Grabtaxi Holdings
23 Mar 2021
The use of deep learning models for forecasting the resource consumption patterns of SQL queries have recently been a popular area of study. With many companies using cloud platforms to power their data lakes for large scale analytic demands, these models form a critical part of the pipeline in managing cloud resource provisioning. While these models have demonstrated promising accuracy, training them over large scale industry workloads are expensive. Space inefficiencies of encoding techniques over large numbers of queries and excessive padding used to enforce shape consistency across diverse query plans implies 1) longer model training time and 2) the need for expensive, scaled up infrastructure to support batched training. In turn, we developed Prestroid, a tree convolution based data science pipeline that accurately predicts resource consumption patterns of query traces, but at a much lower cost.
We evaluated our pipeline over 19K Presto OLAP queries from Grab, on a data lake of more than 20PB of data. Experimental results imply that our pipeline outperforms benchmarks on predictive accuracy, contributing to more precise resource prediction for large-scale workloads, yet also reduces per-batch memory footprint by 13.5x and per-epoch training time by 3.45x. We demonstrate direct cost savings of up to 13.2x for large batched model training over Microsoft Azure VMs.
Model counting, a fundamental task in computer science, involves determining the number of satisfying assignments to a Boolean formula, typically represented in conjunctive normal form (CNF). While model counting for CNF formulas has received extensive attention with a broad range of applications, the study of model counting for Pseudo-Boolean (PB) formulas has been relatively overlooked. Pseudo-Boolean formulas, being more succinct than propositional Boolean formulas, offer greater flexibility in representing real-world problems. Consequently, there is a crucial need to investigate efficient techniques for model counting for PB formulas.
In this work, we propose the first exact Pseudo-Boolean model counter, PBCount, that relies on knowledge compilation approach via algebraic decision diagrams. Our extensive empirical evaluation shows that PBCount can compute counts for 1513 instances while the current state-of-the-art approach could only handle 1013 instances. Our work opens up several avenues for future work in the context of model counting for PB formulas, such as the development of preprocessing techniques and exploration of approaches other than knowledge compilation.
Road network and building footprint extraction is essential for many
applications such as updating maps, traffic regulations, city planning,
ride-hailing, disaster response \textit{etc}. Mapping road networks is
currently both expensive and labor-intensive. Recently, improvements in image
segmentation through the application of deep neural networks has shown
promising results in extracting road segments from large scale, high resolution
satellite imagery. However, significant challenges remain due to lack of enough
labeled training data needed to build models for industry grade applications.
In this paper, we propose a two-stage transfer learning technique to improve
robustness of semantic segmentation for satellite images that leverages noisy
pseudo ground truth masks obtained automatically (without human labor) from
crowd-sourced OpenStreetMap (OSM) data. We further propose Pyramid
Pooling-LinkNet (PP-LinkNet), an improved deep neural network for segmentation
that uses focal loss, poly learning rate, and context module. We demonstrate
the strengths of our approach through evaluations done on three popular
datasets over two tasks, namely, road extraction and building foot-print
detection. Specifically, we obtain 78.19\% meanIoU on SpaceNet building
footprint dataset, 67.03\% and 77.11\% on the road topology metric on SpaceNet
and DeepGlobe road extraction dataset, respectively.
Next destination recommendation is an important task in the transportation domain of taxi and ride-hailing services, where users are recommended with personalized destinations given their current origin location. However, recent recommendation works do not satisfy this origin-awareness property, and only consider learning from historical destination locations, without origin information. Thus, the resulting approaches are unable to learn and predict origin-aware recommendations based on the user's current location, leading to sub-optimal performance and poor real-world practicality. Hence, in this work, we study the origin-aware next destination recommendation task. We propose the Spatial-Temporal Origin-Destination Personalized Preference Attention (STOD-PPA) encoder-decoder model to learn origin-origin (OO), destination-destination (DD), and origin-destination (OD) relationships by first encoding both origin and destination sequences with spatial and temporal factors in local and global views, then decoding them through personalized preference attention to predict the next destination. Experimental results on seven real-world user trajectory taxi datasets show that our model significantly outperforms baseline and state-of-the-art methods.
13 Nov 2022
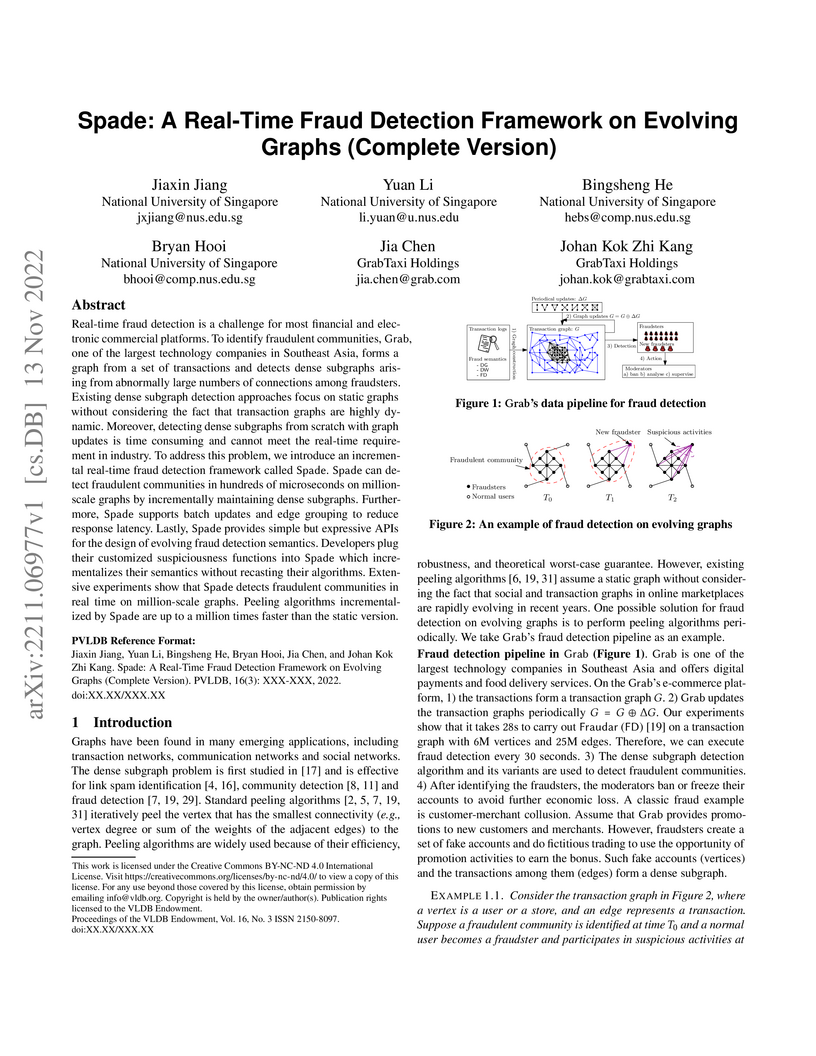
Real-time fraud detection is a challenge for most financial and electronic
commercial platforms. To identify fraudulent communities, Grab, one of the
largest technology companies in Southeast Asia, forms a graph from a set of
transactions and detects dense subgraphs arising from abnormally large numbers
of connections among fraudsters. Existing dense subgraph detection approaches
focus on static graphs without considering the fact that transaction graphs are
highly dynamic. Moreover, detecting dense subgraphs from scratch with graph
updates is time consuming and cannot meet the real-time requirement in
industry. To address this problem, we introduce an incremental real-time fraud
detection framework called Spade. Spade can detect fraudulent communities in
hundreds of microseconds on million-scale graphs by incrementally maintaining
dense subgraphs. Furthermore, Spade supports batch updates and edge grouping to
reduce response latency. Lastly, Spade provides simple but expressive APIs for
the design of evolving fraud detection semantics. Developers plug their
customized suspiciousness functions into Spade which incrementalizes their
semantics without recasting their algorithms. Extensive experiments show that
Spade detects fraudulent communities in real time on million-scale graphs.
Peeling algorithms incrementalized by Spade are up to a million times faster
than the static version.
12 Apr 2025
Detecting fraudulent activities in financial and e-commerce transaction
networks is crucial. One effective method for this is Densest Subgraph
Discovery (DSD). However, deploying DSD methods in production systems faces
substantial scalability challenges due to the predominantly sequential nature
of existing methods, which impedes their ability to handle large-scale
transaction networks and results in significant detection delays. To address
these challenges, we introduce Dupin, a novel parallel processing framework
designed for efficient DSD processing in billion-scale graphs. Dupin is powered
by a processing engine that exploits the unique properties of the peeling
process, with theoretical guarantees on detection quality and efficiency. Dupin
provides userfriendly APIs for flexible customization of DSD objectives and
ensures robust adaptability to diverse fraud detection scenarios. Empirical
evaluations demonstrate that Dupin consistently outperforms several existing
DSD methods, achieving performance improvements of up to 100 times compared to
traditional approaches. On billion-scale graphs, Dupin demonstrates the
potential to enhance the prevention of fraudulent transactions from 45% to
94.5% and reduces density error from 30% to below 5%, as supported by our
experimental results. These findings highlight the effectiveness of Dupin in
real-world applications, ensuring both speed and accuracy in fraud detection.
05 Jun 2025
Pseudo-Boolean model counting involves computing the number of satisfying assignments of a given pseudo-Boolean (PB) formula. In recent years, PB model counting has seen increased interest partly owing to the succinctness of PB formulas over typical propositional Boolean formulas in conjunctive normal form (CNF) at describing problem constraints. In particular, the research community has developed tools to tackle exact PB model counting. These recently developed counters follow one of the two existing major designs for model counters, namely the bottom-up model counter design. A natural question would be whether the other major design, the top-down model counter paradigm, would be effective at PB model counting, especially when the top-down design offered superior performance in CNF model counting literature.
In this work, we investigate the aforementioned top-down design for PB model counting and introduce the first exact top-down PB model counter, PBMC. PBMC is a top-down search-based counter for PB formulas, with a new variable decision heuristic that considers variable coefficients. Through our evaluations, we highlight the superior performance of PBMC at PB model counting compared to the existing state-of-the-art counters PBCount, PBCounter, and Ganak. In particular, PBMC could count for 1849 instances while the next-best competing method, PBCount, could only count for 1773 instances, demonstrating the potential of a top-down PB counter design.
Model counting is a fundamental task that involves determining the number of
satisfying assignments to a logical formula, typically in conjunctive normal
form (CNF). While CNF model counting has received extensive attention over
recent decades, interest in Pseudo-Boolean (PB) model counting is just emerging
partly due to the greater flexibility of PB formulas. As such, we observed
feature gaps in existing PB counters such as a lack of support for projected
and incremental settings, which could hinder adoption. In this work, our main
contribution is the introduction of the PB model counter PBCount2, the first
exact PB model counter with support for projected and incremental model
counting. Our counter, PBCount2, uses our Least Occurrence Weighted Min Degree
(LOW-MD) computation ordering heuristic to support projected model counting and
a cache mechanism to enable incremental model counting. In our evaluations,
PBCount2 completed at least 1.40x the number of benchmarks of competing methods
for projected model counting and at least 1.18x of competing methods in
incremental model counting.
Inference and prediction of routes have become of interest over the past decade owing to a dramatic increase in package delivery and ride-sharing services. Given the underlying combinatorial structure and the incorporation of probabilities, route prediction involves techniques from both formal methods and machine learning. One promising approach for predicting routes uses decision diagrams that are augmented with probability values. However, the effectiveness of this approach depends on the size of the compiled decision diagrams. The scalability of the approach is limited owing to its empirical runtime and space complexity. In this work, our contributions are two-fold: first, we introduce a relaxed encoding that uses a linear number of variables with respect to the number of vertices in a road network graph to significantly reduce the size of resultant decision diagrams. Secondly, instead of a stepwise sampling procedure, we propose a single pass sampling-based route prediction. In our evaluations arising from a real-world road network, we demonstrate that the resulting system achieves around twice the quality of suggested routes while being an order of magnitude faster compared to state-of-the-art.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.