with 60.8% and 81.5% accuracy on COMT and VSP benchmarks respectively, while demonstrating improved generalization across diverse out-of-distribution datasets.
Researchers from Peking University and Huawei Technologies developed a principled framework for adapting pre-trained autoregressive (AR) models into Block-Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). The adapted 7B-class model, NBDIFF-7B, achieved state-of-the-art performance among diffusion LLMs, with a macro average of 64.3 for its base version and 78.8 for its instruct version across diverse benchmarks.
A large language model's (LLM's) out-of-distribution (OOD) generalisation ability is crucial to its deployment. Previous work assessing LLMs' generalisation performance, however, typically focuses on a single out-of-distribution dataset. This approach may fail to precisely evaluate the capabilities of the model, as the data shifts encountered once a model is deployed are much more diverse. In this work, we investigate whether OOD generalisation results generalise. More specifically, we evaluate a model's performance across multiple OOD testsets throughout a finetuning run; we then evaluate the partial correlation of performances across these testsets, regressing out in-domain performance. This allows us to assess how correlated are generalisation performances once in-domain performance is controlled for. Analysing OLMo2 and OPT, we observe no overarching trend in generalisation results: the existence of a positive or negative correlation between any two OOD testsets depends strongly on the specific choice of model analysed.
The Nanbeige4-3B model family from the Nanbeige LLM Lab at Boss Zhipin introduces a 3-billion-parameter language model that consistently outperforms much larger open-source models, setting new state-of-the-art averages in mathematical and scientific reasoning. This performance is achieved through a multi-stage training pipeline incorporating advanced data filtering, a fine-grained learning rate scheduler, dual-level preference distillation, and multi-stage reinforcement learning.
Researchers from UC Berkeley and ByteDance Seed developed Natural Language Actor-Critic (NLAC), an off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm that trains LLM agents using a generative natural language critic to provide rich, explanatory feedback. NLAC demonstrated superior performance and enhanced sample efficiency on multi-turn dialogue and tool-use tasks compared to existing RL methods and strong prompting baselines.
Salesforce AI Research and UNC Chapel Hill developed Active Video Perception (AVP), an iterative evidence-seeking framework for long video understanding that leverages MLLMs in a "Plan–Observe–Reflect" loop. AVP achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across five benchmarks while dramatically reducing inference time by 81.6% and token usage by 87.6% compared to prior agentic methods.
Recent advances in Video Large Language Models (VLLMs) have achieved remarkable video understanding capabilities, yet face critical efficiency bottlenecks due to quadratic computational growth with lengthy visual token sequences of long videos. While existing keyframe sampling methods can improve temporal modeling efficiency, additional computational cost is introduced before feature encoding, and the binary frame selection paradigm is found suboptimal. Therefore, in this work, we propose Dynamic Token compression via LLM-guided Keyframe prior (DyToK), a training-free paradigm that enables dynamic token compression by harnessing VLLMs' inherent attention mechanisms. Our analysis reveals that VLLM attention layers naturally encoding query-conditioned keyframe priors, by which DyToK dynamically adjusts per-frame token retention ratios, prioritizing semantically rich frames while suppressing redundancies. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DyToK achieves state-of-the-art efficiency-accuracy tradeoffs. DyToK shows plug-and-play compatibility with existing compression methods, such as VisionZip and FastV, attaining 4.3x faster inference while preserving accuracy across multiple VLLMs, such as LLaVA-OneVision and Qwen2.5-VL. Code is available at this https URL .
While scaling laws for Large Language Models (LLMs) traditionally focus on proxy metrics like pretraining loss, predicting downstream task performance has been considered unreliable. This paper challenges that view by proposing a direct framework to model the scaling of benchmark performance from the training budget. We find that for a fixed token-to-parameter ratio, a simple power law can accurately describe the scaling behavior of log accuracy on multiple popular downstream tasks. Our results show that the direct approach extrapolates better than the previously proposed two-stage procedure, which is prone to compounding errors. Furthermore, we introduce functional forms that predict accuracy across token-to-parameter ratios and account for inference compute under repeated sampling. We validate our findings on models with up to 17B parameters trained on up to 350B tokens across two dataset mixtures. To support reproducibility and encourage future research, we release the complete set of pretraining losses and downstream evaluation results.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.