image-and-video-processing
Flow-based text-to-image (T2I) models excel at prompt-driven image generation, but falter on Image Restoration (IR), often "drifting away" from being faithful to the measurement. Prior work mitigate this drift with data-specific flows or task-specific adapters that are computationally heavy and not scalable across tasks. This raises the question "Can't we efficiently manipulate the existing generative capabilities of a flow model?" To this end, we introduce FlowSteer (FS), an operator-aware conditioning scheme that injects measurement priors along the sampling path,coupling a frozed flow's implicit guidance with explicit measurement constraints. Across super-resolution, deblurring, denoising, and colorization, FS improves measurement consistency and identity preservation in a strictly zero-shot setting-no retrained models, no adapters. We show how the nature of flow models and their sensitivities to noise inform the design of such a scheduler. FlowSteer, although simple, achieves a higher fidelity of reconstructed images, while leveraging the rich generative priors of flow models.
Zero-Splat TeleAssist introduces a zero-shot pose estimation framework for semantic teleoperation that utilizes commodity CCTV streams and advanced AI models to provide real-time 6-DoF robot poses. This system reduces operator cognitive load by 27% and task completion time by 32% in human-robot interaction tasks.
Learned image reconstruction has become a pillar in computational imaging and inverse problems. Among the most successful approaches are learned iterative networks, which are formulated by unrolling classical iterative optimisation algorithms for solving variational problems. While the underlying algorithm is usually formulated in the functional analytic setting, learned approaches are often viewed as purely discrete. In this chapter we present a unified operator view for learned iterative networks. Specifically, we formulate a learned reconstruction operator, defining how to compute, and separately the learning problem, which defines what to compute. In this setting we present common approaches and show that many approaches are closely related in their core. We review linear as well as nonlinear inverse problems in this framework and present a short numerical study to conclude.
Accurate segmentation of cancerous lesions from 3D computed tomography (CT) scans is essential for automated treatment planning and response assessment. However, even state-of-the-art models combining self-supervised learning (SSL) pretrained transformers with convolutional decoders are susceptible to out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs, generating confidently incorrect tumor segmentations, posing risks for safe clinical deployment. Existing logit-based methods suffer from task-specific model biases, while architectural enhancements to explicitly detect OOD increase parameters and computational costs. Hence, we introduce a plug-and-play and lightweight post-hoc random forests-based OOD detection framework called RF-Deep that leverages deep features with limited outlier exposure. RF-Deep enhances generalization to imaging variations by repurposing the hierarchical features from the pretrained-then-finetuned backbone encoder, providing task-relevant OOD detection by extracting the features from multiple regions of interest anchored to the predicted tumor segmentations. Hence, it scales to images of varying fields-of-view. We compared RF-Deep against existing OOD detection methods using 1,916 CT scans across near-OOD (pulmonary embolism, negative COVID-19) and far-OOD (kidney cancer, healthy pancreas) datasets. RF-Deep achieved AUROC > 93.50 for the challenging near-OOD datasets and near-perfect detection (AUROC > 99.00) for the far-OOD datasets, substantially outperforming logit-based and radiomics approaches. RF-Deep maintained similar performance consistency across networks of different depths and pretraining strategies, demonstrating its effectiveness as a lightweight, architecture-agnostic approach to enhance the reliability of tumor segmentation from CT volumes.
The rapid advancement of generative models, particularly diffusion-based methods, has significantly improved the realism of synthetic images. As new generative models continuously emerge, detecting generated images remains a critical challenge. While fully supervised, and few-shot methods have been proposed, maintaining an updated dataset is time-consuming and challenging. Consequently, zero-shot methods have gained increasing attention in recent years. We find that existing zero-shot methods often struggle to adapt to specific image domains, such as artistic images, limiting their real-world applicability. In this work, we introduce CLIDE, a novel zero-shot detection method based on conditional likelihood approximation. Our approach computes likelihoods conditioned on real images, enabling adaptation across diverse image domains. We extensively evaluate CLIDE, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on a large-scale general dataset and significantly outperform existing methods in domain-specific cases. These results demonstrate the robustness of our method and underscore the need of broad, domain-aware generalization for the AI-generated image detection task. Code is available at this https URL.
Image tile-based approaches are popular in many image processing applications such as denoising (e.g., non-local means). A key step in their use is grouping the images into clusters, which usually proceeds iteratively splitting the images into clusters and fitting a model for the images in each cluster. Linear subspaces have emerged as a suitable model for tile clusters; however, they are not well matched to images patches given that images are non-negative and thus not distributed around the origin in the tile vector space. We study the use of affine subspace models for the clusters to better match the geometric structure of the image tile vector space. We also present a simple denoising algorithm that relies on the affine subspace clustering model using least squares projection. We review several algorithmic approaches to solve the affine subspace clustering problem and show experimental results that highlight the performance improvements in clustering and denoising.
Cross-modal learning has become a fundamental paradigm for integrating heterogeneous information sources such as images, text, and structured attributes. However, multimodal representations often suffer from modality dominance, redundant information coupling, and spurious cross-modal correlations, leading to suboptimal generalization and limited interpretability. In particular, high-variance modalities tend to overshadow weaker but semantically important signals, while naïve fusion strategies entangle modality-shared and modality-specific factors in an uncontrolled manner. This makes it difficult to understand which modality actually drives a prediction and to maintain robustness when some modalities are noisy or missing. To address these challenges, we propose a Dual-Stream Residual Semantic Decorrelation Network (DSRSD-Net), a simple yet effective framework that disentangles modality-specific and modality-shared information through residual decomposition and explicit semantic decorrelation constraints. DSRSD-Net introduces: (1) a dual-stream representation learning module that separates intra-modal (private) and inter-modal (shared) latent factors via residual projection; (2) a residual semantic alignment head that maps shared factors from different modalities into a common space using a combination of contrastive and regression-style objectives; and (3) a decorrelation and orthogonality loss that regularizes the covariance structure of the shared space while enforcing orthogonality between shared and private streams, thereby suppressing cross-modal redundancy and preventing feature collapse. Experimental results on two large-scale educational benchmarks demonstrate that DSRSD-Net consistently improves next-step prediction and final outcome prediction over strong single-modality, early-fusion, late-fusion, and co-attention baselines.
Electron tomography is a powerful tool for understanding the morphology of materials in three dimensions, but conventional reconstruction algorithms typically suffer from missing-wedge artifacts and data misalignment imposed by experimental constraints. Recently proposed supervised machine-learning-enabled reconstruction methods to address these challenges rely on training data and are therefore difficult to generalize across materials systems. We propose a fully self-supervised implicit neural representation (INR) approach using a neural network as a regularizer. Our approach enables fast inline alignment through pose optimization, missing wedge inpainting, and denoising of low dose datasets via model regularization using only a single dataset. We apply our method to simulated and experimental data and show that it produces high-quality tomograms from diverse and information limited datasets. Our results show that INR-based self-supervised reconstructions offer high fidelity reconstructions with minimal user input and preprocessing, and can be readily applied to a wide variety of materials samples and experimental parameters.
We describe SynthPix, a synthetic image generator for Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) with a focus on performance and parallelism on accelerators, implemented in JAX. SynthPix supports the same configuration parameters as existing tools but achieves a throughput several orders of magnitude higher in image-pair generation per second. SynthPix was developed to enable the training of data-hungry reinforcement learning methods for flow estimation and for reducing the iteration times during the development of fast flow estimation methods used in recent active fluids control studies with real-time PIV feedback. We believe SynthPix to be useful for the fluid dynamics community, and in this paper we describe the main ideas behind this software package.
Generative models have the potential to transform the way we emulate Earth's changing climate. Previous generative approaches rely on weather-scale autoregression for climate emulation, but this is inherently slow for long climate horizons and has yet to demonstrate stable rollouts under nonstationary forcings. Here, we introduce Spatiotemporal Pyramid Flows (SPF), a new class of flow matching approaches that model data hierarchically across spatial and temporal scales. Inspired by cascaded video models, SPF partitions the generative trajectory into a spatiotemporal pyramid, progressively increasing spatial resolution to reduce computation and coupling each stage with an associated timescale to enable direct sampling at any temporal level in the pyramid. This design, together with conditioning each stage on prescribed physical forcings (e.g., greenhouse gases or aerosols), enables efficient, parallel climate emulation at multiple timescales. On ClimateBench, SPF outperforms strong flow matching baselines and pre-trained models at yearly and monthly timescales while offering fast sampling, especially at coarser temporal levels. To scale SPF, we curate ClimateSuite, the largest collection of Earth system simulations to date, comprising over 33,000 simulation-years across ten climate models and the first dataset to include simulations of climate interventions. We find that the scaled SPF model demonstrates good generalization to held-out scenarios across climate models. Together, SPF and ClimateSuite provide a foundation for accurate, efficient, probabilistic climate emulation across temporal scales and realistic future scenarios. Data and code is publicly available at this https URL .
Pose estimation of a robot arm from visual inputs is a challenging task. However, with the increasing adoption of robot arms for both industrial and residential use cases, reliable joint angle estimation can offer improved safety and performance guarantees, and also be used as a verifier to further train robot policies. This paper introduces using frontier vision-language models (VLMs) as an ``off-the-shelf" tool to estimate a robot arm's joint angles from a single target image. By evaluating frontier VLMs on both synthetic and real-world image-data pairs, this paper establishes a performance baseline attained by current FLMs. In addition, this paper presents empirical results suggesting that test time scaling or parameter scaling alone does not lead to improved joint angle predictions.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityXidian UniversityHarbin Institute of TechnologyHangzhou Dianzi University
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityXidian UniversityHarbin Institute of TechnologyHangzhou Dianzi University The University of Hong KongShenzhen University
The University of Hong KongShenzhen University Shandong University
Shandong University Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of LeicesterHangzhou Dental Hospital GroupHangzhou Geriatric Stomatology HospitalYunnan Provincial Stomatology HospitalShanghai MediWorks Precision Instruments Co., Ltd
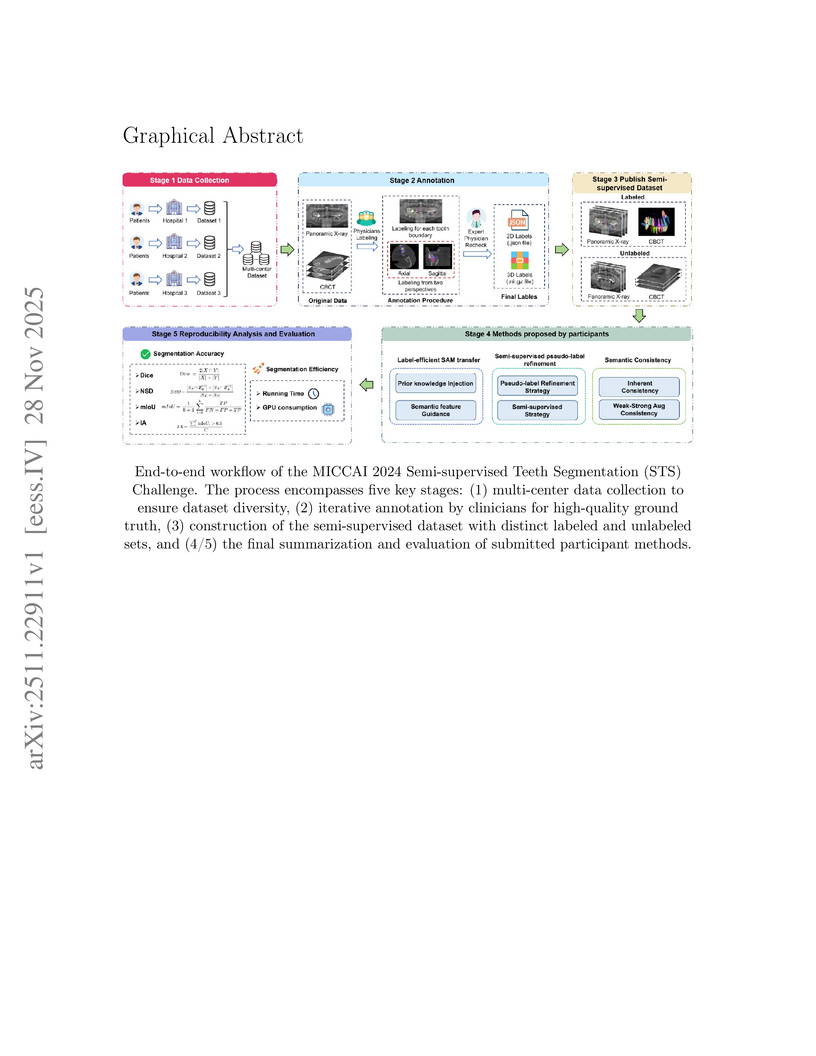
Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of LeicesterHangzhou Dental Hospital GroupHangzhou Geriatric Stomatology HospitalYunnan Provincial Stomatology HospitalShanghai MediWorks Precision Instruments Co., LtdOrthopantomogram (OPGs) and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) are vital for dentistry, but creating large datasets for automated tooth segmentation is hindered by the labor-intensive process of manual instance-level annotation. This research aimed to benchmark and advance semi-supervised learning (SSL) as a solution for this data scarcity problem. We organized the 2nd Semi-supervised Teeth Segmentation (STS 2024) Challenge at MICCAI 2024. We provided a large-scale dataset comprising over 90,000 2D images and 3D axial slices, which includes 2,380 OPG images and 330 CBCT scans, all featuring detailed instance-level FDI annotations on part of the data. The challenge attracted 114 (OPG) and 106 (CBCT) registered teams. To ensure algorithmic excellence and full transparency, we rigorously evaluated the valid, open-source submissions from the top 10 (OPG) and top 5 (CBCT) teams, respectively. All successful submissions were deep learning-based SSL methods. The winning semi-supervised models demonstrated impressive performance gains over a fully-supervised nnU-Net baseline trained only on the labeled data. For the 2D OPG track, the top method improved the Instance Affinity (IA) score by over 44 percentage points. For the 3D CBCT track, the winning approach boosted the Instance Dice score by 61 percentage points. This challenge confirms the substantial benefit of SSL for complex, instance-level medical image segmentation tasks where labeled data is scarce. The most effective approaches consistently leveraged hybrid semi-supervised frameworks that combined knowledge from foundational models like SAM with multi-stage, coarse-to-fine refinement pipelines. Both the challenge dataset and the participants' submitted code have been made publicly available on GitHub (this https URL), ensuring transparency and reproducibility.
Analyzing underwater fish imagery is critical for ecological monitoring but remains difficult due to visual degradation and costly annotations. We introduce FishDetector-R1, a unified MLLM-based framework for fish detection, segmentation, and counting under weak supervision. On the DeepFish dataset, our framework achieves substantial gains over baselines, improving AP by 20% and mIoU by 10%, while reducing MAE by 30% and GAME by 35%. These improvements stem from two key components: a novel detect-to-count prompt that enforces spatially consistent detections and counts, and Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Reward (RLVR) with a complementary scalable paradigm leveraging sparse point labels. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of this reward design. Moreover, the improvement generalizes well to other underwater datasets, confirming strong cross-domain robustness. Overall, FishDetector-R1 provides a reliable and scalable solution for accurate marine visual understanding via weak supervision. The project page for FishDetector-R1 is this https URL.
Video-on-demand streaming has benefitted from \textit{content-adaptive encoding} (CAE), i.e., adaptation of resolution and/or quantization parameters for each scene based on convex hull optimization. However, CAE is very challenging to develop and deploy for interactive game streaming (IGS). Commercial IGS services impose ultra-low latency encoding with no lookahead or buffering, and have extremely tight compute constraints for any CAE algorithm execution. We propose the first CAE approach for resolution adaptation in IGS based on compact encoding metadata from past frames. Specifically, we train a convolutional neural network (CNN) to infer the best resolution from the options available for the upcoming scene based on a running window of aggregated coding block statistics from the current scene. By deploying the trained CNN within a practical IGS setup based on HEVC encoding, our proposal: (i) improves over the default fixed-resolution ladder of HEVC by 2.3 Bjøntegaard Delta-VMAF points; (ii) infers using 1ms of a single CPU core per scene, thereby having no latency overhead.
Computed tomography perfusion (CTP) and magnetic resonance perfusion (MRP) are widely used in acute ischemic stroke assessment and other cerebrovascular conditions to generate quantitative maps of cerebral hemodynamics. While commercial perfusion analysis software exists, it is often costly, closed source, and lacks customizability. This work introduces PyPeT, an openly available Python Perfusion Tool for head CTP and MRP processing. PyPeT is capable of producing cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral blood volume (CBV), mean transit time (MTT), time-to-peak (TTP), and time-to-maximum (Tmax) maps from raw four-dimensional perfusion data. PyPeT aims to make perfusion research as accessible and customizable as possible. This is achieved through a unified framework in which both CTP and MRP data can be processed, with a strong focus on modularity, low computational burden, and significant inline documentation. PyPeT's outputs can be validated through an extensive debug mode in which every step of the process is visualized. Additional validation was performed via visual and quantitative comparison with reference perfusion maps generated by three FDA-approved commercial perfusion tools and a research tool. These comparisons show a mean SSIM around 0.8 for all comparisons, indicating a good and stable correlation with FDA-approved tools. The code for PyPeT is openly available at our GitHub this https URL
Total variation (TV) regularization is a classical tool for image denoising, but its convex ℓ1 formulation often leads to staircase artifacts and loss of contrast. To address these issues, we introduce the Transformed ℓ1 (TL1) regularizer applied to image gradients. In particular, we develop a TL1-regularized denoising model and solve it using the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM), featuring a closed-form TL1 proximal operator and an FFT-based image update under periodic boundary conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior denoising performance, effectively suppressing noise while preserving edges and enhancing image contrast.
The growing demand for low-power and area-efficient TinyML inference on AIoT devices necessitates memory architectures that minimise data movement while sustaining high computational efficiency. This paper presents FERMI-ML, a Flexible and Resource-Efficient Memory-In-Situ (MIS) SRAM macro designed for TinyML acceleration. The proposed 9T XNOR-based RX9T bit-cell integrates a 5T storage cell with a 4T XNOR compute unit, enabling variable-precision MAC and CAM operations within the same array. A 22-transistor (C22T) compressor-tree-based accumulator facilitates logarithmic 1-64-bit MAC computation with reduced delay and power compared to conventional adder trees. The 4 KB macro achieves dual functionality for in-situ computation and CAM-based lookup operations, supporting Posit-4 or FP-4 precision. Post-layout results at 65 nm show operation at 350 MHz with 0.9 V, delivering a throughput of 1.93 TOPS and an energy efficiency of 364 TOPS/W, while maintaining a Quality-of-Result (QoR) above 97.5% with InceptionV4 and ResNet-18. FERMI-ML thus demonstrates a compact, reconfigurable, and energy-aware digital Memory-In-Situ macro capable of supporting mixed-precision TinyML workloads.
Understanding 3D scene-level affordances from natural language instructions is essential for enabling embodied agents to interact meaningfully in complex environments. However, this task remains challenging due to the need for semantic reasoning and spatial grounding. Existing methods mainly focus on object-level affordances or merely lift 2D predictions to 3D, neglecting rich geometric structure information in point clouds and incurring high computational costs. To address these limitations, we introduce Task-Aware 3D Scene-level Affordance segmentation (TASA), a novel geometry-optimized framework that jointly leverages 2D semantic cues and 3D geometric reasoning in a coarse-to-fine manner. To improve the affordance detection efficiency, TASA features a task-aware 2D affordance detection module to identify manipulable points from language and visual inputs, guiding the selection of task-relevant views. To fully exploit 3D geometric information, a 3D affordance refinement module is proposed to integrate 2D semantic priors with local 3D geometry, resulting in accurate and spatially coherent 3D affordance masks. Experiments on SceneFun3D demonstrate that TASA significantly outperforms the baselines in both accuracy and efficiency in scene-level affordance segmentation.
Accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is essential for enabling timely intervention and slowing disease progression. Multimodal diagnostic approaches offer considerable promise by integrating complementary information across behavioral and perceptual domains. Eye-tracking and facial features, in particular, are important indicators of cognitive function, reflecting attentional distribution and neurocognitive state. However, few studies have explored their joint integration for auxiliary AD diagnosis. In this study, we propose a multimodal cross-enhanced fusion framework that synergistically leverages eye-tracking and facial features for AD detection. The framework incorporates two key modules: (a) a Cross-Enhanced Fusion Attention Module (CEFAM), which models inter-modal interactions through cross-attention and global enhancement, and (b) a Direction-Aware Convolution Module (DACM), which captures fine-grained directional facial features via horizontal-vertical receptive fields. Together, these modules enable adaptive and discriminative multimodal representation learning. To support this work, we constructed a synchronized multimodal dataset, including 25 patients with AD and 25 healthy controls (HC), by recording aligned facial video and eye-tracking sequences during a visual memory-search paradigm, providing an ecologically valid resource for evaluating integration strategies. Extensive experiments on this dataset demonstrate that our framework outperforms traditional late fusion and feature concatenation methods, achieving a classification accuracy of 95.11% in distinguishing AD from HC, highlighting superior robustness and diagnostic performance by explicitly modeling inter-modal dependencies and modality-specific contributions.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology introduce FSAR-Cap, a large-scale SAR image captioning dataset created using a two-stage annotation strategy that combines hierarchical templates with manual refinement. This dataset provides 14,480 images with 72,400 fine-grained captions, enabling more sophisticated SAR scene understanding and serving as a robust benchmark for future SAR-specific captioning models.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.