In this paper, we propose, through an objective study, to compare and evaluate the performance of different coding approaches allowing the delivery of an 8K video signal with 4K backward-compatibility on broadcast networks. Presented approaches include simulcast of 8K and 4K single-layer signals encoded using High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) and Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standards, spatial scalability using SHVC with 4K base layer (BL) and 8K enhancement-layer (EL), and super-resolution applied on 4K VVC signal after decoding to reach 8K resolution. For up-scaling, we selected the deep-learning-based super-resolution method called Super-Resolution with Feedback Network (SRFBN) and the Lanczos interpolation filter. We show that the deep-learning-based approach achieves visual quality gain over simulcast, especially on bit-rates lower than 30Mb/s with average gain of 0.77dB, 0.015, and 7.97 for PSNR, SSIM, and VMAF, respectively and out-performs the Lanczos filter in average by 29% of BD-rate savings.
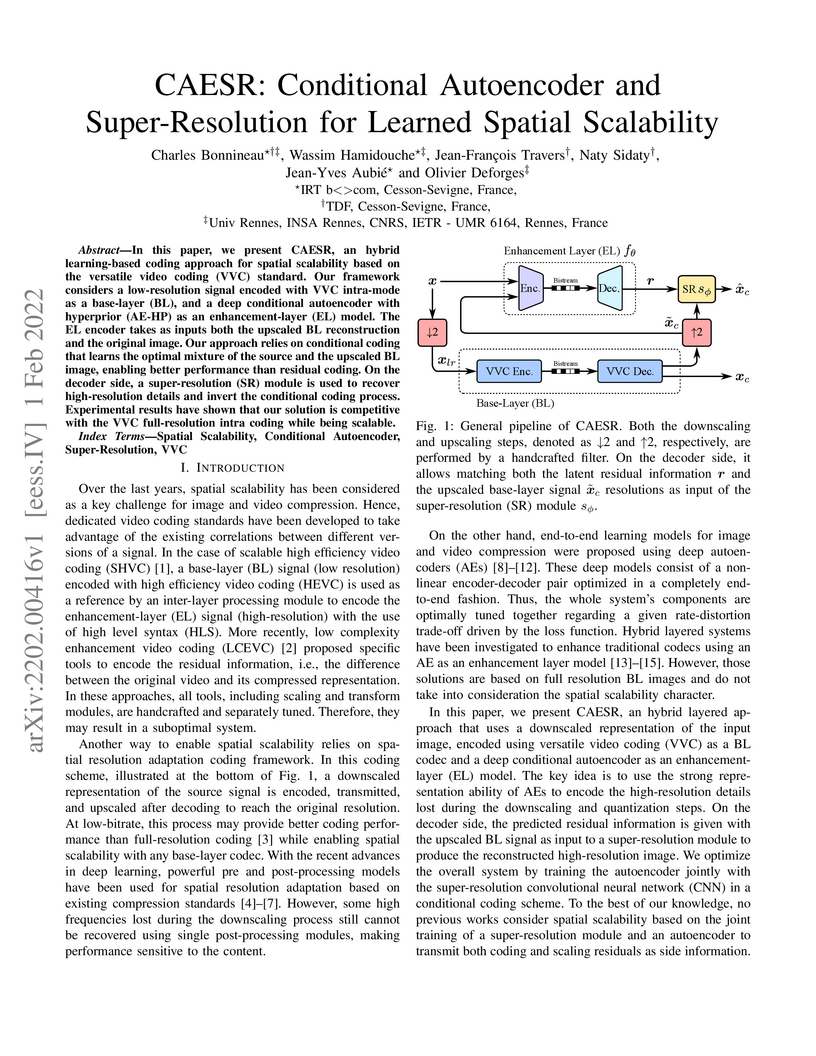
In this paper, we present CAESR, an hybrid learning-based coding approach for spatial scalability based on the versatile video coding (VVC) standard. Our framework considers a low-resolution signal encoded with VVC intra-mode as a base-layer (BL), and a deep conditional autoencoder with hyperprior (AE-HP) as an enhancement-layer (EL) model. The EL encoder takes as inputs both the upscaled BL reconstruction and the original image. Our approach relies on conditional coding that learns the optimal mixture of the source and the upscaled BL image, enabling better performance than residual coding. On the decoder side, a super-resolution (SR) module is used to recover high-resolution details and invert the conditional coding process. Experimental results have shown that our solution is competitive with the VVC full-resolution intra coding while being scalable.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.