CERN
CERNThe measurements of the inclusive J/ψ yield at midrapidity (\left | y \right | < 0.9) and forward rapidity (2.5 < y < 4) in Pb−Pb collisions at sNN=5.02 TeV with the ALICE detector at the LHC are reported. The inclusive J/ψ production yields and nuclear modification factors, RAA, are measured as a function of the collision centrality, J/ψ transverse momentum (pT), and rapidity. The J/ψ average transverse momentum and squared transverse momentum (⟨pT⟩ and ⟨pT2⟩) are evaluated as a function of the centrality at midrapidity. Compared to the previous ALICE publications, here the entire Pb−Pb collisions dataset collected during the LHC Run 2 is used, which improves the precision of the measurements and extends the pT coverage. The pT-integrated RAA shows a hint of an increasing trend towards unity from semicentral to central collisions at midrapidity, while it is flat at forward rapidity. The pT-differential RAA shows a strong suppression at high pT with less suppression at low pT where it reaches a larger value at midrapidity compared to forward rapidity. The ratio of the pT-integrated yields of J/ψ to those of D0 mesons is reported for the first time for the central and semicentral event classes at midrapidity. Model calculations implementing charmonium production via the coalescence of charm quarks and antiquarks during the fireball evolution (transport models) or in a statistical approach with thermal weights are in good agreement with the data at low pT. At higher pT, the data are well described by transport models and a model based on energy loss in the strongly-interacting medium produced in nuclear collisions at the LHC.
We present a Fortran 77/95 code capable of computing QCD corrections in deep inelastic scattering (DIS). The code uses the Projection-to-Born method to augment an existing O(αs2) dijet DIS code, thereby obtaining predictions for photon-mediated neutral-current single-jet DIS production in the laboratory frame. The code is lightweight and fast, and yet includes the most common functionalities found in typical perturbative QCD programs, like automatic renormalisation and factorisation scale uncertainties, options to run and combine multiple seeds, and interfaces to fastjet and LHAPDF. Due to the underlying disent and HOPPET codes, the program also provides stable results in the infrared, relevant for extracting logarithmic coefficients for analytic resummations, and access to the massless DIS structure functions and (reduced) cross sections up to O(αs3).
Researchers at Peking University developed a jet-free, all-particle deep learning framework for Higgs boson pair production (HH → 4b) searches, leveraging low-level particle data. The method improves search significance by over a factor of five, achieving 3.3σ sensitivity for Standard Model HH production with 450 fb⁻¹ of LHC data, which exceeds previous 3 ab⁻¹ HL-LHC projections.
A theoretical analysis reaffirms the Strong CP problem's reality, refuting recent arguments that it is illusory, and establishes that gauged discrete P or CP symmetries offer consistent solutions that naturally arise within quantum gravity frameworks. The work demonstrates that the observable combination of θˉ+θ must be dynamically determined and calculable, rather than an arbitrary value from superselection sectors.
Agent-based modeling plays an essential role in gaining insights into biology, sociology, economics, and other fields. However, many existing agent-based simulation platforms are not suitable for large-scale studies due to the low performance of the underlying simulation engines. To overcome this limitation, we present a novel high-performance simulation engine.
We identify three key challenges for which we present the following solutions. First, to maximize parallelization, we present an optimized grid to search for neighbors and parallelize the merging of thread-local results. Second, we reduce the memory access latency with a NUMA-aware agent iterator, agent sorting with a space-filling curve, and a custom heap memory allocator. Third, we present a mechanism to omit the collision force calculation under certain conditions.
Our evaluation shows an order of magnitude improvement over Biocellion, three orders of magnitude speedup over Cortex3D and NetLogo, and the ability to simulate 1.72 billion agents on a single server.
Supplementary Materials, including instructions to reproduce the results, are available at: this https URL
This paper unifies geometric approaches to Effective Field Theories (EFTs) by demonstrating how on-shell covariant building blocks for scattering amplitudes can be constructed under general field redefinitions. It introduces an unambiguous metric for the functional manifold by using a "Warsaw-like basis," allowing a consistent reduction to existing field space geometry results.
13 Nov 2025
The ALICE Collaboration investigated strange and multi-strange hadron production in proton-proton collisions at 5.02 TeV across varying charged-particle multiplicities, revealing that transverse momentum spectra harden and particle yields evolve with multiplicity, with the Ω baryon exhibiting a faster-than-linear increase, consistent with collective-like effects observed at higher energies.
In this Letter, we initiate a systematic study of the n-point correlation functions (CF) in gauge theories in the sequential light-cone (SLC) limit. Focusing on QCD, we formulate a factorization theorem for the CF of four vector currents in this limit using tools from soft-collinear effective field theory (SCET). This result unveils a duality between CF and Wilson loops in non-conformal field theories, according to which the singular structure of the CF is described by a null polygonal Wilson loop dressed by universal jet functions and current form factors, directly related to well-known ingredients in collider physics. We employ this new factorization theorem to obtain the singular terms of the four-point CF in QCD in the SLC limit up to three loops. This constitutes the first determination of terms beyond one loop and in particular determines, for the first time, conformal-symmetry-breaking terms induced by the non-vanishing β-function of QCD. As a stringent check, we verify that our result satisfies the anomalous conformal Ward identities and its leading-transcendental term reproduces the known correlation function in N=4 SYM to three loops. Our results are easily generalized to the multi-point case, offering a powerful tool for future applications of SCET to the study of the fundamental structure of gauge theories.
Researchers at CERN, EPFL, University of Oregon, UCSD, and University of Utah developed a functional geometry framework for scalar Effective Field Theories, which accounts for derivative-dependent field redefinitions. This framework introduces geometrized vertices that ensure scattering amplitudes are manifestly on-shell covariant and generalizes the geometry-kinematics duality to a broader range of theories.
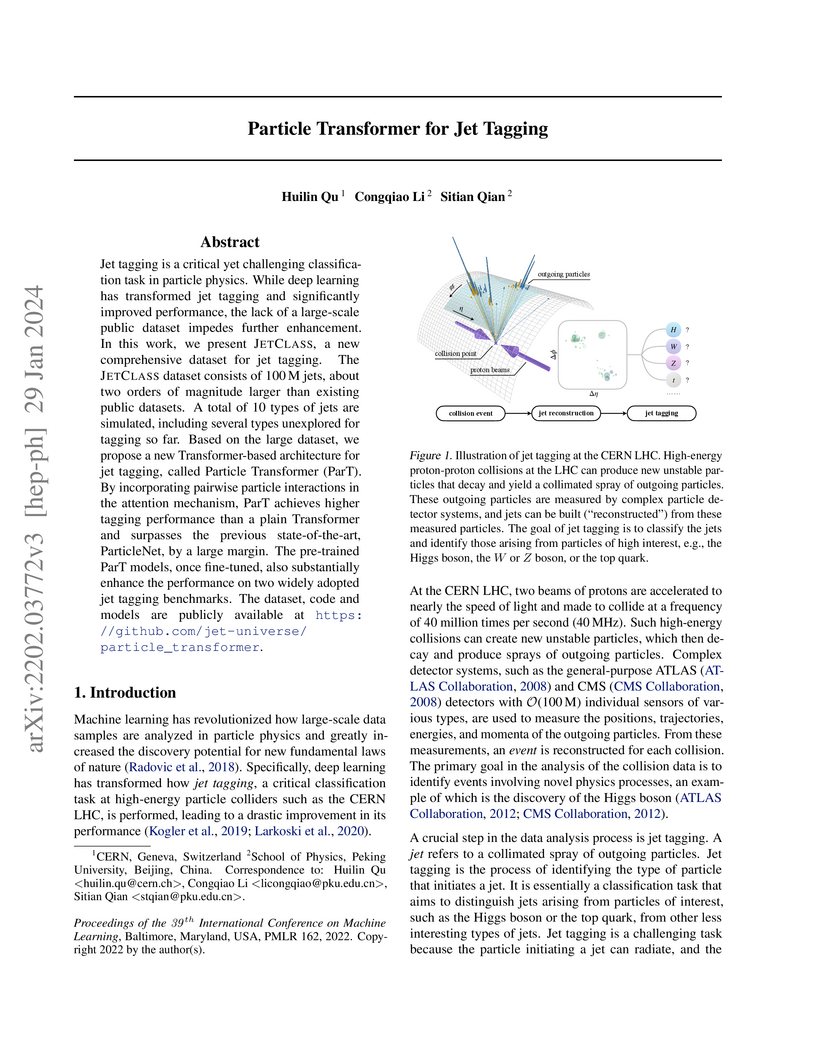
Jet tagging is a critical yet challenging classification task in particle physics. While deep learning has transformed jet tagging and significantly improved performance, the lack of a large-scale public dataset impedes further enhancement. In this work, we present JetClass, a new comprehensive dataset for jet tagging. The JetClass dataset consists of 100 M jets, about two orders of magnitude larger than existing public datasets. A total of 10 types of jets are simulated, including several types unexplored for tagging so far. Based on the large dataset, we propose a new Transformer-based architecture for jet tagging, called Particle Transformer (ParT). By incorporating pairwise particle interactions in the attention mechanism, ParT achieves higher tagging performance than a plain Transformer and surpasses the previous state-of-the-art, ParticleNet, by a large margin. The pre-trained ParT models, once fine-tuned, also substantially enhance the performance on two widely adopted jet tagging benchmarks. The dataset, code and models are publicly available at this https URL.
We compute tree-level n-point scattering amplitudes in scalar field theories in terms of geometric invariants on a fibre bundle. All 0- and 2-derivative interactions are incorporated into a metric on this bundle. The on-shell amplitudes can be efficiently pieced together from covariant Feynman rules, and we present a general closed formula for obtaining the n-point amplitude in this way. The covariant Feynman rules themselves can be derived using a generalization of the normal coordinate expansion of the fibre bundle metric. We demonstrate the efficiency of this approach by computing the covariant Feynman rules up to n=10 points, from which one can obtain the full amplitudes using our general formula. The formalism offers a prototype for obtaining geometric amplitudes in theories with higher-derivative interactions, by passing from the fibre bundle to its jet bundles.
We explore the possibility that the interactions of a light scalar singlet, which mixes with the Standard Model~(SM) Higgs, also receive other UV contributions of comparable size. We focus, in particular, on the flavor aligned limit, where couplings of the light scalar to the SM are almost flavor diagonal, but not necessarily proportional to the Higgs Yukawa couplings. The phenomenology of such a general flavor aligned light scalar differs from both the Higgs-mixed scalar, as well as from a general axion-like particle. We explore this for light scalar masses below a few hundred MeV, such that they can be produced in kaon decays, and in decays of η and η′ mesons, and the transitions described using chiral perturbation theory. We then derive constraints on the light scalar interactions, assuming that light scalar decays are either just into photons or are invisible. We also discuss several UV examples of such light scalar models: a two-Higgs doublet model extended by a light scalar, a light dilaton from the dark sector, and a SM extended by heavy vector-like quarks and a light scalar. For the latter we also performed matching onto low energy theory at one-loop.
Searches for dark photons provide serendipitous discovery potential for other
types of vector particles. We develop a framework for recasting dark photon
searches to obtain constraints on more general theories, which includes a
data-driven method for determining hadronic decay rates. We demonstrate our
approach by deriving constraints on a vector that couples to the B−L
current, a leptophobic B boson that couples directly to baryon number and to
leptons via B-γ kinetic mixing, and on a vector that mediates a
protophobic force. Our approach can easily be generalized to any massive gauge
boson with vector couplings to the Standard Model fermions, and software to
perform any such recasting is provided at this https URL .
A new model derived from N=1 Supersymmetric QCD (SQCD) with N_c = N_f offers a simplified, four-dimensional field theory solution to the axion quality problem. This mechanism leverages the spontaneous breaking of baryon number in the composite sector to provide exponential protection for the QCD axion's shift symmetry, ensuring its viability as a strong CP and dark matter candidate.
07 Oct 2025
Given two otherwise decoupled D-dimensional CFTs which possess a common (finite) symmetry subcategory, one can consider entangled boundary states of their (D+1)-dimensional SymTFTs. This roughly corresponds to performing a gauging of the tensor product of two CFTs, and we call this phenomena ``SymTFT entanglement" (or ``S-entanglement" for short). In the case when these CFTs have semiclassical holographic duals, the S-entanglement relates the bulk gauge charges between two otherwise disconnected AdS spacetimes as we highlight in several top-down examples. We show that taking partial traces of such S-entangled states leads to a streamlined approach to preparing ensemble-averaged CFTs in string theory. This ensemble averaging coincides with that generated by α-states in the baby universe Hilbert space, and we propose a symmetry-enriched generalization of this Hilbert space via generalized global symmetries. We quantify how this symmetry-governed averaging violates holographic factorization and leads to the emergence of bulk global symmetries. We also consider the eternal (two-sided) AdS black hole geometries, where our SymTFT entanglement considerations imply that there exist refinements of the usual theromofield double state preparation of the system. We show that one may prepare the system in such a way that the total CFT data does not factorize into left and right copies. As anticipated by Marolf and Wall \cite{Marolf:2012xe}, we highlight that such considerations are necessary to define the gauge charges of eternal black holes, and in certain cases, can imply that there exist extended bulk objects stretching across the wormhole which cannot be expressed in terms of a product of left and right CFT operators.
The search for heavy resonances beyond the Standard Model (BSM) is a key
objective at the LHC. While the recent use of advanced deep neural networks for
boosted-jet tagging significantly enhances the sensitivity of dedicated
searches, it is limited to specific final states, leaving vast potential BSM
phase space underexplored. We introduce a novel experimental method,
Signature-Oriented Pre-training for Heavy-resonance ObservatioN (Sophon), which
leverages deep learning to cover an extensive number of boosted final states.
Pre-trained on the comprehensive JetClass-II dataset, the Sophon model learns
intricate jet signatures, ensuring the optimal constructions of various jet
tagging discriminates and enabling high-performance transfer learning
capabilities. We show that the method can not only push widespread
model-specific searches to their sensitivity frontier, but also greatly improve
model-agnostic approaches, accelerating LHC resonance searches in a broad
sense.
We point out that using current knowledge of B(KL0→μ+μ−) and B(KL0→γγ), one can extract short-distance information from the combined measurement of the time-integrated CP asymmetry, ACP(K0→μ+μ−), and of B(KS0→μ+μ−). We discuss the interplay between this set of observables, and demonstrate that determining sign[ACP(K0→μ+μ−)] would eliminate the discrete ambiguity in the Standard Model prediction for B(KL0→μ+μ−). We then move on to feasibility studies within an LHCb-like setup, using both time-integrated and time-dependent information, employing K0 and K0 tagging methods. We find that, within an optimistic scenario, the short-distance amplitude, proportional to the CKM parameter combination ∣A2λ5ηˉ∣, could be constrained by LHCb at the level of about 35% of its Standard Model value, and the discrete ambiguity in B(KL0→μ+μ−)SM could be resolved at more than 3σ by the end of the high luminosity LHC.
15 Sep 2025
At hadron colliders, the net transverse momentum of particles that do not interact with the detector (missing transverse momentum, pTmiss) is a crucial observable in many analyses. In the standard model, pTmiss originates from neutrinos. Many beyond-the-standard-model particles, such as dark matter candidates, are also expected to leave the experimental apparatus undetected. This paper presents a novel pTmiss estimator, DeepMET, which is based on deep neural networks that were developed by the CMS Collaboration at the LHC. The DeepMET algorithm produces a weight for each reconstructed particle based on its properties. The estimator is based on the negative vector sum of the weighted transverse momenta of all reconstructed particles in an event. Compared with other estimators currently employed by CMS, DeepMET improves the pTmiss resolution by 10−30%, shows improvement for a wide range of final states, is easier to train, and is more resilient against the effects of additional proton-proton interactions accompanying the collision of interest.
We consider the economical 331 model, based on β=−1/3, with three SU(3) triplets with a softly broken Z2 symmetry. The resulting scalar potential is commonly used in phenomenology. We systematically determine all the potential minima and obtain the conditions under which the electroweak vacuum is global with the help of orbit space methods. For the case the electroweak vacuum is not global, we calculate bounds on the scalar couplings from metastability. We find a parametrisation of the potential couplings in terms of physical quantities and use it to show the available parameter space.
16 Nov 2013
We show that, within the AdS/CFT correspondence, recent formulations of the
information paradox can be reduced to a question about the existence of certain
kinds of operators in the CFT. We describe a remarkably simple construction of
these operators on a given state of the CFT. Our construction leads to a smooth
horizon, addresses the strong subadditivity paradox, while preserving locality
within effective field theory, and reconciles the existence of the interior
with the growth of states with energy in the CFT. We also extend our
construction to non-equilibrium states.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.