ArtiMinds Robotics
05 Jun 2025
QueryCAD presents a deep learning system for extracting precise information from CAD models through natural language queries, integrating an LLM for reasoning with a new open-vocabulary segmentation model, SegCAD. The system achieved 44 correct answers out of 111 questions on a new benchmark and demonstrated its ability to automate robot program synthesis by querying CAD parameters.
Despite the widespread adoption of industrial robots in automotive assembly, wire harness installation remains a largely manual process, as it requires precise and flexible manipulation. To address this challenge, we design a novel AI-based framework that automates cable connector mating by integrating force control with deep visuotactile learning. Our system optimizes search-and-insertion strategies using first-order optimization over a multimodal transformer architecture trained on visual, tactile, and proprioceptive data. Additionally, we design a novel automated data collection and optimization pipeline that minimizes the need for machine learning expertise. The framework optimizes robot programs that run natively on standard industrial controllers, permitting human experts to audit and certify them. Experimental validations on a center console assembly task demonstrate significant improvements in cycle times and robustness compared to conventional robot programming approaches. Videos are available under this https URL.
22 Aug 2024
High-level robot skills represent an increasingly popular paradigm in robot programming. However, configuring the skills' parameters for a specific task remains a manual and time-consuming endeavor. Existing approaches for learning or optimizing these parameters often require numerous real-world executions or do not work in dynamic environments. To address these challenges, we propose MuTT, a novel encoder-decoder transformer architecture designed to predict environment-aware executions of robot skills by integrating vision, trajectory, and robot skill parameters. Notably, we pioneer the fusion of vision and trajectory, introducing a novel trajectory projection. Furthermore, we illustrate MuTT's efficacy as a predictor when combined with a model-based robot skill optimizer. This approach facilitates the optimization of robot skill parameters for the current environment, without the need for real-world executions during optimization. Designed for compatibility with any representation of robot skills, MuTT demonstrates its versatility across three comprehensive experiments, showcasing superior performance across two different skill representations.
RoboGrind developed an integrated system for intuitive and interactive surface treatment, automating tasks like grinding and sanding using industrial robots. The system achieved robust defect detection and precise force-controlled execution, restoring surface roughness on fiberglass workpieces in lab and industrial environments.
While recent advances in deep learning have demonstrated its transformative potential, its adoption for real-world manufacturing applications remains limited. We present an Explanation User Interface (XUI) for a state-of-the-art deep learning-based robot program optimizer which provides both naive and expert users with different user experiences depending on their skill level, as well as Explainable AI (XAI) features to facilitate the application of deep learning methods in real-world applications. To evaluate the impact of the XUI on task performance, user satisfaction and cognitive load, we present the results of a preliminary user survey and propose a study design for a large-scale follow-up study.
Industrial robots are applied in a widening range of industries, but robot programming mostly remains a task limited to programming experts. We propose a natural language-based assistant for programming of advanced, industrial robotic applications and investigate strategies for domain-specific fine-tuning of foundation models with limited data and compute.
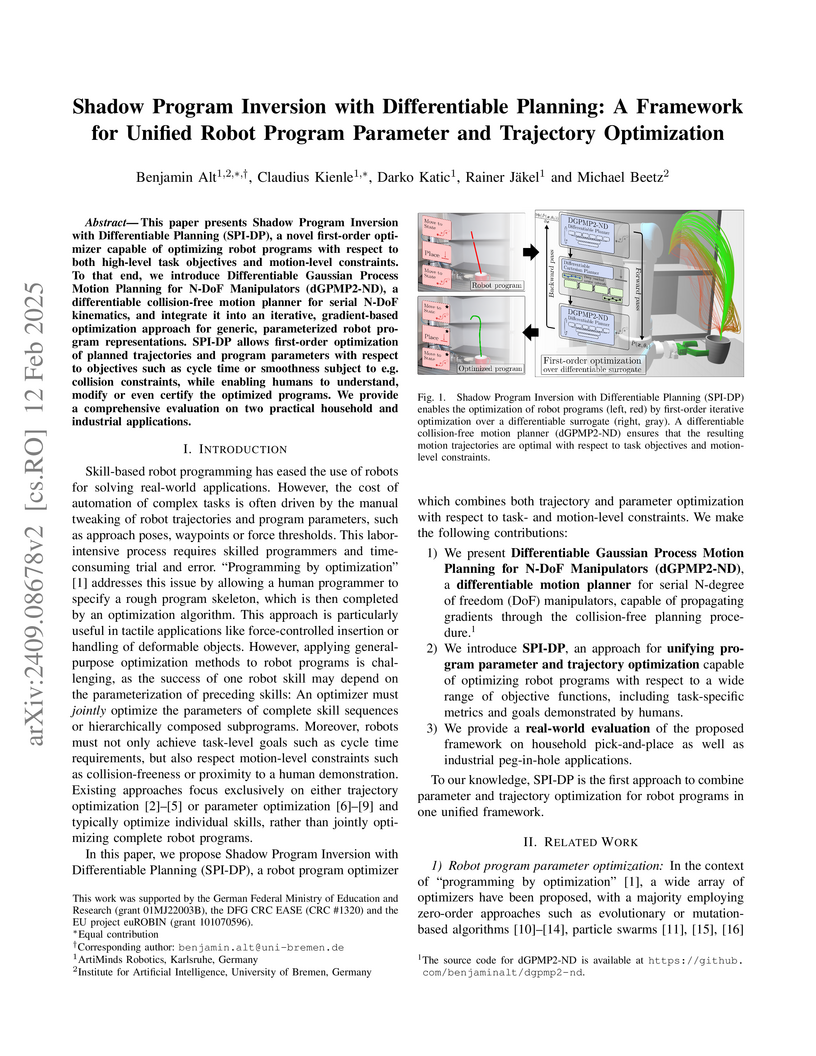
This paper presents SPI-DP, a novel first-order optimizer capable of
optimizing robot programs with respect to both high-level task objectives and
motion-level constraints. To that end, we introduce DGPMP2-ND, a differentiable
collision-free motion planner for serial N-DoF kinematics, and integrate it
into an iterative, gradient-based optimization approach for generic,
parameterized robot program representations. SPI-DP allows first-order
optimization of planned trajectories and program parameters with respect to
objectives such as cycle time or smoothness subject to e.g. collision
constraints, while enabling humans to understand, modify or even certify the
optimized programs. We provide a comprehensive evaluation on two practical
household and industrial applications.
Over the past decade, deep learning helped solve manipulation problems across
all domains of robotics. At the same time, industrial robots continue to be
programmed overwhelmingly using traditional program representations and
interfaces. This paper undertakes an analysis of this "AI adoption gap" from an
industry practitioner's perspective. In response, we propose the BANSAI
approach (Bridging the AI Adoption Gap via Neurosymbolic AI). It systematically
leverages principles of neurosymbolic AI to establish data-driven, subsymbolic
program synthesis and optimization in modern industrial robot programming
workflow. BANSAI conceptually unites several lines of prior research and
proposes a path toward practical, real-world validation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.