Ask or search anything...
Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science and Engineering
Adjusting for Confounders with Text: Challenges and an Empirical Evaluation Framework for Causal Inference
06 May 2022
Causal inference studies using textual social media data can provide actionable insights on human behavior. Making accurate causal inferences with text requires controlling for confounding which could otherwise impart bias. Recently, many different methods for adjusting for confounders have been proposed, and we show that these existing methods disagree with one another on two datasets inspired by previous social media studies. Evaluating causal methods is challenging, as ground truth counterfactuals are almost never available. Presently, no empirical evaluation framework for causal methods using text exists, and as such, practitioners must select their methods without guidance. We contribute the first such framework, which consists of five tasks drawn from real world studies. Our framework enables the evaluation of any casual inference method using text. Across 648 experiments and two datasets, we evaluate every commonly used causal inference method and identify their strengths and weaknesses to inform social media researchers seeking to use such methods, and guide future improvements. We make all tasks, data, and models public to inform applications and encourage additional research.
Political Bias and Factualness in News Sharing across more than 100,000 Online Communities
10 May 2022
As civil discourse increasingly takes place online, misinformation and the
polarization of news shared in online communities have become ever more
relevant concerns with real world harms across our society. Studying online
news sharing at scale is challenging due to the massive volume of content which
is shared by millions of users across thousands of communities. Therefore,
existing research has largely focused on specific communities or specific
interventions, such as bans. However, understanding the prevalence and spread
of misinformation and polarization more broadly, across thousands of online
communities, is critical for the development of governance strategies,
interventions, and community design. Here, we conduct the largest study of news
sharing on reddit to date, analyzing more than 550 million links spanning 4
years. We use non-partisan news source ratings from Media Bias/Fact Check to
annotate links to news sources with their political bias and factualness. We
find that, compared to left-leaning communities, right-leaning communities have
105% more variance in the political bias of their news sources, and more links
to relatively-more biased sources, on average. We observe that reddit users'
voting and re-sharing behaviors generally decrease the visibility of extremely
biased and low factual content, which receives 20% fewer upvotes and 30% fewer
exposures from crossposts than more neutral or more factual content. This
suggests that reddit is more resilient to low factual content than Twitter. We
show that extremely biased and low factual content is very concentrated, with
99% of such content being shared in only 0.5% of communities, giving credence
to the recent strategy of community-wide bans and quarantines.
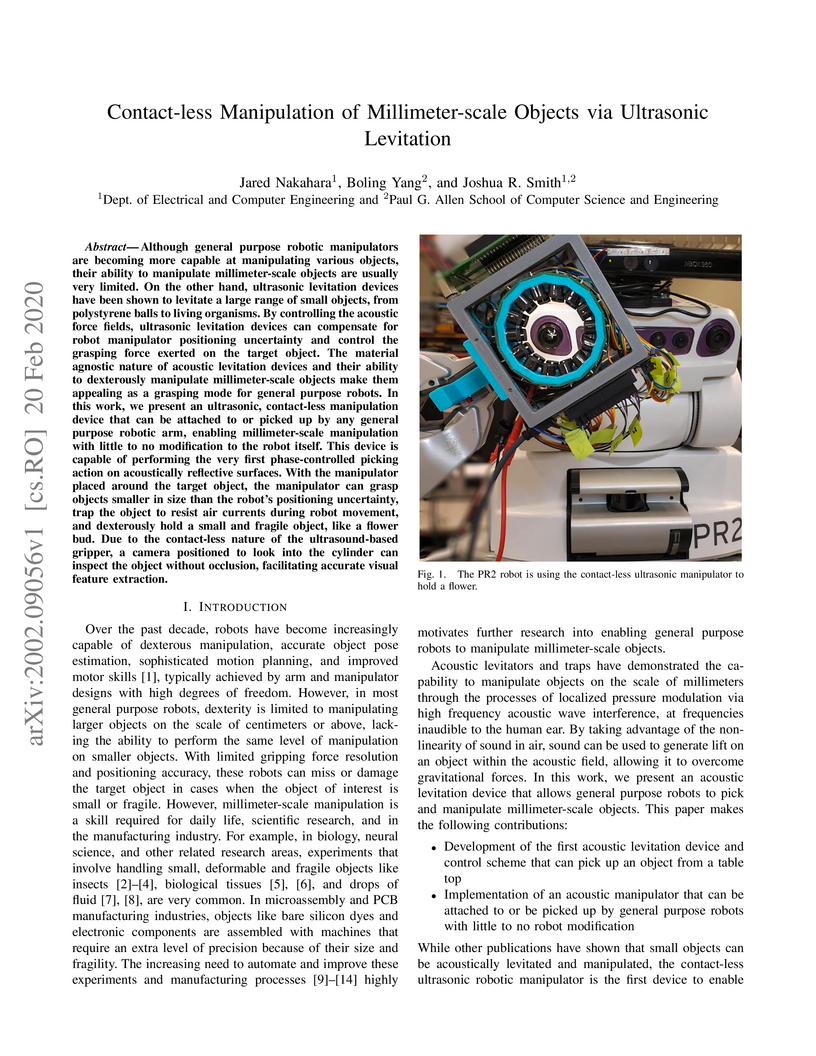
Contact-less manipulation of millimeter-scale objects via ultrasonic levitation
20 Feb 2020
Although general purpose robotic manipulators are becoming more capable at
manipulating various objects, their ability to manipulate millimeter-scale
objects are usually very limited. On the other hand, ultrasonic levitation
devices have been shown to levitate a large range of small objects, from
polystyrene balls to living organisms. By controlling the acoustic force
fields, ultrasonic levitation devices can compensate for robot manipulator
positioning uncertainty and control the grasping force exerted on the target
object. The material agnostic nature of acoustic levitation devices and their
ability to dexterously manipulate millimeter-scale objects make them appealing
as a grasping mode for general purpose robots. In this work, we present an
ultrasonic, contact-less manipulation device that can be attached to or picked
up by any general purpose robotic arm, enabling millimeter-scale manipulation
with little to no modification to the robot itself. This device is capable of
performing the very first phase-controlled picking action on acoustically
reflective surfaces. With the manipulator placed around the target object, the
manipulator can grasp objects smaller in size than the robot's positioning
uncertainty, trap the object to resist air currents during robot movement, and
dexterously hold a small and fragile object, like a flower bud. Due to the
contact-less nature of the ultrasound-based gripper, a camera positioned to
look into the cylinder can inspect the object without occlusion, facilitating
accurate visual feature extraction.
Cherry-Picking with Reinforcement Learning : Robust Dynamic Grasping in Unstable Conditions
Grasping small objects surrounded by unstable or non-rigid material plays a
crucial role in applications such as surgery, harvesting, construction,
disaster recovery, and assisted feeding. This task is especially difficult when
fine manipulation is required in the presence of sensor noise and perception
errors; errors inevitably trigger dynamic motion, which is challenging to model
precisely. Circumventing the difficulty to build accurate models for contacts
and dynamics, data-driven methods like reinforcement learning (RL) can optimize
task performance via trial and error, reducing the need for accurate models of
contacts and dynamics. Applying RL methods to real robots, however, has been
hindered by factors such as prohibitively high sample complexity or the high
training infrastructure cost for providing resets on hardware. This work
presents CherryBot, an RL system that uses chopsticks for fine manipulation
that surpasses human reactiveness for some dynamic grasping tasks. By
integrating imprecise simulators, suboptimal demonstrations and external state
estimation, we study how to make a real-world robot learning system sample
efficient and general while reducing the human effort required for supervision.
Our system shows continual improvement through 30 minutes of real-world
interaction: through reactive retry, it achieves an almost 100% success rate on
the demanding task of using chopsticks to grasp small objects swinging in the
air. We demonstrate the reactiveness, robustness and generalizability of
CherryBot to varying object shapes and dynamics (e.g., external disturbances
like wind and human perturbations). Videos are available at
this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.
 Adobe
Adobe

 Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University