Universität zu Köln
For galaxies hosting supermassive black holes (SMBHs), it has been observed
that the mass of the central black hole (M_BH) tightly correlates with the
effective or central velocity dispersion (sigma) of the host galaxy. The origin
of this M_BH - sigma scaling relation is assumed to lie in the merging history
of the galaxies but many open questions about its origin and the behavior in
different mass ranges still need to be addressed. The goal of this work is to
study the black-hole scaling relations for low black-hole masses, where the
regime of intermediate-mass black holes (IMBHs) in globular clusters (GCs) is
entered. We collect all existing reports of dynamical black-hole measurements
in globular clusters, providing black-hole masses or upper limits for 14
candidates. We plot the black-hole masses versus different cluster parameters
including total mass, velocity dispersion, concentration and half-mass radius.
We search for trends and test the correlations in order to quantify their
significance using a set of different statistical approaches. For correlations
showing a large significance we perform a linear fit, accounting for
uncertainties and upper limits. We find a clear correlation between the mass of
the IMBH and the velocity dispersion of the globular cluster. As expected, the
total mass of the globular cluster then also correlates with the mass of the
IMBH. While the slope of the M_BH - sigma correlation differs strongly from the
one observed for SMBHs, the other scaling relations M_BH - M_TOT, and M_BH - L
are similar to the correlations in galaxies. Significant correlations of
black-hole mass with other cluster properties were not found in the present
sample.
Much of the current theory of adaptation is based on Gillespie's mutational
landscape model (MLM), which assumes that the fitness values of genotypes
linked by single mutational steps are independent random variables. On the
other hand, a growing body of empirical evidence shows that real fitness
landscapes, while possessing a considerable amount of ruggedness, are smoother
than predicted by the MLM. In the present article we propose and analyse a
simple fitness landscape model with tunable ruggedness based on the Rough Mount
Fuji (RMF) model originally introduced by Aita et al. [Biopolymers 54:64-79
(2000)] in the context of protein evolution. We provide a comprehensive
collection of results pertaining to the topographical structure of RMF
landscapes, including explicit formulae for the expected number of local
fitness maxima, the location of the global peak, and the fitness correlation
function. The statistics of single and multiple adaptive steps on the RMF
landscape are explored mainly through simulations, and the results are compared
to the known behavior in the MLM model. Finally, we show that the RMF model can
explain the large number of second-step mutations observed on a highly-fit
first step backgound in a recent evolution experiment with a microvirid
bacteriophage [Miller et al., Genetics 187:185-202 (2011)].
 UCLA
UCLA Space Telescope Science InstituteUniversität zu KölnUniversidad Nacional de La PlataINAF-Istituto di RadioastronomiaUniversità di FirenzeInstituto de Astrofísica de La PlataCentro de Estudios de Física del Cosmos de Aragón (CEFCA)Observatorio Astronómico NacionalINAF - Osservatorio Astrofisco di ArcetriINAF Osservatorio di Astrofisica e Scienza dello Spazio di BolognaUniversit
Di Bologna
Space Telescope Science InstituteUniversität zu KölnUniversidad Nacional de La PlataINAF-Istituto di RadioastronomiaUniversità di FirenzeInstituto de Astrofísica de La PlataCentro de Estudios de Física del Cosmos de Aragón (CEFCA)Observatorio Astronómico NacionalINAF - Osservatorio Astrofisco di ArcetriINAF Osservatorio di Astrofisica e Scienza dello Spazio di BolognaUniversit
Di BolognaWe present \textit{JWST} NIRSpec and MIRI MRS observations of the central kiloparsec of M58 (NGC 4579), a nearby LINER galaxy hosting a low-luminosity AGN (LLAGN; Lbol∼1042 erg s−1) with a low-power jet. These data provide an unprecedented view of the warm molecular gas phase and reveal clear signatures of feedback. We detect 44 H2 lines, including bright pure rotational lines (S(1)-S(18)) and rovibrational lines up to ν=2, probing a wide range of excitation conditions. Excitation diagrams show that rotational lines follow a power-law temperature distribution with an exponential cutoff, consistent with heating by low-velocity shocks. H2 rovibrational lines deviate from thermal models primarily because of sub-thermal excitation at low density. Additionally, there may be a 10% contribution by AGN X-ray heating in the nucleus. The dust lanes associated with the spiral inflow appear dynamically undisturbed but show signs of shock heating, while the inner ∼200 pc exhibits turbulent kinematics produced by outflowing molecular gas. These results reveal the subtle yet measurable impact of LLAGN feedback on the interstellar medium, demonstrating that even weak, vertically oriented jets and low radiative accretion rates can perturb molecular gas and regulate nuclear reservoirs. This study highlights JWST's transformative ability to uncover hidden modes of AGN feedback.
16 Sep 2025
We show a simple and systematic way to certify any given bipartite state as the unique joint 1-eigenstate of two separable projectors, each of which can be measured with simple local observables. This is practically useful, as the detection probabilities of the two stabilizer projectors relate directly to the fidelity of certification. The same result gives a simple and effective lower bound on the entanglement fidelity of a quantum channel in terms of two ensemble fidelities.
We then generalise the bipartite result recursively to multipartite systems, showing that every n-party pure state is the unique joint 1-eigenstate of 2n−1 separable projectors, and an upper bound of the infidelity of the state in terms of the infidelities of the separable stabilizer projectors.
18 Nov 2025
Understanding the computational complexity of quantum states is a central challenge in quantum many-body physics. In qubit systems, fermionic Gaussian states can be efficiently simulated on classical computers and hence can be employed as a natural baseline for evaluating quantum complexity. In this work, we develop a framework for quantifying fermionic magic resources, also referred to as fermionic non-Gaussianity, which constitutes an essential resource for universal quantum computation. We leverage the algebraic structure of the fermionic commutant to define the fermionic antiflatness (FAF)-an efficiently computable and experimentally accessible measure of non-Gaussianity, with a clear physical interpretation in terms of Majorana fermion correlation functions. Studying systems in equilibrium, we show that FAF detects phase transitions, reveals universal features of critical points, and uncovers special solvable points in many-body systems. Extending the analysis to out-of-equilibrium settings, we demonstrate that fermionic magic resources become more abundant in highly excited eigenstates of many-body systems. We further investigate the growth and saturation of FAF under ergodic many-body dynamics, highlighting the roles of conservation laws and locality in constraining the increase of non-Gaussianity during unitary evolution. This work provides a framework for probing quantum many-body complexity from the perspective of fermionic Gaussian states and opens up new directions for investigating fermionic magic resources in many-body systems. Our results establish fermionic non-Gaussianity, alongside entanglement and non-stabilizerness, as a resource relevant not only to foundational studies but also to experimental platforms aiming to achieve quantum advantage.
The thermalizing dynamics of many-body systems is often described through the
lens of the Eigenstate Thermalization Hypothesis (ETH).
ETH postulates that the statistical properties of observables, when expressed
in the energy eigenbasis, are described by smooth functions,
that also describe correlations among the matrix elements. However, the form
of these functions is usually left undetermined. In this work, we investigate
the structure of such smooth functions by focusing on their Fourier transform,
recently identified as free cumulants. Using non-linear hydrodynamics, we
provide a prediction for the late-time behavior of time-ordered free cumulants
in the thermodynamic limit. The prediction is further corroborated by
large-scale numerical simulations of a non-integrable spin-1 Ising model,
which exhibits diffusive transport behavior. Good agreement is observed in both
infinite and finite-temperature regimes and for a collection of local
observables. Our results indicate that the smooth multi-point correlation
functions within the ETH framework admit a universal hydrodynamic description
at low frequencies.
25 Aug 2025
This research introduces Operator Stabilizer Entropy (OSE), a new measure for quantifying "magic" in quantum operators within the Heisenberg picture, acting as a dual to state-based magic theories. OSE demonstrates inherent locality, grows at most linearly with time, provides tighter lower bounds on circuit T-count, and saturates to a constant value in dual-unitary XXZ circuits.
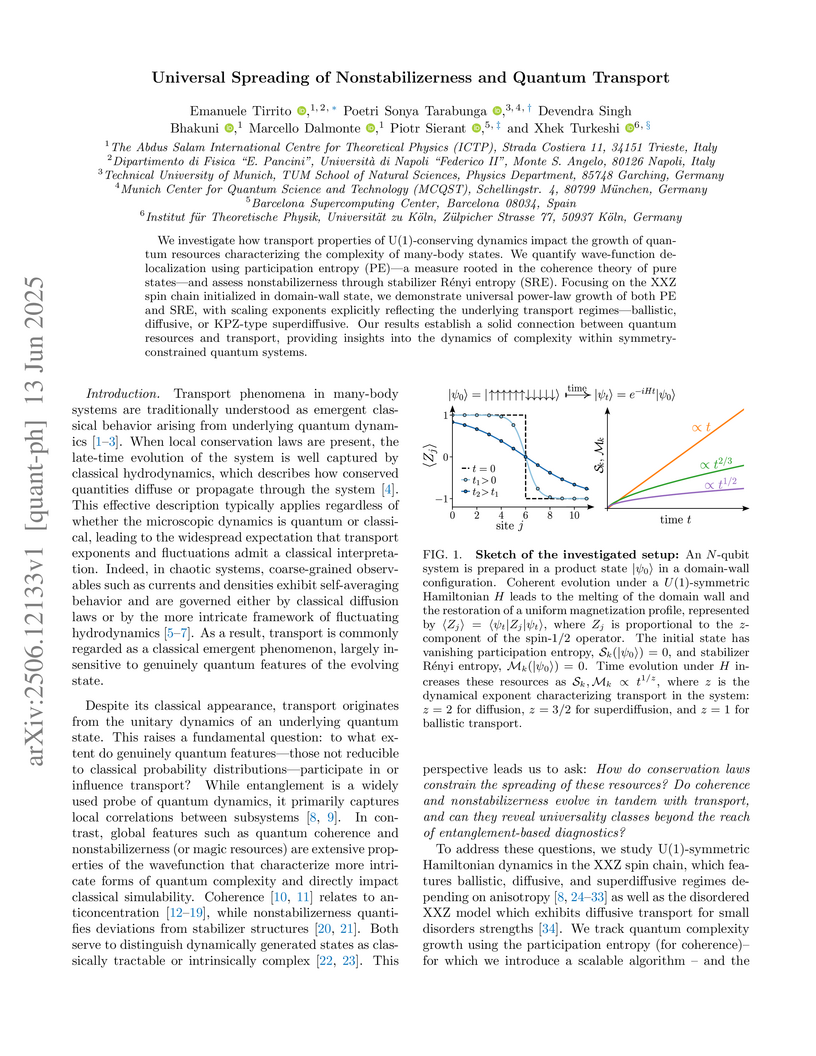
We investigate how transport properties of U(1)-conserving dynamics impact
the growth of quantum resources characterizing the complexity of many-body
states. We quantify wave-function delocalization using participation entropy
(PE), a measure rooted in the coherence theory of pure states, and assess
nonstabilizerness through stabilizer R\'enyi entropy (SRE). Focusing on the XXZ
spin chain initialized in domain-wall state, we demonstrate universal power-law
growth of both PE and SRE, with scaling exponents explicitly reflecting the
underlying transport regimes, ballistic, diffusive, or KPZ-type superdiffusive.
Our results establish a solid connection between quantum resources and
transport, providing insights into the dynamics of complexity within
symmetry-constrained quantum systems.
26 Sep 2025
We investigate the emergence of quantum complexity and chaos in doped Clifford circuits acting on qudits of odd prime dimension d. Using doped Clifford Weingarten calculus and a replica tensor network formalism, we derive exact results and perform large-scale simulations in regimes challenging for tensor network and Pauli-based methods. We begin by analyzing generalized stabilizer entropies, computable magic monotones in many-qudit systems, and identify a dynamical phase transition in the doping rate, marking the breakdown of classical simulability and the onset of Haar-random behavior. The critical behavior is governed by the qudit dimension and the magic content of the non-Clifford gate. Using the qudit T-gate as a benchmark, we show that higher-dimensional qudits converge faster to Haar-typical stabilizer entropies. For qutrits (d=3), analytical predictions match numerics on brickwork circuits, showing that locality plays a limited role in magic spreading. We also examine anticoncentration and entanglement growth, showing that O(logN) non-Clifford gates suffice for approximating Haar expectation values to precision ε, and relate antiflatness measures to stabilizer entropies in qutrit systems. Finally, we analyze out-of-time-order correlators and show that a finite density of non-Clifford gates is needed to induce chaos, with a sharp transition fixed by the local dimension, twice that of the magic transition. Altogether, these results establish a unified framework for diagnosing complexity in doped Clifford circuits and deepen our understanding of resource theories in multiqudit systems.
In recent years, strong expectations have been raised for the possible power
of quantum computing for solving difficult optimization problems, based on
theoretical, asymptotic worst-case bounds. Can we expect this to have
consequences for Linear and Integer Programming when solving instances of
practically relevant size, a fundamental goal of Mathematical Programming,
Operations Research and Algorithm Engineering? Answering this question faces a
crucial impediment: The lack of sufficiently large quantum platforms prevents
performing real-world tests for comparison with classical methods.
In this paper, we present a quantum analog for classical runtime analysis
when solving real-world instances of important optimization problems. To this
end, we measure the expected practical performance of quantum computers by
analyzing the expected gate complexity of a quantum algorithm. The lack of
practical quantum platforms for experimental comparison is addressed by hybrid
benchmarking, in which the algorithm is performed on a classical system,
logging the expected cost of the various subroutines that are employed by the
quantum versions. In particular, we provide an analysis of quantum methods for
Linear Programming, for which recent work has provided asymptotic speedup
through quantum subroutines for the Simplex method. We show that a practical
quantum advantage for realistic problem sizes would require quantum gate
operation times that are considerably below current physical limitations.
Hybrid evolution protocols, composed of unitary dynamics and repeated, weak or projective measurements, give rise to new, intriguing quantum phenomena, including entanglement phase transitions and unconventional conformal invariance. Defying the complications imposed by the non-linear and stochastic nature of the measurement process, we introduce a scenario of measurement-induced many body evolution, which possesses an exact analytical solution: bosonic Gaussian measurements. The evolution features a competition between the continuous observation of linear boson operators and a free Hamiltonian, and it is characterized by a unique and exactly solvable covariance matrix. Within this framework, we then consider an elementary model for quantum criticality, the free boson conformal field theory, and investigate in which way criticality is modified under measurements. Depending on the measurement protocol, we distinguish three fundamental scenarios (a) enriched quantum criticality, characterized by a logarithmic entanglement growth with a floating prefactor, or the loss of criticality, indicated by an entanglement growth with either (b) an area-law or (c) a volume-law. For each scenario, we discuss the impact of imperfect measurements, which reduce the purity of the wavefunction and are equivalent to Markovian decoherence, and present a set of observables, e.g., real-space correlations, the relaxation time, and the entanglement structure, to classify the measurement-induced dynamics for both pure and mixed states. Finally, we present an experimental tomography scheme, which grants access to the density operator of the system by using the continuous measurement record only.
This is an introductory text on the more topological aspects of contact geometry, written for the Handbook of Differential Geometry vol. 2. After discussing (and proving) some of the fundamental results of contact topology (neighbourhood theorems, isotopy extension theorems, approximation theorems), I move on to a detailed exposition of the original proof of the Lutz-Martinet theorem. The text ends with a guide to the literature.
27 Feb 2025
Anticoncentration describes how an ensemble of quantum states spreads over
the allowed Hilbert space, leading to statistically uniform output probability
distributions. In this work, we investigate the anticoncentration of random
Clifford circuits toward the overlap distribution of random stabilizer states.
Using exact analytical techniques and extensive numerical simulations based on
Clifford replica tensor networks, we demonstrate that random Clifford circuits
fully anticoncentrate in logarithmic circuit depth, namely higher-order moments
of the overlap distribution converge to those of random stabilizer states.
Moreover, we investigate the effect of introducing a controlled number of
non-Clifford (magic) resources into Clifford circuits. We show that inserting a
polylogarithmic in qudit number of T-states is sufficient to drive the
overlap distribution toward the Porter-Thomas statistics, effectively
recovering full quantum randomness. In short, this fact presents doped tensor
networks and shallow Clifford circuits as pseudo-magic quantum states. Our
results clarify the interplay between Clifford dynamics, magic resource
injection, and quantum complexity, with implications for quantum circuit
sampling and benchmarking of computational quantum advantage.
01 Sep 2025
We consider the problem of sequentially testing for changes in the mean parameter of a time series, compared to a benchmark period. Most tests in the literature focus on the null hypothesis of a constant mean versus the alternative of a single change at an unknown time. Yet in many applications it is unrealistic that no change occurs at all, or that after one change the time series remains stationary forever. We introduce a new setup, modeling the sequence of means as a piecewise constant function with arbitrarily many changes. Instead of testing for a change, we ask whether the evolving sequence of means, say (μn)n≥1, stays within a narrow corridor around its initial value, that is, μn∈[μ1−Δ,μ1+Δ] for all n≥1. Combining elements from multiple change point detection with a Hölder-type monitoring procedure, we develop a new online monitoring tool. A key challenge in both construction and proof of validity is that the risk of committing a type-I error after any time n fundamentally depends on the unknown future of the time series. Simulations support our theoretical results and we present two real-world applications: (1) healthcare monitoring, with a focus on blood glucose tracking, and (2) political consensus analysis via citizen opinion polls.
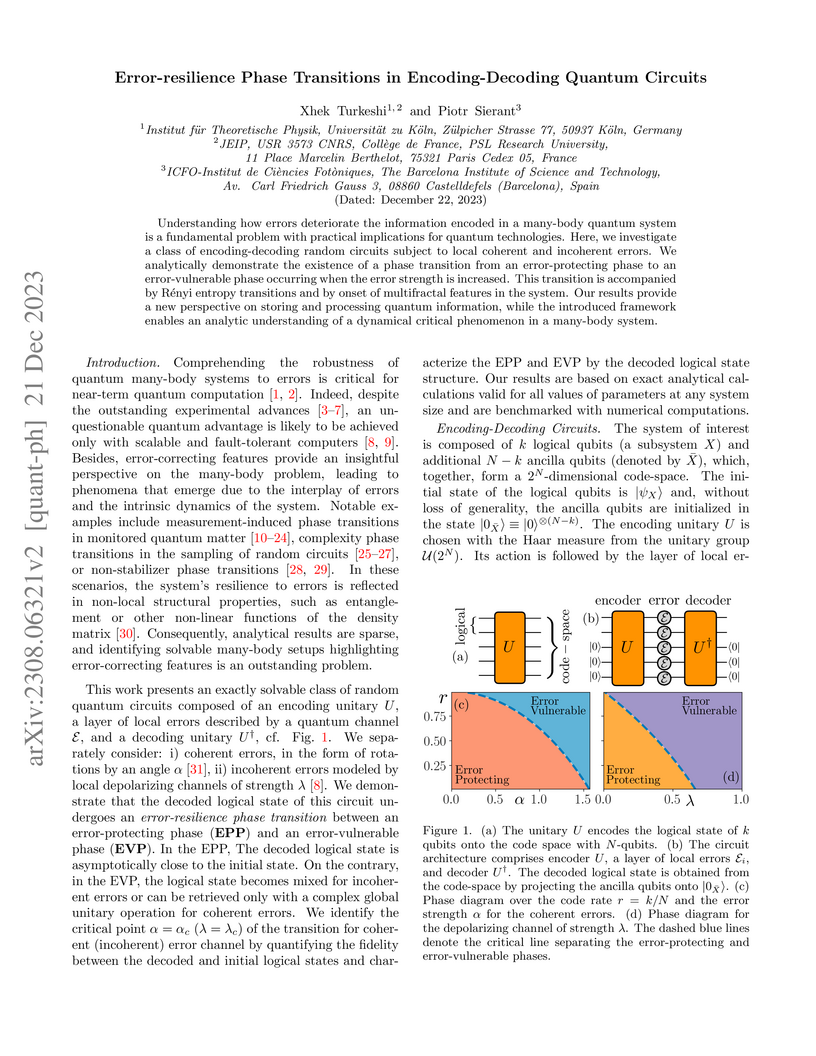
Understanding how errors deteriorate the information encoded in a many-body
quantum system is a fundamental problem with practical implications for quantum
technologies. Here, we investigate a class of encoding-decoding random circuits
subject to local coherent and incoherent errors. We analytically demonstrate
the existence of a phase transition from an error-protecting phase to an
error-vulnerable phase occurring when the error strength is increased. This
transition is accompanied by R\'enyi entropy transitions and by onset of
multifractal features in the system. Our results provide a new perspective on
storing and processing quantum information, while the introduced framework
enables an analytic understanding of a dynamical critical phenomenon in a
many-body system.
27 Sep 2025
We propose a new analytical tool called time-reversal positivity. It is an analogue of the Majorana reflection positivity in time-reversal symmetric case. This new time-reversal positivity can fully explain the relationship between time-reversal symmetry and the sign-free property in quantum Monte Carlo simulations. Using a cone-theoretical method, we show the ground state uniqueness for the time-reversal symmetric non-hermitian Hubbard model.
Local operator entanglement (LOE) dictates the complexity of simulating
Heisenberg evolution using tensor network methods, and serves as strong
dynamical signature of quantum chaos. We show that LOE is also sensitive to how
non-Clifford a unitary is: its magic resources. In particular, we prove that
LOE is always upper-bound by three distinct magic monotones: T-count, unitary
nullity, and operator stabilizer R\'enyi entropy. Moreover, in the average case
for large, random circuits, LOE and magic monotones approximately coincide. Our
results imply that an operator evolution that is expensive to simulate using
tensor network methods must also be inefficient using both stabilizer and Pauli
truncation methods. A direct corollary of our bounds is that any quantum
chaotic dynamics cannot be simulated classically. Entanglement in operator
space therefore measures a unified picture of non-classical resources, in stark
contrast to the Schr\"odinger picture.
12 Sep 2025
Monitoring a quantum system can profoundly alter its dynamical properties, leading to nontrivial emergent phenomena. In this work, we demonstrate that dynamical measurements strongly influence the evolution of symmetry in many-body quantum systems. Specifically, we demonstrate that monitored systems governed by non-Hermitian dynamics exhibit a quantum Mpemba effect, where systems with stronger initial asymmetry relax faster to a symmetric state. Crucially, this phenomenon is purely measurement-induced: in the absence of measurements, we find states where the corresponding unitary evolution does not display any Mpemba effect. Furthermore, we uncover a novel measurement-induced symmetry restoration mechanism: below a critical measurement rate, the symmetry remains broken, but beyond a threshold, it is fully restored in the thermodynamic limit--along with the emergence of the quantum Mpemba effect.
29 Jun 2025
We present high-resolution Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array observations of the 22 GHz H2O maser line in the extended Sagittarius B2 cloud. We detect 499 H2O masers across the observed velocities between -39 and 172 km s−1. To investigate the nature of the masers, we analyze their spatial distribution and cross-match with catalogs of HII regions and protostellar cores. 62% of masers are associated with protostellar cores and 32% with HII regions. The nature of the remaining 6% of sources was not established, but is likely associated with protostellar cores. Based on the spatial extent of the groups of masers, we classify them as either outflow-associated or young stellar object (YSO)-associated. We identify 144 unique sites of maser emission: 23 are associated with HII regions and 94 with protostellar cores, of which 33 are associated with protostellar outflows and 18 with YSOs.
The outflow-associated H2O maser emission is confined to within <2000 au of the central continuum source, despite shocked SiO emission extending over tens of thousands of au. The YSO-associated masers show a lack of detections at 5 < V_{rel} < 30 km s−1, which we suggest may be due to maser self-absorption. We show how H2O masers trace the large-scale material flow in Sgr B2 N (North) also seen in SiO and mm continuum emission. Finally, we find that protostellar cores with associated H2O masers tend to have brighter 3 mm continuum emission on average, although there is no strong correlation between maser brightness and continuum flux.
Free fermionic Gaussian, a.k.a. matchgate, random circuits exhibit atypical behavior compared to generic interacting systems. They produce anomalously slow entanglement growth, characterized by diffusive scaling S(t)∼t, and evolve into volume-law entangled states at late times, S∼N, which are highly unstable to measurements. Here, we investigate how doping such circuits with non-Gaussian resources (gates) restores entanglement structures of typical dynamics. We demonstrate that ballistic entanglement growth S(t)∼t is recovered after injecting an extensive total amount of non-Gaussian gates, also restoring Kardar-Parisi-Zhang fluctuations. When the evolution is perturbed with measurements, we uncover a measurement-induced phase transition between an area-law and a power-law entangled phase, S∼Nα, with α controlled by the doping. A genuine volume-law entangled phase is recovered only when non-Gaussian gates are injected at an extensive rate. Our findings bridge the dynamics of free and interacting fermionic systems, identifying non-Gaussianity as a key resource driving the emergence of non-integrable behavior.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.