efficient-transformers
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai Innovation Institute introduced RoPE++, an extension of Rotary Position Embeddings that re-incorporates the previously discarded imaginary component of attention scores to improve long-context modeling in Large Language Models. This method consistently outperforms standard RoPE on various benchmarks and offers significant KV-cache and parameter efficiency.
Researchers at ShanghaiTech University and Ant Group developed FlashMHF, an efficient multi-head Feed-Forward Network (FFN) for Transformer architectures that integrates a multi-head design with an I/O-aware fused kernel. This approach consistently improves language modeling perplexity and downstream task accuracy while reducing peak memory usage by 3-5x and accelerating inference up to 1.08x compared to standard FFNs.
The paper introduces Group Representational Position Encoding (GRAPE), a unified group-theoretic framework that re-conceptualizes and unifies existing positional encoding mechanisms like RoPE and ALiBi. It provides a principled design space for new encodings, demonstrating improved training stability and superior zero-shot performance in large language models.
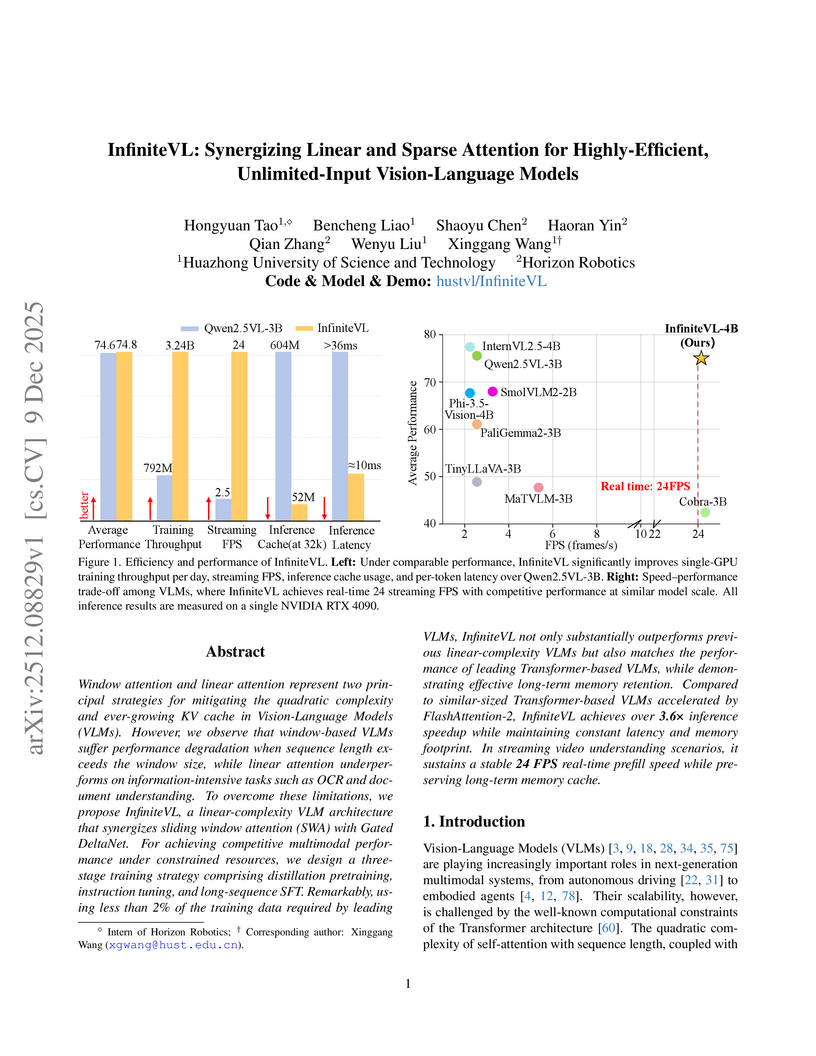
Window attention and linear attention represent two principal strategies for mitigating the quadratic complexity and ever-growing KV cache in Vision-Language Models (VLMs). However, we observe that window-based VLMs suffer performance degradation when sequence length exceeds the window size, while linear attention underperforms on information-intensive tasks such as OCR and document understanding. To overcome these limitations, we propose InfiniteVL, a linear-complexity VLM architecture that synergizes sliding window attention (SWA) with Gated DeltaNet. For achieving competitive multimodal performance under constrained resources, we design a three-stage training strategy comprising distillation pretraining, instruction tuning, and long-sequence SFT. Remarkably, using less than 2\% of the training data required by leading VLMs, InfiniteVL not only substantially outperforms previous linear-complexity VLMs but also matches the performance of leading Transformer-based VLMs, while demonstrating effective long-term memory retention. Compared to similar-sized Transformer-based VLMs accelerated by FlashAttention-2, InfiniteVL achieves over 3.6\times inference speedup while maintaining constant latency and memory footprint. In streaming video understanding scenarios, it sustains a stable 24 FPS real-time prefill speed while preserving long-term memory cache. Code and models are available at this https URL.
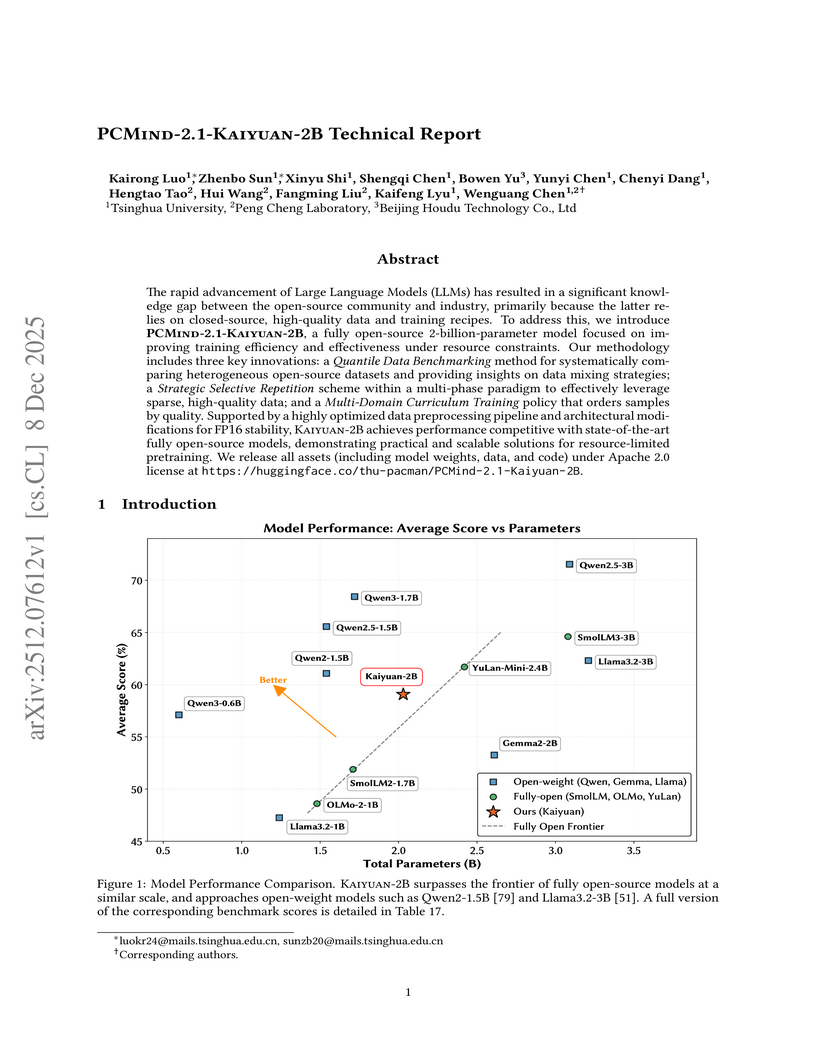
Researchers from Tsinghua University and Peng Cheng Laboratory developed PCMind-2.1-Kaiyuan-2B, a fully open-source 2-billion-parameter language model. It achieves competitive performance in Chinese language understanding, mathematical reasoning, and code generation by employing a multi-phase curriculum training with strategic data repetition and architectural modifications for FP16 stability, attaining an overall average score of 59.07% across evaluated benchmarks and outperforming several existing open-source models in its class.
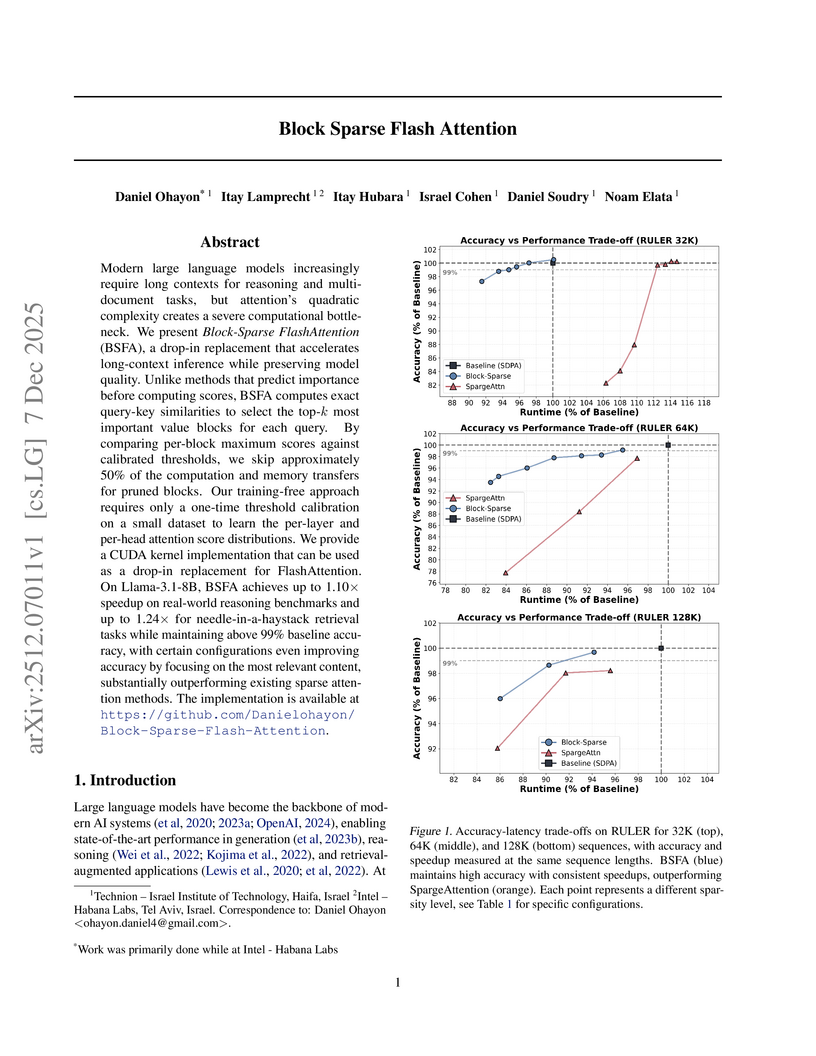
Modern large language models increasingly require long contexts for reasoning and multi-document tasks, but attention's quadratic complexity creates a severe computational bottleneck. We present Block-Sparse FlashAttention (BSFA), a drop-in replacement that accelerates long-context inference while preserving model quality. Unlike methods that predict importance before computing scores, BSFA computes exact query-key similarities to select the top-k most important value blocks for each query. By comparing per-block maximum scores against calibrated thresholds, we skip approximately 50% of the computation and memory transfers for pruned blocks. Our training-free approach requires only a one-time threshold calibration on a small dataset to learn the per-layer and per-head attention score distributions. We provide a CUDA kernel implementation that can be used as a drop-in replacement for FlashAttention. On Llama-3.1-8B, BSFA achieves up to 1.10x speedup on real-world reasoning benchmarks and up to 1.24x for needle-in-a-haystack retrieval tasks while maintaining above 99% baseline accuracy, with certain configurations even improving accuracy by focusing on the most relevant content, substantially outperforming existing sparse attention methods. The implementation is available at this https URL
Understanding and reconstructing the complex geometry and motion of dynamic scenes from video remains a formidable challenge in computer vision. This paper introduces D4RT, a simple yet powerful feedforward model designed to efficiently solve this task. D4RT utilizes a unified transformer architecture to jointly infer depth, spatio-temporal correspondence, and full camera parameters from a single video. Its core innovation is a novel querying mechanism that sidesteps the heavy computation of dense, per-frame decoding and the complexity of managing multiple, task-specific decoders. Our decoding interface allows the model to independently and flexibly probe the 3D position of any point in space and time. The result is a lightweight and highly scalable method that enables remarkably efficient training and inference. We demonstrate that our approach sets a new state of the art, outperforming previous methods across a wide spectrum of 4D reconstruction tasks. We refer to the project webpage for animated results: this https URL.
Researchers at Southern Methodist University systematically compared various memory encoding and injection methods for transformer-based world models, finding that State-Space Models (SSMs) combined with attention-based injection offer a scalable approach for enhancing long-term recall. This hybrid strategy significantly improved consistency over extended imagination horizons compared to a vanilla Vision Transformer, effectively mitigating perceptual drift.
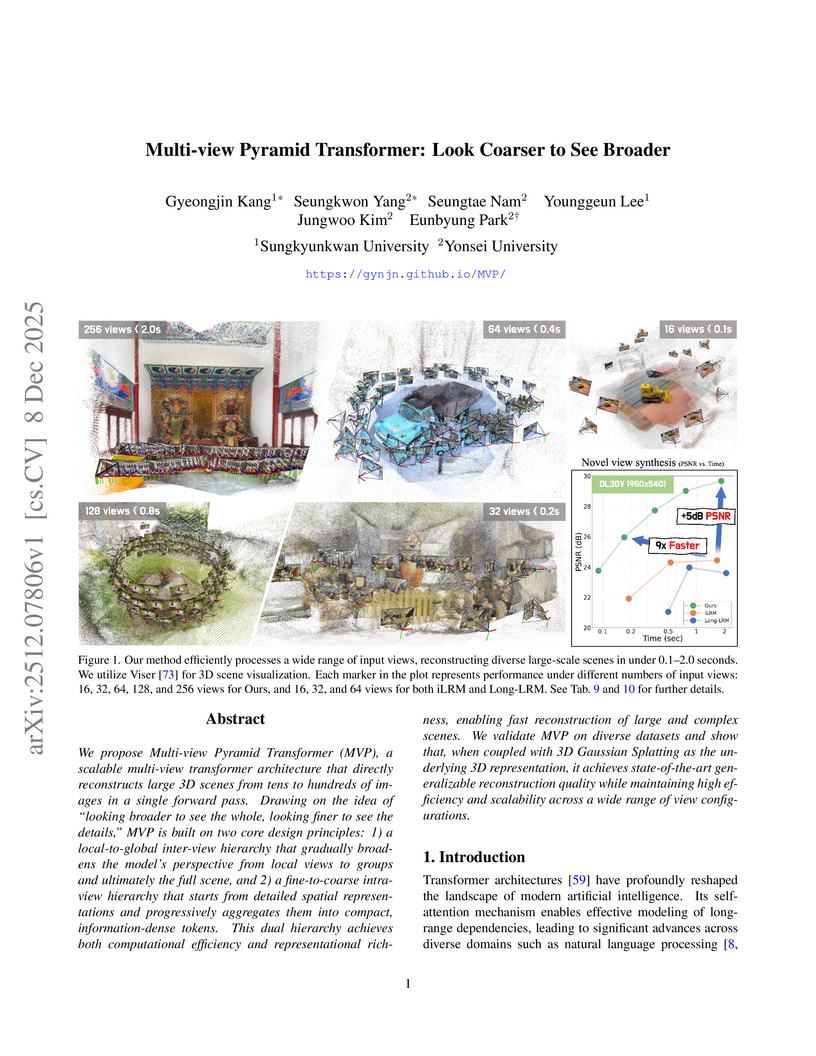
The Multi-view Pyramid Transformer (MVP) introduces a scalable architecture for efficient 3D reconstruction from numerous input images, leveraging a dual attention hierarchy and pyramidal feature aggregation. It processes up to 128 views in under one second on a single H100 GPU, achieving superior quality compared to prior single-pass models and often matching or exceeding optimization-based 3D Gaussian Splatting on various benchmarks.
This research from NYU develops and validates hyperparameter scaling rules for matrix-preconditioned optimizers like Muon and Shampoo, enabling consistent speedups of 1.3x to 1.4x over AdamW for large language models. The work provides a framework for reliably comparing and deploying advanced optimizers at scale by showing how proper hyperparameter transfer unlocks their full compute-efficiency potential.
The Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc. developed a theoretical formulation that justifies token-level optimization for sequence-level rewards in Large Language Model (LLM) reinforcement learning, identifying training–inference discrepancy and policy staleness as key instability factors. Their work also provides empirically validated strategies, including Routing Replay and clipping, to achieve stable and high-performing RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLMs.
Researchers developed a metric to quantify visual token information in Vision Large Language Models, uncovering that information becomes uniform and diminishes in deeper layers. This insight led to a hybrid token pruning strategy that reduces inference latency by up to 73% and FLOPs by 74.4% in LLaVA-1.5-7B while maintaining performance.
Researchers from Peking University and Huawei Technologies developed a principled framework for adapting pre-trained autoregressive (AR) models into Block-Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). The adapted 7B-class model, NBDIFF-7B, achieved state-of-the-art performance among diffusion LLMs, with a macro average of 64.3 for its base version and 78.8 for its instruct version across diverse benchmarks.
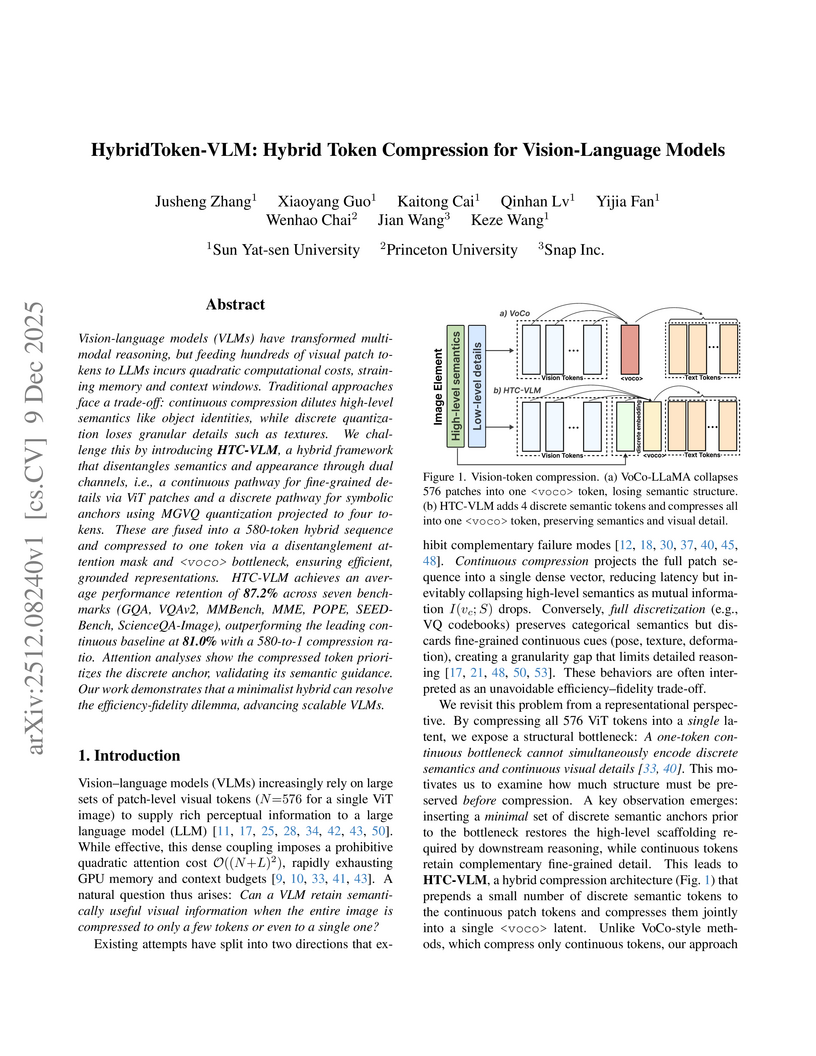
Vision-language models (VLMs) have transformed multimodal reasoning, but feeding hundreds of visual patch tokens into LLMs incurs quadratic computational costs, straining memory and context windows. Traditional approaches face a trade-off: continuous compression dilutes high-level semantics such as object identities, while discrete quantization loses fine-grained details such as textures. We introduce HTC-VLM, a hybrid framework that disentangles semantics and appearance through dual channels, i.e., a continuous pathway for fine-grained details via ViT patches and a discrete pathway for symbolic anchors using MGVQ quantization projected to four tokens. These are fused into a 580-token hybrid sequence and compressed into a single voco token via a disentanglement attention mask and bottleneck, ensuring efficient and grounded representations. HTC-VLM achieves an average performance retention of 87.2 percent across seven benchmarks (GQA, VQAv2, MMBench, MME, POPE, SEED-Bench, ScienceQA-Image), outperforming the leading continuous baseline at 81.0 percent with a 580-to-1 compression ratio. Attention analyses show that the compressed token prioritizes the discrete anchor, validating its semantic guidance. Our work demonstrates that a minimalist hybrid design can resolve the efficiency-fidelity dilemma and advance scalable VLMs.
TWINFLOW introduces a self-adversarial flow framework that enables competitive one-step image generation on large multi-modal models like Qwen-Image-20B. The method reduces inference computational cost by up to 100x while maintaining image quality and diversity, bypassing the need for external discriminators or frozen teacher models.
Recent advances in Video Large Language Models (VLLMs) have achieved remarkable video understanding capabilities, yet face critical efficiency bottlenecks due to quadratic computational growth with lengthy visual token sequences of long videos. While existing keyframe sampling methods can improve temporal modeling efficiency, additional computational cost is introduced before feature encoding, and the binary frame selection paradigm is found suboptimal. Therefore, in this work, we propose Dynamic Token compression via LLM-guided Keyframe prior (DyToK), a training-free paradigm that enables dynamic token compression by harnessing VLLMs' inherent attention mechanisms. Our analysis reveals that VLLM attention layers naturally encoding query-conditioned keyframe priors, by which DyToK dynamically adjusts per-frame token retention ratios, prioritizing semantically rich frames while suppressing redundancies. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DyToK achieves state-of-the-art efficiency-accuracy tradeoffs. DyToK shows plug-and-play compatibility with existing compression methods, such as VisionZip and FastV, attaining 4.3x faster inference while preserving accuracy across multiple VLLMs, such as LLaVA-OneVision and Qwen2.5-VL. Code is available at this https URL .
Large reasoning models (LRMs) often cost significant key-value (KV) cache overhead, due to their linear growth with the verbose chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning process. This costs both memory and throughput bottleneck limiting their efficient deployment. Towards reducing KV cache size during inference, we first investigate the effectiveness of existing KV cache eviction methods for CoT reasoning. Interestingly, we find that due to unstable token-wise scoring and the reduced effective KV budget caused by padding tokens, state-of-the-art (SoTA) eviction methods fail to maintain accuracy in the multi-batch setting. Additionally, these methods often generate longer sequences than the original model, as semantic-unaware token-wise eviction leads to repeated revalidation during reasoning. To address these issues, we present \textbf{SkipKV}, a \textbf{\textit{training-free}} KV compression method for selective \textit{eviction} and \textit{generation} operating at a coarse-grained sentence-level sequence removal for efficient CoT reasoning. In specific, it introduces a \textit{sentence-scoring metric} to identify and remove highly similar sentences while maintaining semantic coherence. To suppress redundant generation, SkipKV dynamically adjusts a steering vector to update the hidden activation states during inference enforcing the LRM to generate concise response. Extensive evaluations on multiple reasoning benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of SkipKV in maintaining up to 26.7% improved accuracy compared to the alternatives, at a similar compression budget. Additionally, compared to SoTA, SkipKV yields up to 1.6× fewer generation length while improving throughput up to 1.7×.
RELIC, an interactive video world model from researchers including those at Adobe Research, enables real-time, memory-aware exploration of diverse scenes for extended durations (up to 20 seconds) from a single image and text prompt. It demonstrates superior visual quality and precise action control compared to state-of-the-art baselines, generalizing across various artistic styles.
Autoregressive(AR)-diffusion hybrid paradigms combine AR's structured modeling with diffusion's photorealistic synthesis, yet suffer from high latency due to sequential AR generation and iterative denoising. In this work, we tackle this bottleneck and propose a unified AR-diffusion framework Fast-ARDiff that jointly optimizes both components, accelerating AR speculative decoding while simultaneously facilitating faster diffusion decoding. Specifically: (1) The entropy-informed speculative strategy encourages draft model to produce higher-entropy representations aligned with target model's entropy characteristics, mitigating entropy mismatch and high rejection rates caused by draft overconfidence. (2) For diffusion decoding, rather than treating it as an independent module, we integrate it into the same end-to-end framework using a dynamic scheduler that prioritizes AR optimization to guide the diffusion part in further steps. The diffusion part is optimized through a joint distillation framework combining trajectory and distribution matching, ensuring stable training and high-quality synthesis with extremely few steps. During inference, shallow feature entropy from AR module is used to pre-filter low-entropy drafts, avoiding redundant computation and improving latency. Fast-ARDiff achieves state-of-the-art acceleration across diverse models: on ImageNet 256×256, TransDiff attains 4.3× lossless speedup, and NextStep-1 achieves 3× acceleration on text-conditioned generation. Code will be available at this https URL.
Traditional Transformers face a major bottleneck in long-sequence time series forecasting due to their quadratic complexity (O(T2)) and their limited ability to effectively exploit frequency-domain information. Inspired by RWKV's O(T) linear attention and frequency-domain modeling, we propose FRWKV, a frequency-domain linear-attention framework that overcomes these limitations. Our model integrates linear attention mechanisms with frequency-domain analysis, achieving O(T) computational complexity in the attention path while exploiting spectral information to enhance temporal feature representations for scalable long-sequence modeling. Across eight real-world datasets, FRWKV achieves a first-place average rank. Our ablation studies confirm the critical roles of both the linear attention and frequency-encoder components. This work demonstrates the powerful synergy between linear attention and frequency analysis, establishing a new paradigm for scalable time series modeling. Code is available at this repository: this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.