ESPCI ParisTech
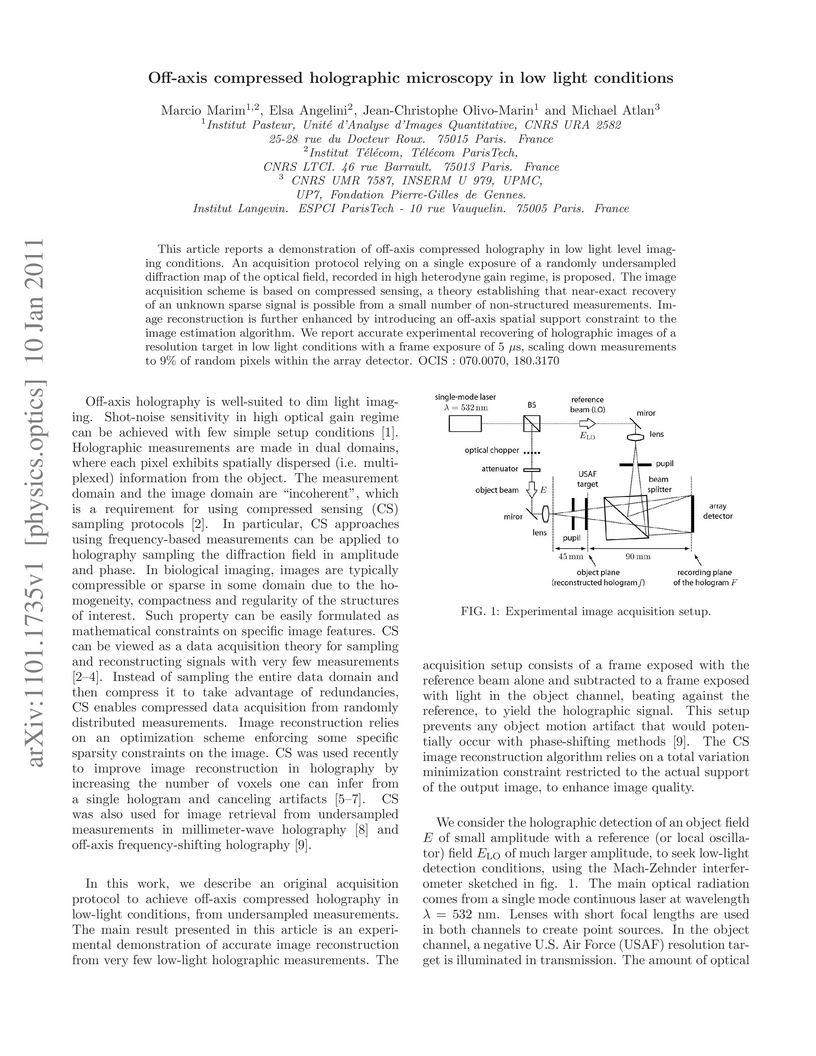
This Letter reports a demonstration of off-axis compressed holography in low-light level imaging conditions. An acquisition protocol relying on a single exposure of a randomly undersampled diffraction map of the optical field, recorded in the high heterodyne gain regime, is proposed. The image acquisition scheme is based on compressed sensing, a theory establishing that near-exact recovery of an unknown sparse signal is possible from a small number of nonstructured measurements. Image reconstruction is further enhanced by introducing an off-axis spatial support constraint to the image estimation algorithm. We report accurate experimental recovering of holographic images of a resolution target in low-light conditions with a frame exposure of 5 \mu s, scaling down measurements to 9% of random pixels within the array detector.
We study constraint satisfaction problems on the so-called 'planted' random ensemble. We show that for a certain class of problems, e.g. graph coloring, many of the properties of the usual random ensemble are quantitatively identical in the planted random ensemble. We study the structural phase transitions, and the easy/hard/easy pattern in the average computational complexity. We also discuss the finite temperature phase diagram, finding a close connection with the liquid/glass/solid phenomenology.
31 Jan 2024
We study the yielding transition in soft jammed materials under oscillatory shear, employing a novel methodology that combines rheological measurements with detailed dynamical observations. This method provides a comprehensive view of the intricate interactions between macroscopic mechanical behavior, mesoscopic deformation patterns, and microscopic dynamics during yielding. Our findings reveal two distinct yielding behaviors: at one end, a smooth, uniform transition, characterized by homogeneous strain fields, and Fickian, Gaussian microscopic dynamics; at the other, a sharp transition defined by pronounced shear banding, with the dynamics within shear bands being governed exclusively by the local strain, and exhibiting non-Gaussian, cooperative nature. The viscoplastic fragility emerges as a key macroscopic predictor of these intricate behaviors across micro- and meso-scales, providing a new perspective to understand and quantify ductile and brittle yielding in soft materials.
08 Jun 2012
In this letter, we present the study of the high-frequency mixing properties of ion irradiated YBa2Cu3O7 Josephson nano-junctions. The frequency range, spanning above and below the characteristic frequencies fc of the junctions, permits clear observation of the transition between two mixing regimes. The experimental conversion gain was found to be in good agreement with the prediction of the three ports model. Finally, we discuss the potential of the junctions to build a Josephson mixer operating in the terahertz frequency range.
13 Nov 2015
Zero-Group Velocity (ZGV) Lamb waves are studied in a structure composed of two plates bonded by an adhesive layer. The dispersion curves are calculated for a Duralumin/epoxy/Duralumin sample, where the adhesion is modeled by a normal and a tangential spring at both interfaces. Several ZGV modes are identified and their frequency dependence on interfacial stiffnesses and on the bonding layer thickness are numerically studied. Then, experiments achieved with laser ultrasonic techniques are presented. Local resonances are measured using superimposed source and probe. Knowing the thicknesses and elastic constants of the Duralumin and epoxy layers, the comparison between theoretical and experimental ZGV resonances leads to an evaluation of the interfacial stiffnesses. A good agreement with theoretical dispersion curves confirms the identification of the resonances and the parameter estimations. This non-contact technique is promising for the local evaluation of bonded structures.
Recent progress in solid state quantum information processing has stimulated the search for ultra-low-noise amplifiers and frequency converters in the microwave frequency range, which could attain the ultimate limit imposed by quantum mechanics. In this article, we report the first realization of an intrinsically phase-preserving, non-degenerate superconducting parametric amplifier, a so far missing component. It is based on the Josephson ring modulator, which consists of four junctions in a Wheatstone bridge configuration. The device symmetry greatly enhances the purity of the amplification process and simplifies both its operation and analysis. The measured characteristics of the amplifier in terms of gain and bandwidth are in good agreement with analytical predictions. Using a newly developed noise source, we also show that our device operates within a factor of three of the quantum limit. This development opens new applications in the area of quantum analog signal processing.
We report on local superficial blood flow monitoring in biological tissue from laser Doppler holographic imaging. In time averaging recording conditions, holography acts as a narrowband bandpass filter, which, combined with a frequency shifted reference beam, permits frequency selective imaging in the radiofrequency range. These Doppler images are acquired with an off axis Mach Zehnder interferometer. Microvascular hemodynamic components mapping is performed in the cerebral cortex of the mouse and the eye fundus of the rat with near-infrared laser light without any exogenous marker. These measures are made from a basic inverse method analysis of local first order optical fluctuation spectra at low radiofrequencies, from 0 Hz to 100 kHz. Local quadratic velocity is derived from Doppler broadenings induced by fluid flows, with elementary diffusing wave spectroscopy formalism in backscattering configuration. We demonstrate quadratic mean velocity assessment in the 0.1 to 10 millimeters per second range in vitro and imaging of superficial blood perfusion with a spatial resolution of about 10 micrometers in rodent models of cortical and retinal blood flow.
Variation and selection are the core principles of Darwinian evolution, yet quantitatively relating the diversity of a population to its capacity to respond to selection is challenging. Here, we examine this problem at a molecular level in the context of populations of partially randomized proteins selected for binding to well-defined targets. We built several minimal protein libraries, screened them in vitro by phage display and analyzed their response to selection by high-throughput sequencing. A statistical analysis of the results reveals two main findings: first, libraries with same sequence diversity but built around different "frameworks" typically have vastly different responses, second, the distribution of responses within a library follows a simple scaling law. We show how an elementary probabilistic model based on extreme value theory rationalizes these findings. Our results have implications for designing synthetic protein libraries, for estimating the density of functional biomolecules in sequence space, for characterizing diversity in natural populations and for experimentally investigating the concept of evolvability, or potential for future evolution.
16 May 2014
Many experimental and numerical studies report a large reduction of the
recirculation bubble in Backward-Facing Step flows or airfoils in stall
situation when excited at the natural shedding frequency f0. Through a
simple experiment using Dielectric Barrier Discharge actuator, we find a
different result. For a given Reynolds number, the frequency of the
perturbation is varied for a fixed duty-cycle dc = 27%. Through phase-averaging
of Particle Image Velocimetry measurements, we show that the actuation creates
a forced vortex which interacts with the natural shedding with a different
phase velocity than the unforced one. The largest reduction of the
recirculation bubble (-35%) is obtained in a very narrow frequency range around
0.73f0 where early vortex pairing occurs between forced and unforced
vortices. Phase averaging shows that in this case, the actuation clearly forces
the vortex pairing in the shear layer. On the contrary, when the forcing
frequency is higher, the shear layer behaves like an amplifier synchronized on
the forced frequency, leading to a constant 10% reduction of the recirculation
bubble.
19 Sep 2018
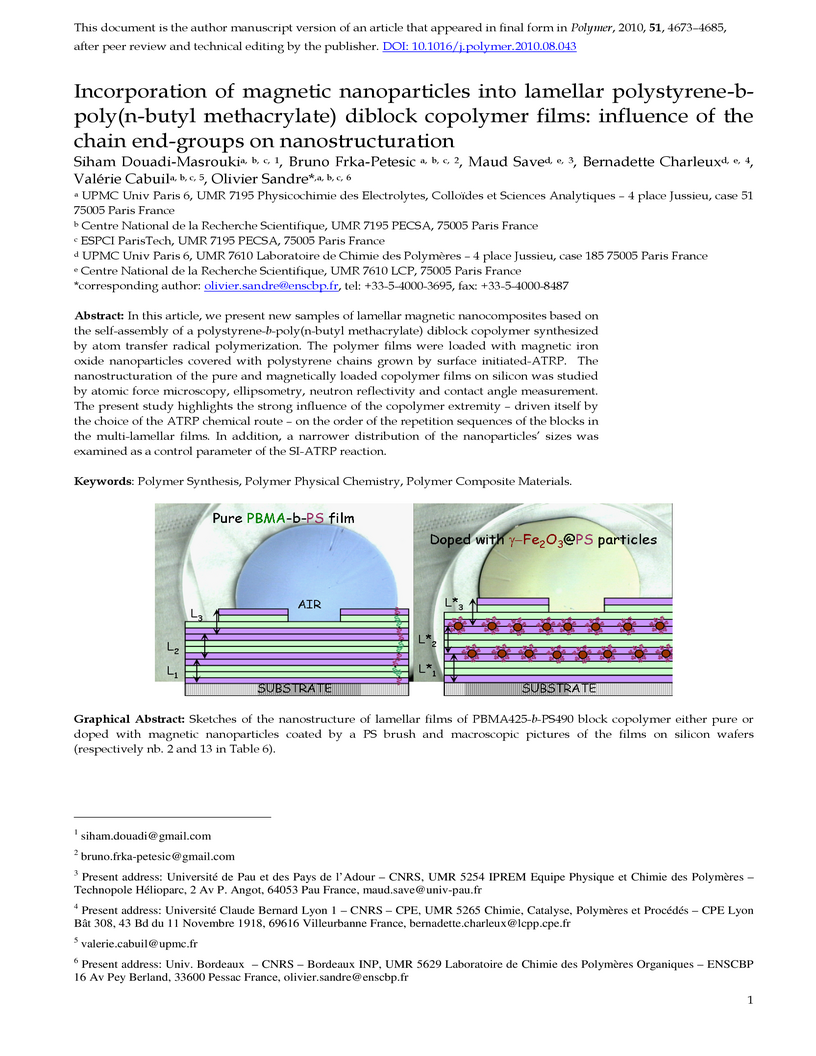
In this article, we present new samples of lamellar magnetic nanocomposites
based on the self-assembly of a polystyrene-b-poly(n-butyl methacrylate)
diblock copolymer synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization. The
polymer films were loaded with magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles covered with
polystyrene chains grown by surface initiated-ATRP. The nanostructuration of
the pure and magnetically loaded copolymer films on silicon was studied by
atomic force microscopy, ellipsometry, neutron reflectivity and contact angle
measurement. The present study highlights the strong influence of the copolymer
extremity - driven itself by the choice of the ATRP chemical route - on the
order of the repetition sequences of the blocks in the multi-lamellar films. In
addition, a narrower distribution of the nanoparticles' sizes was examined as a
control parameter of the SI-ATRP reaction.
Imaging techniques such as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and diffuse optical tomography (DOT) achieve deep, non-invasive sensing in turbid media, but they are constrained by the photon budget. Wavefront shaping (WFS) can enhance signal strength via interference at specific locations within scattering media, enhancing light-matter interactions and potentially extending the penetration depth of these techniques. Interpreting the resulting measurements rests on the knowledge of optical sensitivity - a relationship between detected signal changes and perturbations at a specific location inside the medium. However, conventional diffusion-based sensitivity models rely on assumptions that become invalid under coherent illumination. In this work, we develop a microscopic theory for optical sensitivity that captures the inherent interference effects that diffusion theory necessarily neglects. We analytically show that under random illumination, the microscopic and diffusive treatments coincide. Using our microscopic approach, we explore WFS strategies for enhancing optical sensitivity beyond the diffusive result. We demonstrate that the input state obtained through phase conjugation at a given point inside the system leads to the largest enhancement of optical sensitivity but requires an input wavefront that depends on the target position. In sharp contrast, the maximum remission eigenchannel leads to a global enhancement of the sensitivity map with a fixed input wavefront. This global enhancement equals to remission enhancement and preserves the spatial distribution of the sensitivity, making it compatible with existing DOT reconstruction algorithms. Our results establish the theoretical foundation for integrating wavefront control with diffuse optical imaging, enabling deeper tissue penetration through improved signal strength in biomedical applications.
18 Jul 2014
A non contact technique using Zero-Group Velocity (ZGV) Lamb modes is developed to probe the bonding between two solid plates coupled by a thin layer. The layer thickness is assumed to be negligible compared with the plate thickness and the acoustic wavelength. The coupling layer is modeled by a normal and a tangential spring to take into account the normal and shear interfacial stresses. Theoretical ZGV frequencies are determined for a symmetrical bi-layer structure and the effect of the interfacial stiffnesses on the cut-off and ZGV frequencies are evaluated. Experiments are conducted with two glass plates bonded by a drop of water, oil, or salol, leading to a few micrometer thick layer. An evaluation of normal and shear stiffnesses, is obtained using ZGV resonances locally excited and detected with laser ultrasonic techniques.
05 May 2015
Turbulent shear flows have triggered fundamental research in nonlinear dynamics, like transition scenarios, pattern formation and dynamical modeling. In particular, the control of nonlinear dynamics is subject of research since decades. In this publication, actuated turbulent shear flows serve as test-bed for a nonlinear feedback control strategy which can optimize an arbitrary cost function in an automatic self-learning manner. This is facilitated by genetic programming providing an analytically treatable control law. Unlike control based on PID laws or neural networks, no structure of the control law needs to be specified in advance. The strategy is first applied to low-dimensional dynamical systems featuring aspects of turbulence and for which linear control methods fail. This includes stabilizing an unstable fixed point of a nonlinearly coupled oscillator model and maximizing mixing, i.e.\ the Lyapunov exponent, for forced Lorenz equations. For the first time, we demonstrate the applicability of genetic programming control to four shear flow experiments with strong nonlinearities and intrinsically noisy measurements. These experiments comprise mixing enhancement in a turbulent shear layer, the reduction of the recirculation zone behind a backward facing step, and the optimized reattachment of separating boundary layers. Genetic programming control has outperformed tested optimized state-of-the-art control and has even found novel actuation mechanisms.
Multimode fibers (MMFs) are attractive ultra-thin replacements for
state-of-the-art endoscopes, but the phase randomization in propagation through
MMFs poses a major hurdle for imaging and focusing of light. Recently, this
challenge has been addressed by pre-measuring the compensation for the fiber's
complex input-output modes relations. Unfortunately, the sensitivity of this
approach to fiber bending and temperature variations renders it inappropriate
for many applications. Here, we demonstrate a truly endoscopic robust method
for controlled in-situ focusing and scanning through a flexible uncharacterized
MMF, whereby all the instrumentation is situated at the proximal end. We show
that in graded-index (GRIN) fibers, light patterns at the proximal end allow
retrieving information about the distal light distribution. We utilize these
properties and two-photon fluorescence for robust controlled focusing through
bended GRIN fibers. Our results carry potential for lensless two-photon
micro-endoscopy.
We propose here to combine sideband holography with stroboscopic illumination
synchronized with the vibration of an object. By sweeping the optical frequency
of the reference beam such a way the holographic detection is tuned on the
successive sideband harmonic ranks, we are able to image the instantaneous
velocities of the object. Since the stroboscopic illumination is made with an
electronic device, the method is compatible with fast (up to several MHz)
vibration motions. The method is demonstrated with a vibrating clarinet reed
excited sinusoidally at 2 kHz, and a stroboscopic illumination with cyclic
ratio 0.15. Harmonic rank up to n = ±100 are detected, and a movie of the
instantaneous velocities is reported.
Multiple scattering of waves in disordered media is a nightmare whether it be for detection or imaging purposes. The best approach so far to get rid of multiple scattering is optical coherence tomography. It basically combines confocal microscopy and coherence time-gating to discriminate ballistic photons from a predominant multiple scattering background. Nevertheless, the imaging depth range remains limited to 1 mm at best in human soft tissues. Here we propose a matrix approach of optical imaging to push back this fundamental limit. By combining a matrix discrimination of ballistic waves and iterative time-reversal, we show both theoretically and experimentally an extension of the imaging-depth limit by at least a factor two compared to optical coherence tomography. In particular, the reported experiment demonstrates imaging through a strongly scattering layer from which only one reflected photon over 1000 billion is ballistic. This approach opens a new route towards ultra-deep tissue imaging.
29 Oct 2015
The structure of the ultimately-thin crystalline allotrope of silicon oxide,
prepared onto a ruthenium surface, is unveiled down to atomic scale with
chemical sensitivity, thanks to high resolution scanning tunneling microscopy
and first principle calculations. An ordered oxygen lattice is imaged which
coexists with the two-dimensional monolayer oxide. This coexistence signals a
displacive transformation from an oxygen reconstructed-Ru(0001) to silicon
oxide, along which latterally-shifted domains form, each with equivalent and
degenerate epitaxial relationships with the substrate. The unavoidable
character of defects at boundaries between these domains appeals for the
development of alternative methods capable of producing single-crystalline
two-dimensional oxides.
01 Jul 2016
There is a huge abundance of viruses and membrane vesicles in seawater. We describe a new full-field, incoherently illuminated, shot-noise limited, common-path interferometric detection method that we couple with the analysis of Brownian motion to detect, quantify, and differentiate biotic nanoparticles. We validated the method with calibrated nanoparticles and homogeneous DNA or this http URL. The smallest virus size that we characterized with a suitable signal-to-noise ratio was around 30 nm in diameter. Analysis of Brownian motions revealed anisotropic trajectories for this http URL further applied the method for vesicles detection and for analysis of coastal and oligotrophic samples from Tara Oceans circumnavigation.
23 Apr 2024
We consider a version of the classical Hamiltonian FPU (Fermi-Pasta-Ulam)
problem with nonlinear force-strain relation in which a hardening response is
taken over by a softening regime above a critical strain value. We show that in
addition to pulses (solitary waves) this discrete system also supports
non-topological and dissipation-free fronts (kinks). Moreover, we demonstrate
that these two types of supersonic traveling wave solutions belong to the same
family. Within this family, solitary waves exist for continuous ranges of
velocity that extend up to a limiting speed corresponding to kinks. As the kink
velocity limit is approached from above or below, the solitary waves become
progressively more broad and acquire the structure of a kink-antikink bundle.
Direct numerical simulations and Floquet analysis of linear stability suggest
that all of the obtained solutions are effectively stable. To motivate and
support our study of the discrete problem we also analyze a quasicontinuum
approximation with temporal dispersion. We show that this model captures the
main effects observed in the discrete problem both qualitatively and
quantitatively.
31 Jan 2014
We present a combined experimental and theoretical study of the proximity effect in an atomic-scale controlled junction between two different superconductors. Elaborated on a Si(111) surface, the junction comprises a Pb nanocrystal with an energy gap of 1.2 meV, connected to a crystalline atomic monolayer of lead with a gap of 0.23 meV. Using in situ scanning tunneling spectroscopy we probe the local density of states of this hybrid system both in space and in energy, at temperatures below and above the critical temperature of the superconducting monolayer. Direct and inverse proximity effects are revealed with high resolution. Our observations are precisely explained with the help of a self-consistent solution of the Usadel equations. In particular, our results demonstrate that in the vicinity of the Pb islands, the Pb monolayer locally develops a finite proximity-induced superconducting order parameter, well above its own bulk critical temperature. This leads to a giant proximity effect where the superconducting correlations penetrate inside the monolayer a distance much larger than in a non-superconducting metal.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.