Institute of Fundamental Physics IFF-CSIC
27 Feb 2025
The study of many-body quantum systems out of equilibrium remains a
significant challenge with complexity barriers arising in both state and
operator-based representations. In this work, we review recent approaches based
on finding better contraction strategies for the full spatio-temporal tensor
networks that encode the path integral of the dynamics, as well as the
conceptual integration of influence functionals, process tensors, and transfer
matrices within the tensor network formalism. We discuss recent algorithmic
developments, highlight the complexity of influence functionals in various
dynamical regimes and present consistent results of different communities,
showing how ergodic dynamics render these functionals exponentially difficult
to compress. Finally, we provide an outlook on strategies to encode
complementary influence functional overlaps, paving the way for accurate
descriptions of open and closed quantum systems with tensor networks.
04 Sep 2025
Continuously monitored quantum systems are emerging as promising platforms for quantum metrology, where a central challenge is to identify measurement strategies that optimally extract information about unknown parameters encoded in the complex quantum state of emitted radiation. Different measurement strategies effectively access distinct temporal modes of the emitted field, and the resulting choice of mode can strongly impact the information available for parameter estimation. While a ubiquitous approach in quantum optics is to select frequency modes through spectral filtering, the metrological potential of this technique has not yet been systematically quantified. We develop a theoretical framework to assess this potential by modeling spectral detection as a cascaded quantum system, allowing us to reconstruct the full density matrix of frequency-filtered photonic modes and to compute their associated Fisher information. This framework provides a minimal yet general method to benchmark the performance of spectral measurements in quantum optics, allowing to identify optimal filtering strategies in terms of frequency selection, detector linewidth, and metrological gain accessible through higher-order frequency-resolved correlations and mean-field engineering. These results lay the groundwork for identifying and designing optimal sensing strategies in practical quantum-optical platforms.
Institute of Fundamental Physics IFF-CSICUniversity of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU)Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESYEUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH (CERN)Donostia International Physics CenterMunich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST)IKERBASQUE-Basque Foundation for ScienceEHU Quantum CenterMax-Plank-Institut f ̈ur QuantenoptikRWTH Aachen University
In this manuscript, we explore the intersection of QML and TN in the context
of the one-dimensional ANNNI model with a transverse field. The study aims to
concretely connect QML and TN by combining them in various stages of algorithm
construction, focusing on phase diagram reconstruction for the ANNNI model,
with supervised and unsupervised techniques. The model's significance lies in
its representation of quantum fluctuations and frustrated exchange
interactions, making it a paradigm for studying magnetic ordering, frustration,
and the presence of a floating phase. It concludes with discussions of the
results, including insights from increased system sizes and considerations for
future work, such as addressing limitations in QCNN and exploring more
realistic implementations of QC.
30 Sep 2025
We propose a deterministic single-photon source in the terahertz (THz) regime, triggered by a sequence of coherent optical pulses. The scheme leverages the permanent dipole moment of a single-polar quantum emitter to induce THz transitions between optically dressed states, enhanced by a resonant coupling to a hybrid THz cavity. We present a cavity design that delivers high efficiency, purity, and indistinguishability while also enabling easy tunability of the emission frequency across the THz range. A key challenge in this new class of dressed-state sources is that, unlike standard solid-state single-photon sources, the dressed nature of the transitions can lead to undesired optical repumping during emission due to spontaneous photon emission in the visible range, which reduces the purity of the THz single-photon state. We show that this issue can be mitigated through optimized pulse areas and a sufficiently high Purcell rate, criteria that are met by our proposed cavity design. Finally, we demonstrate the significant purity enhancement of postselected THz photons by means of optical heralding, illustrating the new opportunities unlocked by the unique integration of terahertz and visible technologies with dressed polar quantum emitters.
We study the noisy dynamics of periodically driven, discrete-step quantum walks in a one-dimensional photonic lattice. We find that in the bulk, temporal noise that is constant within a Floquet period leads to decoherence-free momentum subspaces, whereas fully random noise destroys coherence in a few time-steps. When considering topological edge states, we observe decoherence no matter the type of temporal noise. To explain these results, we derive a non-perturbative master equation to describe the system's dynamics and experimentally confirm our findings in a discrete mesh photonic lattice implemented in a double-fibre ring setup. Surprisingly, our results show that a class of bulk states can be more robust to a certain type of noise than topological edge states.
The distribution of entanglement across distant qubits is a central challenge for the operation of scalable quantum computers and large-scale quantum networks. Existing approaches rely on deterministic state transfer schemes or probabilistic protocols that require active control or measurement and postselection. Here we demonstrate an alternative, fully autonomous process, where two remote qubits are entangled through their coupling to a quantum-correlated photonic reservoir. In our experiment, a Josephson parametric converter produces a Gaussian, continuous-variable entangled state of propagating microwave fields that drives two spatially separated superconducting transmon qubits into a stationary, discrete-variable entangled state. Beyond entanglement distribution, we also show that superconducting qubits can be used to directly certify two-mode squeezing, with higher sensitivity and without the need for calibrated noise-subtraction. These results establish networks of qubits interfaced with distributed continuous-variable entangled states as a powerful new platform for both foundational studies and quantum-technology relevant applications.
12 Jun 2025
We investigate the interactions between two-level emitters mediated by
time-dependent, one-dimensional, structured photonic baths, focusing on Floquet
topological lattices. Building on the framework of periodically driven photonic
lattices, we demonstrate and characterize the emergence of tunable-range
emitter's interactions mediated by bound states absent in static photonic
lattices. In particular, we show that one can not only obtain different spatial
interaction dependencies with respect to the static bath scenarios, but also in
qualitatively different regimes due to the time-dependent nature of the bath,
for example, when the emitters have different frequencies. This work sheds
light on the interplay between non-equilibrium photonics and quantum optics and
can serve as the basis for analyzing Floquet photonic lattices in higher
dimensions.
12 Nov 2024
Photonic quantum metrology enables the measurement of physical parameters with precision surpassing classical limits by using quantum states of light. However, generating states providing a large metrological advantage is hard because standard probabilistic methods suffer from low generation rates. Deterministic protocols using non-linear interactions offer a path to overcome this problem, but they are currently limited by the errors introduced during the interaction time. Thus, finding strategies to minimize the interaction time of these non-linearities is still a relevant question. In this work, we introduce and compare different deterministic strategies based on continuous and programmable Jaynes-Cummings and Kerr-type interactions, aiming to maximize the metrological advantage while minimizing the interaction time. We find that programmable interactions provide a larger metrological advantage than continuous operations at the expense of slightly larger interaction times. We show that while for Jaynes-Cummings non-linearities the interaction time grows with the photon number, for Kerr-type ones it decreases, favoring the scalability to big photon numbers. Finally, we also optimize different measurement strategies for the deterministically generated states based on photon-counting and homodyne detection.
07 May 2025
Non-reciprocal couplings or drivings are known to induce steady-state,
directional, amplification in driven-dissipative bosonic lattices. This
amplification phenomenon has been recently linked to the existence of a
non-zero topological invariant defined with the system's dynamical matrix, and
thus, it depends critically on the couplings' structure. In this work, we
demonstrate the emergence of unconventional, non-reciprocal, long-range
dissipative couplings induced by the interaction of the bosonic chain with a
chiral, multimode channel, and then study their impact on topological
amplification phenomena. We show that these couplings can lead to topological
invariant values greater than one which induce topological, multimode
amplification and metastability behaviour. Besides, we also show how these
couplings can also display topological amplifying phases that are dynamically
stable in the presence of local parametric drivings. Finally, we conclude by
showing how such phenomena can be naturally obtained in two-dimensional
topological insulators hosting multiple edge modes.
The field of superconducting qubits is constantly evolving with new circuit designs. However, when it comes to qubit readout, the use of simple transverse linear coupling remains overwhelmingly prevalent. This standard readout scheme has significant drawbacks: in addition to the Purcell effect, it suffers from a limitation on the maximal number of photons in the readout mode, which restricts the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the Quantum Non-Demolition (QND) nature of the readout. Here, we explore the high-power regime by engineering a nonlinear coupling between a transmon qubit and its readout mode. Our approach builds upon previous work by Dassonneville et al. [Physical Review X 10, 011045 (2020)], on qubit readout with a non-perturbative cross-Kerr coupling in a transmon molecule. We demonstrate a readout fidelity of 99.21% with 89 photons utilizing a parametric amplifier. At this elevated photon number, the QND nature remains high at 96.7%. Even with up to 300 photons, the QNDness is only reduced by a few percent. This is qualitatively explained by deriving a critical number of photons associated with the nonlinear coupling, yielding a theoretical value of nˉrcrit=377 photons for our sample's parameters. These results highlight the promising performance of the transmon molecule in the high-power regime, establishing it as a compelling platform for high-fidelity qubit readout.
In the out-of-equilibrium evolution induced by a quench, fast degrees of freedom generate long-range entanglement that is hard to encode with standard tensor networks. However, local observables only sense such long-range correlations through their contribution to the reduced local state as a mixture. We present a tensor network method that identifies such long-range entanglement and efficiently transforms it into mixture, much easier to represent. In this way, we obtain an effective description of the time-evolved state as a density matrix that captures the long-time behavior of local operators with finite computational resources.
29 Apr 2025
Long-range quantum systems, in which the interactions decay as
1/rα, are of increasing interest due to the variety of experimental
set-ups in which they naturally appear. Motivated by this, we study fundamental
properties of long-range spin systems in thermal equilibrium, focusing on the
weak regime of α>D. Our main result is a proof of analiticity of their
partition functions at high temperatures, which allows us to construct a
classical algorithm with sub-exponential runtime
exp(O(log2(N/ϵ))) that approximates the log-partition
function to small additive error ϵ. As by-products, we establish the
equivalence of ensembles and the Gaussianity of the density of states, which we
verify numerically in both the weak and strong long-range regimes. This also
yields constraints on the appearance of various classes of phase transitions,
including thermal, dynamical and excited-state ones. Our main technical
contribution is the extension to the quantum long-range regime of the
convergence criterion for cluster expansions of Koteck\'y and Preiss.
Discrete-step walks describe the dynamics of particles in a lattice subject to hopping or splitting events at discrete times. Despite being of primordial interest to the physics of quantum walks, the topological properties arising from their discrete-step nature have been hardly explored. Here we report the observation of topological phases unique to discrete-step walks. We use light pulses in a double-fibre ring setup whose dynamics maps into a two-dimensional lattice subject to discrete splitting events. We show that the number of edge states is not simply described by the bulk invariants of the lattice (i.e., the Chern number and the Floquet winding number) as would be the case in static lattices and in lattices subject to smooth modulations. The number of edge states is also determined by a topological invariant associated to the discrete-step unitary operators acting at the edges of the lattice. This situation goes beyond the usual bulk-edge correspondence and allows manipulating the number of edge states without the need to go through a gap closing transition. Our work opens new perspectives for the engineering of topological modes for particles subject to quantum walks.
01 Aug 2025
In recent years, Born-Markov master equations based on tracing out the electromagnetic degrees of freedom have been extensively employed in the description of quantum optical phenomena originating from photon-mediated interactions in quantum emitter ensembles. The breakdown of these effective models, built on assumptions such as ensemble spectral homogeneity, an unstructured photonic density of states, and weak light-matter coupling, has also recently attracted considerable attention. Here, we investigate the accuracy of this well-established framework beyond the most conventional, and extensively explored, spontaneous emission configuration. Specifically, we consider a system comprising two coherently driven and detuned quantum emitters, embedded within a hybrid photonic-plasmonic cavity, formed by a metallic nanorod integrated into a high-refractive-index dielectric microresonator. The local density of photonic states in this structure exhibits a complex frequency dependence, making it a compelling platform for exploring photon-mediated interactions beyond the assumptions above. We benchmark this modeling approach for the quantum dynamics of the emitter pair against exact calculations based on a macroscopic field quantization formalism, providing an illustrative assessment of its validity in significantly structured and dispersive photonic environments. Our analysis reveals four distinct regimes of laser driving and frequency splitting that lead to markedly different levels of accuracy in the effective model.
08 Apr 2024
Satellite mission planning for Earth observation satellites is a
combinatorial optimization problem that consists of selecting the optimal
subset of imaging requests, subject to constraints, to be fulfilled during an
orbit pass of a satellite. The ever-growing amount of satellites in orbit
underscores the need to operate them efficiently, which requires solving many
instances of the problem in short periods of time. However, current classical
algorithms often fail to find the global optimum or take too long to execute.
Here, we approach the problem from a quantum computing point of view, which
offers a promising alternative that could lead to significant improvements in
solution quality or execution speed in the future. To this end, we study a
planning problem with a variety of intricate constraints and discuss methods to
encode them for quantum computers. Additionally, we experimentally assess the
performance of quantum annealing and the quantum approximate optimization
algorithm on a realistic and diverse dataset. Our results identify key aspects
like graph connectivity and constraint structure that influence the performance
of the methods. We explore the limits of today's quantum algorithms and
hardware, providing bounds on the problems that can be currently solved
successfully and showing how the solution degrades as the complexity grows.
This work aims to serve as a baseline for further research in the field and
establish realistic expectations on current quantum optimization capabilities.
09 Jun 2025
The rapid growth of entanglement under unitary time evolution is the primary
bottleneck for modern tensor-network techniques--such as Matrix Product States
(MPS)--when computing time-dependent expectation values. This {entanglement
barrier} restricts classical simulations and, conversely, underpins the quantum
advantage anticipated from future devices. Here we show that, for
one-dimensional Hamiltonian dynamics, the spatio-temporal tensor network
encoding the evolved wave function amplitudes can be contracted efficiently
along the left-right (spatial) direction. Exploiting this structure, we develop
a hybrid Tensor-Network/Monte-Carlo (TN-MC) algorithm that samples the wave
function and evaluates expectation values of generic local operators with
computational cost that scales only polynomially in time. The accurate
contraction of the wave function amplitudes is a consequence of the favorable
scaling with time of the generalised temporal entropies. We find that their
real part either saturates or, at most, grows logarithmically with time,
revealing new instances of continuous dynamical quantum phase transitions
(DQPTs) which we characterize. Our results therefore show that, when computing
expectation values of local operators, the entanglement barrier in
one-dimensional Hamiltonian evolution can be bypassed with a TN-MC blend.
20 Sep 2024
The complexity of simulating the out-of-equilibrium evolution of local
operators in the Heisenberg picture is governed by the operator entanglement,
which grows linearly in time for generic non-integrable systems, leading to an
exponential increase in computational resources. A promising approach to
simplify this challenge involves discarding parts of the operator and focusing
on a subspace formed by "light" Pauli strings - strings with few Pauli matrices
- as proposed by Rakovszki et al. [PRB 105, 075131 (2022)]. In this work, we
investigate whether this strategy can be applied to quenches starting from
homogeneous product states. For ergodic dynamics, these initial states grant
access to a wide range of equilibration temperatures. By concentrating on the
desired matrix elements and retaining only the portion of the operator that
contains Pauli strings parallel to the initial state, we uncover a complex
scenario. In some cases, the light Pauli strings suffice to describe the
dynamics, enabling efficient simulation with current algorithms. However, in
other cases, heavier strings become necessary, pushing computational demands
beyond our current capabilities. We analyze this behavior using a newly
introduced measure of complexity, the Operator Weight Entropy, which we compute
for different operators across most points on the Bloch sphere.
30 Sep 2025
We propose a deterministic single-photon source in the terahertz (THz) regime, triggered by a sequence of coherent optical pulses. The scheme leverages the permanent dipole moment of a single-polar quantum emitter to induce THz transitions between optically dressed states, enhanced by a resonant coupling to a hybrid THz cavity. We present a cavity design that delivers high efficiency, purity, and indistinguishability while also enabling easy tunability of the emission frequency across the THz range. A key challenge in this new class of dressed-state sources is that, unlike standard solid-state single-photon sources, the dressed nature of the transitions can lead to undesired optical repumping during emission due to spontaneous photon emission in the visible range, which reduces the purity of the THz single-photon state. We show that this issue can be mitigated through optimized pulse areas and a sufficiently high Purcell rate, criteria that are met by our proposed cavity design. Finally, we demonstrate the significant purity enhancement of postselected THz photons by means of optical heralding, illustrating the new opportunities unlocked by the unique integration of terahertz and visible technologies with dressed polar quantum emitters.
16 May 2024
This work discusses the solution of partial differential equations (PDEs)
using matrix product states (MPS). The study focuses on the search for the
lowest eigenstates of a Hamiltonian equation, for which five algorithms are
introduced: imaginary-time evolution, steepest gradient descent, an improved
gradient descent, an implicitly restarted Arnoldi method, and density matrix
renormalization group (DMRG) optimization. The first four methods are
engineered using a framework of limited-precision linear algebra, where
operations between MPS and matrix product operators (MPOs) are implemented with
finite resources. All methods are benchmarked using the PDE for a quantum
harmonic oscillator in up to two dimensions, over a regular grid with up to
228 points. Our study reveals that all MPS-based techniques outperform
exact diagonalization techniques based on vectors, with respect to memory
usage. Imaginary-time algorithms are shown to underperform any type of gradient
descent, both in terms of calibration needs and costs. Finally, Arnoldi like
methods and DMRG asymptotically outperform all other methods, including exact
diagonalization, as problem size increases, with an exponential advantage in
memory and time usage.
25 Jun 2025
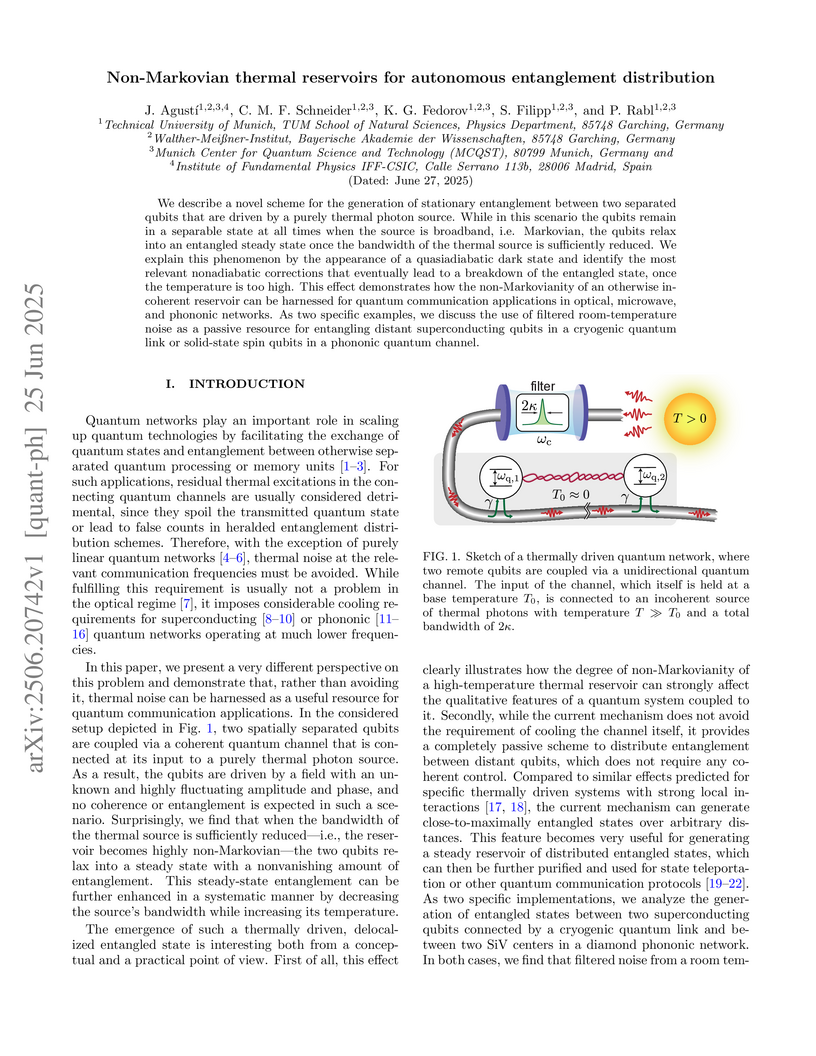
We describe a novel scheme for the generation of stationary entanglement between two separated qubits that are driven by a purely thermal photon source. While in this scenario the qubits remain in a separable state at all times when the source is broadband, i.e. Markovian, the qubits relax into an entangled steady state once the bandwidth of the thermal source is sufficiently reduced. We explain this phenomenon by the appearance of a quasiadiabatic dark state and identify the most relevant nonadiabatic corrections that eventually lead to a breakdown of the entangled state, once the temperature is too high. This effect demonstrates how the non-Markovianity of an otherwise incoherent reservoir can be harnessed for quantum communication applications in optical, microwave, and phononic networks. As two specific examples, we discuss the use of filtered room-temperature noise as a passive resource for entangling distant superconducting qubits in a cryogenic quantum link or solid-state spin qubits in a phononic quantum channel.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.