Russian Quantum Center
01 Nov 2024
The decoy-state method is a prominent approach to enhance the performance of quantum key distribution (QKD) systems that operate with weak coherent laser sources. Due to the limited transmissivity of single photons in optical fiber, current experimental decoy-state QKD setups increase their secret key rate by raising the repetition rate of the transmitter. However, this usually leads to correlations between subsequent optical pulses. This phenomenon leaks information about the encoding settings, including the intensities of the generated signals, which invalidates a basic premise of decoy-state QKD. Here we characterize intensity correlations between the emitted optical pulses in two industrial prototypes of decoy-state BB84 QKD systems and show that they significantly reduce the asymptotic key rate. In contrast to what has been conjectured, we experimentally confirm that the impact of higher-order correlations on the intensity of the generated signals can be much higher than that of nearest-neighbour correlations.
23 Sep 2025
Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) provides one of the most promising quantum frameworks for addressing discrete optimization problems with broad real-world applications, particularly quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problems. However, the widely used hybrid quantum--classical implementation faces significant challenges due to statistical noise and barren plateaus. A prominent approach to mitigate these issues is fixed-point QAOA (fpQAOA), where circuit parameters are trained on small problem instances and subsequently transferred to larger ones. In this work, we develop a modified fpQAOA scheme that combines (i) considering the probability of achieving a target approximation ratio (AR) rather than requiring the exact optimum, (ii) setting the number of layers equal to the problem size with the sine--cosine encoding of QAOA angles, and (iii) rescaling the problem coefficient matrices to unit Frobenius norm. We demonstrate that this combination leads to a decreasing median number of shots required to obtain approximate solutions as the problem size increases, with ARs being within a few percent from the optimum for the considered problem classes. Extrapolation of these results suggests an O(1) shot complexity while retaining at most quadratic circuit depth, underscoring the potential of our approach to overcome key bottlenecks in QAOA implementations and scalability estimations. Remarkably, omitting even a single one of the modifications (i)--(iii) results in exponential growth of the number of shots required as the problem size increases.
07 Nov 2025
This research details an exact classical rewriting method for CSS-preserving stabilizer circuits into probabilistic classical circuits, achieving zero computational overhead. It also introduces a unified algebraic framework using Z4-valued quadratic forms to represent and compose general stabilizer operations, explaining simulation complexity through contextual hidden variable models with dynamically updating reference frames.
23 Jun 2025
National University of Defense TechnologyUniversity of VigoNational Research University “Higher School of Economics”Russian Quantum CenterProkhorov General Physics Institute of Russian Academy of SciencesNTI Center for Quantum Communications, National University of Science and Technology MISiSInstitute of Automation and Electrometry of Siberian Branch of RAS
Quantum key distribution systems offer cryptographic security, provided that all their components are thoroughly characterised. However, certain components might be vulnerable to a laser-damage attack, particularly when attacked at previously untested laser parameters. Here we show that exposing 1550-nm fiber-optic isolators to 17-mW average power, 1061-nm picosecond attacking pulses reduces their isolation below a safe threshold. Furthermore, the exposure to 1160-mW sub-nanosecond pulsed illumination permanently degrades isolation at 1550 nm while the isolators maintain forward transparency. These threats are not addressed by the currently-practiced security analysis.
Understanding the properties of biological systems is an exciting avenue for applying advanced approaches to solving corresponding computational tasks. A specific class of problems that arises in the resolution of biological challenges is optimization. In this work, we present the results of a proof-of-concept study that applies a quantum-inspired optimization algorithm to simulate a viral response. We formulate an Ising-type model to describe the patterns of gene activity in host responses. Reducing the problem to the Ising form allows the use of available quantum and quantum-inspired optimization tools. We demonstrate the application of a quantum-inspired optimization algorithm to this problem. Our study paves the way for exploring the full potential of quantum and quantum-inspired optimization tools in biological applications.
28 Oct 2024
Practically relevant problems of quadratic optimization often contain multidimensional arrays of variables interconnected by linear constraints, such as equalities and inequalities. The values of each variable depend on its specific meaning and can be binary, integer, discrete, and continuous. These circumstances make it technically difficult to reduce the original problem statement to the QUBO form. The paper identifies and considers three main transformations of the original problem statement, namely, the transition from a multidimensional to a one-dimensional array of variables, the transition in mixed problems to binary variables, and the inclusion of linear constraints in the objective function in the form of quadratic penalties. Convenient formulas for calculations are presented and proven, simplifying the implementation of these transformations. In particular, the formulas for the transition in the problem statement from a multidimensional to a one-dimensional array of variables are based on the use of the Kronecker product of matrices. The considered transformations are illustrated by numerous examples.
24 Mar 2017
Superpositions of macroscopically distinct quantum states, introduced in Schroedinger's famous Gedankenexperiment, are an epitome of quantum "strangeness" and a natural tool for determining the validity limits of quantum physics. The optical incarnation of Schroedinger's cat - the superposition of two opposite-amplitude coherent states - is also the backbone of quantum information processing in the continuous-variable domain. However, existing preparation methods limit the amplitudes of the component coherent states by about 2, which curtails the state's usefulness for fundamental and practical applications. Here we produce higher-amplitude optical Schroedinger's cats from two such states of lower amplitudes. The protocol consists in bringing the initial states into interference on a beamsplitter and a subsequent heralding quadrature measurement in one of the output channels. In the experiment, we convert a pair of negative squeezed Schroedinger's cat states of amplitude 1.25 to a single positive Schroedinger's cat of amplitude 2.15 with success probability of ~0.2. This amplitude is comparable to the highest values obtained for this state in any physical system. Our technique can be realized in an iterative manner, in principle allowing creation of Schroedinger's cat states of arbitrarily high amplitude.
05 Oct 2025
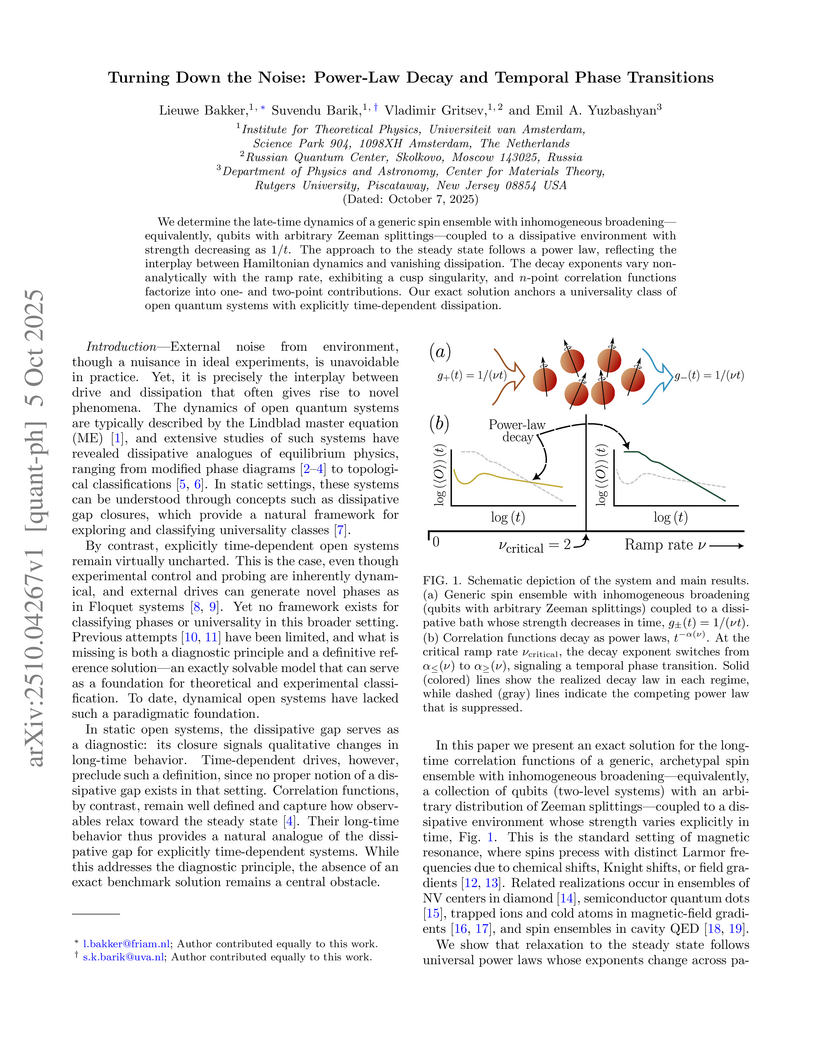
We determine the late-time dynamics of a generic spin ensemble with inhomogeneous broadening - equivalently, qubits with arbitrary Zeeman splittings - coupled to a dissipative environment with strength decreasing as 1/t. The approach to the steady state follows a power law, reflecting the interplay between Hamiltonian dynamics and vanishing dissipation. The decay exponents vary non-analytically with the ramp rate, exhibiting a cusp singularity, and n-point correlation functions factorize into one- and two-point contributions. Our exact solution anchors a universality class of open quantum systems with explicitly time-dependent dissipation.
Two-dimensional magnetic materials (2D-MM) are an exciting playground for
fundamental research, and for spintronics and quantum sensing. However, their
large-grain large-area synthesis using scalable vapour deposition methods is
still an unsolved challenge. Here, we develop a tailored approach for
centimetre-scale growth of semiconducting 2D-MM CrCl3 films on mica substrate,
via physical vapour transport deposition. A controlled synthesis protocol,
enabled via innovations concerning light management, very-high carrier-gas
flow, precursor flux, and oxygen/moisture removal, is critical for wafer-scale
growth. Optical, stoichiometric, structural, and magnetic characterization
identify crystalline, phase-pure 2D-MM CrCl3. Substrate temperature tunes
thickness of films from few-layers to tens of nanometres. Further,
selective-area growth and large-area transfer are demonstrated.
Substrate-dependent growth features are explained by density functional theory
and state-of-the-art machine learning interatomic potential-based atomic-scale
simulations. This scalable vapour deposition approach can be applied for growth
of several 2D-MM, and low growth temperature (~500 C) will enable creation of
hybrid heterostructures.
07 Apr 2025
Rydberg atom arrays is a promising platform for programmable quantum
simulators and universal quantum processors. A major challenge threatening the
scalability of this platform is the limited qubit connectivity due to the
finite range of interactions between atoms. We discuss an approach to realize
dynamical all-to-all connectivity between qubits with the use of moving atoms,
which we referred to as messenger qubits, that interact with the computational
qubits of the processor. We propose four specific architectures capitalizing on
this idea and compare them one to another, as well as to alternative
approaches. We argue that the use of messenger qubits, while posing new
technological challenges, promises further development of the
Rydberg-atom-based platform.
This chapter describes the discovery and stable generation of temporal
dissipative Kerr solitons in continuous-wave (CW) laser driven optical
microresonators. The experimental signatures as well as the temporal and
spectral characteristics of this class of bright solitons are discussed.
Moreover, analytical and numerical descriptions are presented that do not only
reproduce qualitative features but can also be used to accurately model and
predict the characteristics of experimental systems. Particular emphasis lies
on temporal dissipative Kerr solitons with regard to optical frequency comb
generation where they are of particular importance. Here, one example is
spectral broadening and self-referencing enabled by the ultra-short pulsed
nature of the solitons. Another example is dissipative Kerr soliton formation
in integrated on-chip microresonators where the emission of a dispersive wave
allows for the direct generation of unprecedentedly broadband and coherent
soliton spectra with smooth spectral envelope.
30 Sep 2025
Terahertz (THz) electromagnetic pulses offer a promising route for the ultrafast manipulation of magnetization in ferromagnetic materials. While previous studies have demonstrated the excitation of spin dynamics using linearly polarized THz fields, the role of circular polarization and the effects of rapidly oscillating, time-dependent field profiles remained insufficiently understood. We have developed a unified theoretical framework for describing the excitation of spin precession via Zeeman interaction in magnetic materials by high frequency pulses of arbitrary polarization with temporal Gaussian profile. In the regime of long pulses (at least several oscillations are within the pulse duration), a circularly polarized magnetic field acts as an effective rectified magnetic field along the pulse propagation, while linear polarized pulses excite no free precession. In the regime of short pulses (less than one oscillation is within the pulse duration), pulses of any polarization, including linear one can excite free spin precession. There is an optimal pulse duration which maximizes amplitude of the spin precession. It depends on magnetic parameters of the sample and the external magnetic field, as well as on the carrier frequency of the pulse and its amplitude. These findings bridge key gaps in the understanding of THz-induced spin dynamics and provide insights into the design of light-controlled magnetization schemes using tailored electromagnetic pulses.
01 Sep 2017
Parasitic two-level tunneling systems (TLS) emerge in amorphous dielectrics
and constitute a serious nuisance for various microfabricated devices, where
they act as a source of noise and decoherence. Here, we demonstrate a new test
bed for the study of TLS in various materials which provides access to
properties of individual TLS as well as their ensemble response. We terminate a
superconducting transmission-line resonator with a capacitor that hosts TLS in
its dielectric. By tuning TLS via applied mechanical strain, we observe the
signatures of individual TLS strongly coupled to the resonator in its
transmission characteristics and extract the coupling components of their
dipole moments and energy relaxation rates. The strong and well-defined
coupling to the TLS bath results in pronounced resonator frequency fluctuations
and excess phase noise, through which we can study TLS ensemble effects such as
spectral diffusion, and probe theoretical models of TLS interaction.
14 Oct 2025
In the field of quantum technology, single photons have emerged as a pivotal resource, prompting the development of heralded single photon sources (HSPS) with enhanced generation probability. The majority of such sources are based on spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC), but they exhibit a low single photon generation probability. The multiplexing principle (arXiv:quant-ph/0205103) has been proposed as a solution to this problem. This paper presents a demonstration of a time-multiplexed HSPS based on the SPDC process, including accurate calculations and modeling of key source characteristics, specifically purity and heralding efficiency. Furthermore, the paper provides an analysis and approximation of the probability of a single photon post-application of time multiplexing.
10 Oct 2025
We experimentally demonstrate a power limiter based on single-walled carbon nanotubes dispersed in a polymer matrix. This simple fiber-optic device permanently increases its attenuation when subjected to 50-mW or higher cw illumination at 1550 nm and initiates a fiber-fuse effect at 1 to 5 W. It may be used for protecting quantum key distribution equipment from light-injection attacks. We demonstrate its compatibility with phase- and polarisation-encoding quantum key distribution systems.
07 May 2025
A quantum processor, like any computing device, requires the development of
both hardware and the necessary set of software solutions, starting with
quantum algorithms and ending with means of accessing quantum devices. As part
of the roadmap for the development of the high-tech field of quantum computing
in the period from 2020 to 2024, a set of software solutions for quantum
computing devices was developed. This software package includes a set of
quantum algorithms for solving prototypes of applied tasks, monitoring and
benchmarking tools for quantum processors, error suppression and correction
methods, tools for compiling and optimizing quantum circuits, as well as
interfaces for remote cloud access. This review presents the key results
achieved, among which it is necessary to mention the execution of quantum
algorithms using a cloud-based quantum computing platform.
06 Apr 2016
The parquet decomposition of the self-energy into classes of diagrams, those associated with specific scattering processes, can be exploited for different scopes. In this work, the parquet decomposition is used to unravel the underlying physics of non-perturbative numerical calculations. We show the specific example of dynamical mean field theory (DMFT) and its cluster extensions (DCA) applied to the Hubbard model at half-filling and with hole doping: These techniques allow for a simultaneous determination of two-particle vertex functions and self-energies, and hence, for an essentially "exact" parquet decomposition at the single-site or at the cluster level. Our calculations show that the self-energies in the underdoped regime are dominated by spin scattering processes, consistent with the conclusions obtained by means of the fluctuation diagnostics approach [Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 236402 (2015)]. However, differently from the latter approach, the parquet procedure displays important changes with increasing interaction: Even for relatively moderate couplings, well before the Mott transition, singularities appear in different terms, with the notable exception of the predominant spin-channel. We explain precisely how these singularities, which partly limit the utility of the parquet decomposition, and - more generally - of parquet-based algorithms, are never found in the fluctuation diagnostics procedure. Finally, by a more refined analysis, we link the occurrence of the parquet singularities in our calculations to a progressive suppression of charge fluctuations and the formation of an RVB state, which are typical hallmarks of a pseudogap state in DCA.
27 Nov 2017
We adapt the Quantum Monte Carlo method to the cascaded formalism of quantum optics, allowing us to simulate the emission of photons of known energy. Statistical processing of the photon clicks thus collected agrees with the theory of frequency-resolved photon correlations, extending the range of applications based on correlations of photons of prescribed energy, in particular those of a photon-counting character. We apply the technique to autocorrelations of photon streams from a two-level system under coherent and incoherent pumping, including the Mollow triplet regime where we demonstrate the direct manifestation of leapfrog processes in producing an increased rate of two-photon emission events.
28 Jul 2016
The squeezed state of the electromagnetic field can be generated in many
nonlinear optical processes and finds a wide range of applications in quantum
information processing and quantum metrology. This article reviews the basic
properties of single-and dual-mode squeezed light states, methods of their
preparation and detection, as well as their quantum technology applications.
12 Nov 2025
We present an experimental demonstration of boson sampling enhanced by optical feedback lines, a novel approach that introduces temporal correlations among photons to amplify computational complexity. We utilize a 25-mode femtosecond laser-written interferometer with five output channels connected to five input channels to create correlations between consecutive photon arrival events. We have reconstructed the unitary matrix of the chip and have conducted Bayesian analysis to validate the sampler and confirm that the system exhibits behavior distinct from standard boson sampling. We also built a theoretical description of the system based on the transformation of annihilation operators and, using it, delivered the structure of the transmission matrix and the complexity of our boson sampler in terms of a conventional boson sampler. This work advances photonic quantum computing by demonstrating a resource-efficient method to increase sampling complexity, paving the way for scalable demonstration of quantum advantage with single photons.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.