Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul
29 May 2025
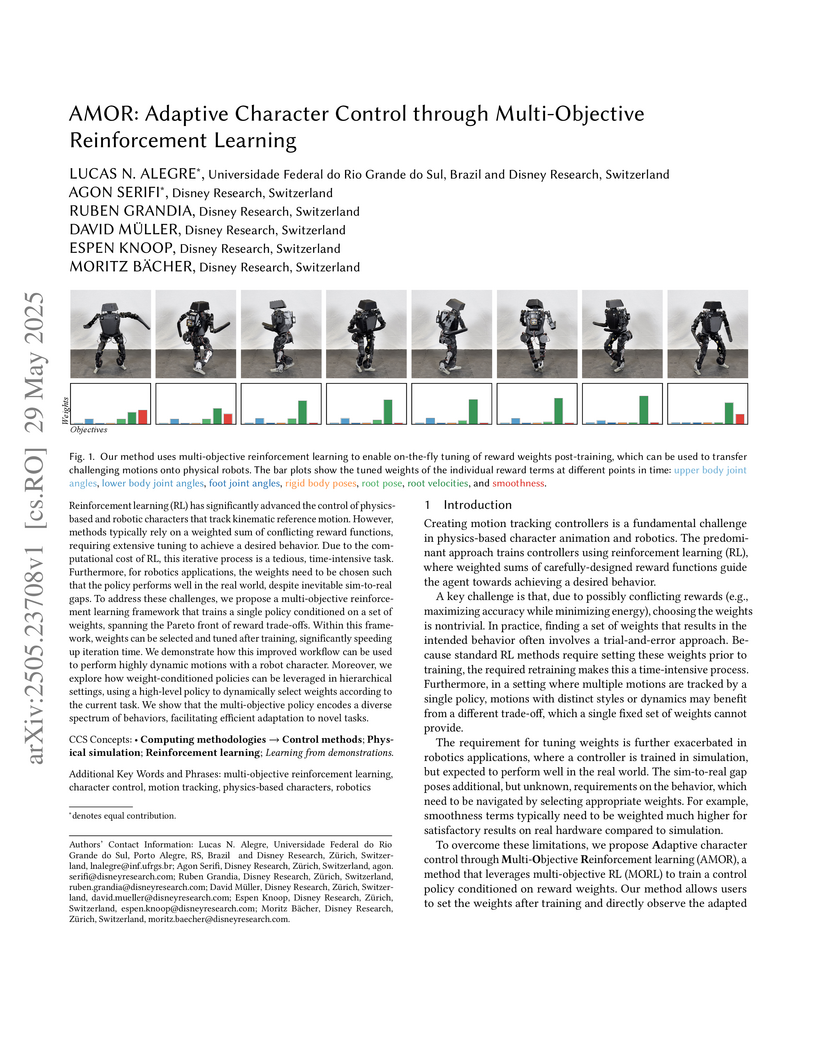
AMOR, developed by Disney Research, presents a multi-objective reinforcement learning framework that enables adaptive character control by training a single policy conditioned on reward weights. This approach allows for on-the-fly, post-training adjustment of character behavior and significantly facilitates sim-to-real transfer, exemplified by a bipedal robot executing a complex double pirouette.
18 Sep 2025
Globular clusters (GCs) are dense star clusters found in all massive galaxies. Recent work has established that they follow a tight relation between their internal stellar velocity dispersion σ and luminosity, enabling accurate distance measurements. In this work, we aim to apply this GC velocity dispersion (GCVD) distance method to measure the distance to M 104 (NGC 4594, the Sombrero galaxy). We have measured internal stellar velocity dispersions for 85 globular clusters (GCs) and one ultra-compact dwarf galaxy around M 104 using high-resolution multi-object integrated-light spectroscopy with FLAMES/GIRAFFE on the Very Large Telescope. The measured velocity dispersions range from σ=4−30 km s−1, with a mean uncertainty of Δσ=2.5 km s−1. For a subset of 77 GCs with V-band magnitudes and reliable velocity dispersion measurements above \sigma > 4 km s−1, we constructed the MV-σ relation to measure the distance to M 104, finding D=9.00±0.29 (stat.) ±0.26 (sys.) Mpc. The GCs follow the Milky Way and M 31 MV−σ relation closely, with the exception of the luminous ultra-compact dwarf SUCD1, which is nearly one magnitude brighter than the mean relation. 29 GCs in the sample have sizes determined from Hubble Space Telescope imaging which allowed us to determine their masses and V-band dynamical mass-to-light ratios (M/LV). We find a mean =2.6±0.8M⊙/L⊙ for the luminous (M_V < -8 mag) M 104 GCs, which is higher than the Milky Way GCs, but is reminiscent of the brightest GCs in Centaurus A. With the exception of SUCD1, the GCs of M 104 follow the GCVD relation irrespective of their mass-to-light ratio.
Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are found at the centre of every massive
galaxy, with their masses tightly connected to their host galaxies through a
co-evolution over cosmic time. For massive ellipticals, the SMBH mass
(MBH) strongly correlates with the central stellar velocity
dispersion (σe), via the MBH−σe relation. However, SMBH
mass measurements have traditionally relied on central stellar dynamics in
nearby galaxies (z < 0.1), limiting our ability to explore the SMBHs across
cosmic time. In this work, we present a self-consistent analysis combining 2D
stellar dynamics and lens modelling of the Cosmic Horseshoe gravitational lens
system (z=0.44), one of the most massive galaxies ever observed. Using
integral-field spectroscopic data from MUSE and high-resolution imaging from
HST, we model the radial arc and stellar kinematics, constraining the galaxy's
central mass distribution and SMBH mass. Bayesian model comparison yields a
5σ detection of an ultramassive black hole (UMBH) with
$\log_{10}(M_\text{BH}/M_{\odot}) = 10.56^{+0.07}_{-0.08} \pm
(0.12)^\text{sys}$, consistent across various systematic tests. Our findings
place the Cosmic Horseshoe ∼1.5σ above the MBH−σe
relation, supporting an emerging trend observed in BGCs and other massive
galaxies. This suggests a steeper MBH−σe relationship at the
highest masses, potentially driven by a different co-evolution of SMBHs and
their host galaxies. Future surveys will uncover more radial arcs, enabling the
detection of SMBHs over a broader redshift and mass range. These discoveries
will further refine our understanding of the MBH−σe relation
and its evolution across cosmic time.
15 Sep 2025
White dwarfs with infrared excess emission provide a window into the late stages of stellar evolution and the dynamics of circumstellar environments. Using data from the Hobby-Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment (HETDEX), we characterized 30 white dwarfs exhibiting infrared excess, including 29 DA and 1 DB stars. While an infrared excess can arise from dusty disks or cool (sub-)stellar companions, our sample is limited to stellar companions due to our selection based on SDSS photometry, which is sensitive to excess emission at wavelengths \lambda < 1\,\mu\mathrm{m}. Our sample contains 22 newly identified excess sources not previously reported in the literature. Spectroscopic observations are available for 10 sources via SDSS, of which only 8 have prior spectroscopic classifications in the literature.
In this paper, we present the determination of the effective temperature and surface gravity of these white dwarfs. We used the Balmer line profiles to compare with current atmospheric models to determine the photospheric parameters of the white dwarfs, minimizing contamination introduced by the infrared source. We used photometric data from the SDSS and the \textit{Gaia} mission to resolve the degeneracies between hot and cold solutions from spectroscopy, constraining the photospheric parameters. These results help refine our understanding of white dwarf evolution in binary systems, focusing on stellar companions that cause the infrared excess.
This study contributes to identifying systems with potential substellar companions or unresolved stellar partners, adding to the growing effort to map out the fate of planetary systems after their host stars evolve beyond the main sequence.
We investigate and update observational constraints on cosmological parameters within the ΛCDM and dynamical dark energy frameworks, using a new compilation of the transverse (or 2D) BAO data, measurements that provide a relatively model-independent estimate of the BAO angular scale at a given redshift. Firstly, we assess the consistency of this compilation with CMB-Planck data and recent BAO results from the DESI collaboration. After confirming minimal tension with CMB data, we perform a series of joint analyses combining CMB data with the 2D~BAO compilation, as well as with several recent Type Ia supernova (SNIa) samples. In all cases, we compare the constraining power of the 2D~BAO data with that of DESI~DR2 samples. Our results indicate that combining 2D~BAO with CMB and SNIa data provides observational constraints that are competitive with those obtained using DESI~DR2. Although the precision of DESI~DR2 results remains higher, as expected due to the more accurate 3D measurements, the 2D~BAO compilation yields strong constraints. For example, in the ΛCDM context, we find H0=68.16−0.37+0.41km s−1Mpc−1 (CMB + 2D~BAO) and \Sigma m_{\nu} < 0.081~\mathrm{eV} (95\%~CL). These results are comparable to analogous analyses using DESI~DR2. Several other cases are analyzed and presented in the main text. Due to these results, we conclude that this new 2D~BAO compilation is both robust and competitive in constraining cosmological parameters, and, importantly, it does not exhibit significant tension with CMB measurements.
We present a Bayesian latent model to describe the scaling relation between globular cluster populations and their host galaxies, updating the framework proposed in de Souza 2015. GC counts are drawn from a negative-binomial (NB) process linked to host stellar mass, augmented with a newly introduced Gaussian observation layer that enables efficient propagation of measurement errors. The revised formulation preserves the underlying NB process while improving computational tractability. The code snippets, implemented in Nimble and PyMC are released under the MIT license at this https URL
07 Nov 2025
CSICUniversität HeidelbergUniversity of TurkuUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulCentro de Astrobiología (CAB)INTAUniversidade Federal de Santa MariaObservatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN-IGN)Finnish Centre for Astronomy with ESOObservatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN-IGN)-Observatorio de MadridUniversidad de Concepciٞn
We present a study of the cold molecular gas kinematics in the inner ~ 4-7 kpc (projected sizes) of three nearby Seyfert galaxies, with AGN luminosities of ~ 1044 erg/s, using observations of the CO(2-1) emission line, obtained with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) at ~ 0.5-0.8′′ (~ 150-400 pc) spatial resolutions. After modeling the CO profiles with multiple Gaussian components, we detected regions with double-peak profiles that exhibit kinematics distinct from the dominant rotational motion. In NGC 6860, a molecular outflow surrounding the bipolar emission of the [O III] ionized gas is observed extending up to Rout ~ 560 pc from the nucleus. There is evidence of molecular inflows along the stellar bar, although an alternative scenario, involving a decoupled rotation in a circumnuclear disk (CND) can also explain the observed kinematics. Mrk 915 shows double-peak CO profiles along one of its spiral arms. Due to its ambiguous disk orientation, part of the CO emission can be interpreted as a molecular gas inflow or an outflow reaching Rout ~ 2.8 kpc. MCG -01-24-012 has double-peak profiles associated with a CND, perpendicular to the [O III] bipolar emission. The CO in the CND is rotating while outflowing within Rout ~ 3 kpc, with the disturbances possibly being caused by the passage of the ionized gas outflow. Overall, the mass inflow rates are larger than the accretion rate needed to produce the observed luminosities, suggesting that only a fraction of the inflowing gas ends up feeding the central black holes. Although we found signatures of AGN feedback on the cold molecular phase, the mass outflow rates of ~ 0.09-3 M⊙/yr indicate an overall weak impact at these AGN luminosities. Nonetheless, we may be witnessing the start of the depletion and ejection of the molecular gas reservoir that has accumulated over time.
 University of CambridgeOhio State UniversityUniversidade Federal do ABCUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do NorteInstituto de Astrofísica de CanariasUniversidade de São PauloUniversidad de ValparaísoUniversidade Federal de Santa CatarinaPontificia Universidad Católica de ValparaísoUniversidade do Estado do Rio de JaneiroINESC TECUniversidad Adolfo IbáñezObservatório NacionalUniversidade Federal de ItajubáUniversidad de La SerenaNational Astronomical Observatories of ChinaUniversidade Estadual de Ponta GrossaGran Telescopio Canarias, SpainAcademia de Ciencias de la República Checa
University of CambridgeOhio State UniversityUniversidade Federal do ABCUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do NorteInstituto de Astrofísica de CanariasUniversidade de São PauloUniversidad de ValparaísoUniversidade Federal de Santa CatarinaPontificia Universidad Católica de ValparaísoUniversidade do Estado do Rio de JaneiroINESC TECUniversidad Adolfo IbáñezObservatório NacionalUniversidade Federal de ItajubáUniversidad de La SerenaNational Astronomical Observatories of ChinaUniversidade Estadual de Ponta GrossaGran Telescopio Canarias, SpainAcademia de Ciencias de la República ChecaThe Southern Photometric Local Universe Survey (S-PLUS) is a project to map
∼9300 sq deg of the sky using twelve bands (seven narrow and five
broadbands). Observations are performed with the T80-South telescope, a robotic
telescope located at the Cerro Tololo Observatory in Chile. The survey
footprint consists of several large contiguous areas, including fields at high
and low galactic latitudes, and towards the Magellanic Clouds. S-PLUS uses
fixed exposure times to reach point source depths of about 21 mag in the
griz and 20 mag in the u and the narrow filters. This paper describes the
S-PLUS Data Release 4 (DR4), which includes calibrated images and derived
catalogues for over 3000 sq deg, covering the aforementioned area. The
catalogues provide multi-band photometry performed with the tools
\texttt{DoPHOT} and \texttt{SExtractor} -- point spread function (\PSF) and
aperture photometry, respectively. In addition to the characterization, we also
present the scientific potential of the data. We use statistical tools to
present and compare the photometry obtained through different methods. Overall
we find good agreement between the different methods, with a slight systematic
offset of 0.05\,mag between our \PSF and aperture photometry. We show that the
astrometry accuracy is equivalent to that obtained in previous S-PLUS data
releases, even in very crowded fields where photometric extraction is
challenging. The depths of main survey (MS) photometry for a minimum
signal-to-noise ratio S/N=3 reach from ∼19.5 for the bluer bands to
∼21.5 mag on the red. The range of magnitudes over which accurate \PSF
photometry is obtained is shallower, reaching ∼19 to ∼20.5 mag
depending on the filter. Based on these photometric data, we provide
star-galaxy-quasar classification and photometric redshift for millions of
objects.
01 Oct 2025
 Tel Aviv UniversityUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulPolish Academy of SciencesNSF NOIRLabInternational Gemini ObservatoryHeidelberg Institute for Theoretical StudiesInternational Gemini Observatory/NSF NOIRLabUniversidad Nacional Autonoma de MexicoAstronomical Observatory BelgradeObservatorio NacionalLaborat´orio Nacional de Astrof´ısica (LNA)Universitȁt HeidelbergMax Planck Institut für AstronomieINAF/Astronomical Observatory of Padova
Tel Aviv UniversityUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulPolish Academy of SciencesNSF NOIRLabInternational Gemini ObservatoryHeidelberg Institute for Theoretical StudiesInternational Gemini Observatory/NSF NOIRLabUniversidad Nacional Autonoma de MexicoAstronomical Observatory BelgradeObservatorio NacionalLaborat´orio Nacional de Astrof´ısica (LNA)Universitȁt HeidelbergMax Planck Institut für AstronomieINAF/Astronomical Observatory of PadovaEddington ratio is a paramount parameter governing the accretion history and life cycles of Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs). This short review presents a multi-faceted view of the importance of the Eddington ratio spanning varied AGN studies. We find that the Eddington ratio is crucial for standardizing the Radius-Luminosity (R-L) relation - a necessary step for employing quasars (QSOs) as standardizable cosmological probes to help clarify the standing of the Hubble tension. In this data-driven era, we consolidated disparate aspects by developing novel relations borne out of large datasets, such as the robust, nearly universal anti-correlation between fractional variability and Eddington ratio derived from Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) data, which is vital for interpreting forthcoming high-cadence surveys like Rubin Observatory's LSST. Addressing the conundrum where JWST results suggest an overabundance of massive high-redshift black holes, we demonstrate that local AGNs offer clarification: Changing-Look AGNs (CLAGNs), driven by rapid Eddington ratio shifts, cluster in the low-accretion regime, a rate independently confirmed by our integral field spectroscopy and photoionization modeling of a well-known Seyfert 2 galaxy, rich in high-ionization, forbidden, coronal lines. Conversely, for the high-redshift, high-luminosity population where traditional reverberation mapping (RM) is highly impractical, photometric reverberation mapping (PRM) offers a rapid alternative to constrain accretion disk sizes, enabling efficient estimates of black hole masses and Eddington ratios. Finally, we developed tailored semi-empirical spectral energy distributions (SEDs) for extremely high-accretion quasars, successfully validating their characteristic extreme physical conditions.
Studying the SDSS-DR16 quasar catalog, we detect a baryon acoustic oscillation (BAO) signal in the two-point angular correlation function with a statistical significance of 3σ, at an effective redshift of zeff=1.725. Using a simple parameterization-comprising a polynomial plus a Gaussian function-we measure the transverse BAO scale as θBAO=1.928∘±0.094∘. This measurement is obtained from a narrow redshift shell, z∈[1.72,1.73] (i.e., Δz=0.01), thin enough that projection-effect corrections are negligible, making it only weakly dependent on the assumed fiducial cosmology. The only assumption adopted is isotropy in the computation of the correlation function, further ensuring that the result depends only weakly on specific cosmological-model hypotheses. We also investigate possible systematics that could affect the detection or significance of the BAO signal and find them to be subdominant or implausible. When combined with other transverse BAO measurements from the literature, our result shows good concordance-within the 1σ confidence level-with the cosmological parameter values reported by the Planck and DESI collaborations. This new measurement of the transverse BAO scale, obtained from the SDSS quasar sample with minimal cosmological-model assumptions, provides an additional independent constraint for updated statistical studies aimed at probing the nature of dark energy.
In the context of the interaction between a moving plane shock wave and an inclined wall (wedge), it is possible to distinguish four distinct shock reflection configurations. These shock wave reflections, which depend on the characteristics of the incident shock wave and the geometry of the surface that it interacts with, are (i) regular reflection (RR), (ii) simple Mach reflection (SMR), (iii) transition Mach reflection (TMR), and (iv) double Mach reflection (DMR). The impact of these shock reflections on flow properties can be significant so understanding them is important when predicting the behavior of shock waves in more complex flow configurations. Previous research works have explored the referred shock reflections through both numerical and experimental approaches, employing various gases and different flow and geometrical configurations. The present study involves the use of a high-fidelity computational fluid dynamics (CFD) tool, known as PeleC, which is a compressible solver based on AMReX specifically designed to handle complex flow configurations. Accordingly, by solving the time-dependent Euler equations for various 2D flow configurations, this work studies shock wave reflections accounting for four different Mach-based operating conditions and compares and analyzes the resulting density profiles on the wedge wall with experimental data. To strike a balance between model accuracy and computational efficiency, adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) is incorporated, and a mesh independence study is performed by varying the number of AMR levels. The results of this study demonstrate the capabilities of the CFD tool employed as it accurately predicts the sensitivity of wave characteristics to different operating conditions.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Space Telescope Science Institute
Space Telescope Science Institute University of Southampton
University of Southampton The Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech MITUniversity of Belgrade
MITUniversity of Belgrade The Ohio State UniversityWayne State UniversityUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul
The Ohio State UniversityWayne State UniversityUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul University of St Andrews
University of St Andrews Durham UniversityJet Propulsion LaboratoryUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversität HamburgBrigham Young UniversityUniversity of Central LancashireUniversidad de ValenciaUniversidade Federal de Santa MariaMIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space ResearchUniversity of WyomingInstitute of high-energy PhysicsLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)NRC Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Research CentreEureka Scientific Inc.The University of KentuckyAstronomical Observatory BelgradeSpectral Sciences Inc.Rubin Observatory Project OfficeUniversit
di PadovaINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova
Durham UniversityJet Propulsion LaboratoryUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversität HamburgBrigham Young UniversityUniversity of Central LancashireUniversidad de ValenciaUniversidade Federal de Santa MariaMIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space ResearchUniversity of WyomingInstitute of high-energy PhysicsLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP)NRC Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Research CentreEureka Scientific Inc.The University of KentuckyAstronomical Observatory BelgradeSpectral Sciences Inc.Rubin Observatory Project OfficeUniversit
di PadovaINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di PadovaThe AGN Space Telescope and Optical Reverberation Mapping 2 (STORM 2) campaign targeted Mrk 817 with intensive multi-wavelength monitoring and found its soft X-ray emission to be strongly absorbed. We present results from 157 near-IR spectra with an average cadence of a few days. Whereas the hot dust reverberation signal as tracked by the continuum flux does not have a clear response, we recover a dust reverberation radius of ∼90 light-days from the blackbody dust temperature light-curve. This radius is consistent with previous photometric reverberation mapping results when Mrk 817 was in an unobscured state. The heating/cooling process we observe indicates that the inner limit of the dusty torus is set by a process other than sublimation, rendering it a luminosity-invariant `dusty wall' of a carbonaceous composition. Assuming thermal equilibrium for dust optically thick to the incident radiation, we derive a luminosity of ∼6×1044 erg s−1 for the source heating it. This luminosity is similar to that of the obscured spectral energy distribution, assuming a disk with an Eddington accretion rate of m˙∼0.2. Alternatively, the dust is illuminated by an unobscured lower luminosity disk with m˙∼0.1, which permits the UV/optical continuum lags in the high-obscuration state to be dominated by diffuse emission from the broad-line region. Finally, we find hot dust extended on scales >140−350 pc, associated with the rotating disk of ionised gas we observe in spatially-resolved [SIII] λ9531 images. Its likely origin is in the compact bulge of the barred spiral host galaxy, where it is heated by a nuclear starburst.
11 Nov 2025
Visibility graphs are spatial interpretations of time series. When derived from the time evolution of physical systems, the graphs associated with such series may exhibit properties that can reflect aspects such as ergodicity, criticality, or other dynamical behaviors. It is important to describe how the criticality of a system is manifested in the structure of the corresponding graphs or, in a particular way, in the spectra of certain matrices constructed from them. In this paper, we show how the critical behavior of an Ising spin system manifests in the spectra of the adjacency and Laplacian matrices constructed from an ensemble of time evolutions simulated via Monte Carlo (MC) Markov Chains, even for small systems and short MC steps. In particular, we show that the number of spanning trees -- or its logarithm -- , which represents a kind of \emph{structural entropy} or \emph{topological complexity} here obtained from Kirchhoff's theorem, can, in an alternative way, describe the criticality of the spin system. These findings parallel those obtained from the spectra of correlation matrices, which similarly encode signatures of critical and chaotic behavior.
09 Jul 2025
We report the detection of a gravitationally lensed galaxy by the nearby spiral galaxy CGCG 012-070 (z=0.048) using Integral Field Unit (IFU) observations with the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) instrument on board the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The lensed galaxy is identified through the flux distributions of emission lines in the rest-frame optical, consistent with a source located at a redshift of z∼2.89. The system is detected in [O III]λλ4959,5007, Hβ, and Hα emission lines, exhibiting line ratios typical of a star-forming galaxy. The emission-line flux distributions reveal three distinct components, which are modeled using an elliptical power-law (EPL) mass profile for the lens galaxy. This model provides a good characterization of the source and reveals a disturbed star-forming morphology consistent with those of galaxies at cosmic noon.
In this study, we used geometric distances at high redshifts (both luminosity and angular) to perform a cosmographic analysis with the Padé method, which stabilizes the behaviour of the cosmographic series in this redshift regime. However, in our analyses, we did not assume the validity of the Cosmic Distance Duality Relation (CDDR), but allowed for potential violations, such as dL(z)=η(z)(1+z)2dA(z), where three different functional forms of η(z) are considered. By incorporating updated data from supernovae (SN), baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO), and cosmic chronometers (CC), we obtained observational constraints on cosmographic models alongside possible CDDR violations. Interestingly, we found that potential CDDR violations introduce new statistical correlations among cosmographic parameters such as H0, q0, and j0. Nonetheless, within this framework, we did not observe significant deviations from the CDDR, and our results remain consistent with the predictions of the ΛCDM model. In the same time, this work provides a novel and straightforward method for testing the CDDR by fixing the background evolution through cosmographic techniques, paving the way for new geometric observational tests of possible deviations from standard cosmology.
Curtin UniversityUniversity of GranadaUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel HillThe University of SydneyUniversity of HertfordshireUniversidade Federal do Rio Grande do SulARC Centre of Excellence for Dark Matter Particle PhysicsCentro Brasileiro de Pesquisas FísicasUniversidade de São Paulo European Southern ObservatoryELTE Eötvös Loránd UniversityInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchKonkoly ObservatoryHUN-REN Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth SciencesObservatorio NacionalMTA Centre of ExcellenceCentre for Astrophysics ResearchMCTIArtificial Intelligence for Physics Laboratory
European Southern ObservatoryELTE Eötvös Loránd UniversityInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchKonkoly ObservatoryHUN-REN Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth SciencesObservatorio NacionalMTA Centre of ExcellenceCentre for Astrophysics ResearchMCTIArtificial Intelligence for Physics Laboratory
 European Southern ObservatoryELTE Eötvös Loránd UniversityInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchKonkoly ObservatoryHUN-REN Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth SciencesObservatorio NacionalMTA Centre of ExcellenceCentre for Astrophysics ResearchMCTIArtificial Intelligence for Physics Laboratory
European Southern ObservatoryELTE Eötvös Loránd UniversityInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchKonkoly ObservatoryHUN-REN Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth SciencesObservatorio NacionalMTA Centre of ExcellenceCentre for Astrophysics ResearchMCTIArtificial Intelligence for Physics LaboratoryResearchers investigated AT2022zod, an extreme, short-lived optical flare in an elliptical galaxy, concluding it is likely a tidal disruption event caused by an intermediate-mass black hole (around 5.4 × 10⁵ to 1.3 × 10⁶ M⊙). This event potentially reveals an elusive off-nuclear massive black hole residing in an ultra-compact dwarf galaxy, informing future transient surveys and black hole census efforts.
06 Oct 2025
The properties of massive and compact early-type galaxies provide important constraints on early galaxy formation. Among these, massive relic galaxies, characterized by old stellar populations and minimal late-time accretion, are considered preserved compact galaxies from the high-z Universe. We investigate compact and massive galaxies (CMGs) using the TNG50 cosmological simulation, applying uniform selection criteria matching observational surveys at z=0, z=0.3, and z=0.7, enabling direct comparisons with observed compact galaxies. CMGs are classified according to their stellar mass assembly histories to examine how compactness relates to dynamical properties and chemical enrichment across cosmic time. Our results show that simulated CMGs follow the observed mass-size relation, with the number of objects increasing at higher redshifts, in line with observational trends. Dynamically, while observations suggest relic galaxies are outliers in the stellar mass-velocity dispersion plane, simulated compacts show relatively uniform velocity dispersions across different accretion histories. Observed relics are more metal-rich than other compact galaxies with extended star formation, deviating from the local mass-metallicity relation. In contrast, simulated CMGs are overall more metal-rich than the quiescent population, regardless of accretion history. The deviation from the mass-metallicity relation decreases with redshift. These results suggest that the extreme characteristics of CMGs in TNG50, particularly in metallicity and dynamics, are less pronounced than in observed relics. Nonetheless, these results offer a theoretical framework to assess the properties of such extreme objects from different epochs, highlighting both alignment with and deviations between the models.
Strong gravitational lensing and stellar dynamics are independent and powerful methods to probe the total gravitational potential of galaxies, and thus, their total mass profile. However, inherent degeneracies in the individual models makes it difficult to obtain a full understanding of the distribution of baryons and dark matter (DM), although such degeneracies might be broken by the combination of these two tracers, leading to more reliable measurements of the mass distribution of the lens galaxy. We use mock data from IllustrisTNG50 to compare how dynamical-only, lens-only, and joint modelling can constrain the mass distribution of early-type galaxies (ETGs). The joint model consistently outperforms the other models, achivieng a 2% accuracy in recovering the total mass within 2.5Reff. The Einstein radius is robustly recovered for both lens-only and joint models, with the first showing a median fractional error of −5% and the latter a fractional error consistent with zero. The stellar mass-to-light ratio and total mass density slope are well recovered by all models. In particular, the dynamical-only model achieves an accuracy of 1% for the stellar mass-to-light ratio, while the accuracy of the mass density slope is typically of the order of 5% for all models. However, all models struggle to constrain integrated quantities involving DM and the halo parameters. Nevertheless, imposing more restrictive assumptions on the DM halo, such as fixing the scale radius, could alleviate some of the issues. Finally, we verify that the number of kinematical constraints (15,35,55 bins) on the kinematical map does not impact the models outcomes.
11 Nov 2025
We use JWST/NIRSpec observations of the radio galaxy 3C 293 to map the emission, extinction, and kinematics of hot molecular and ionized gas, as well as stellar kinematics, within the inner ~ 2 kpc. The stellar velocity field is well described by a rotating disk model, with its kinematical center offset by ~ 0.5 arcsec from the continuum peak. The hot molecular gas is traced by the H22.12μm emission line, and the ionized gas by [Fe II]1.64μm and Paα. The gas presents three main kinematic components: a rotating disk seen as a narrow component (σ ~ 100 kms−1); a blueshifted broad outflow (σ ~ 250 kms−1); and a fast ionized outflow as a very broad component (σ ~ 640 kms−1). Extinction maps reveal high AV values, up to ~ 35, spatially coincident with dust lanes seen in optical images. In addition to the disk and outflows components, inflows along the dust lanes are detected in H2 gas, with a mass inflow rate of M˙in ~ 4 x 10−4 M⊙ yr−1, which is lower than the AGN accretion rate. For the outflows, we derive peak mass-outflow rates of 0.08 ± 0.02 M⊙yr−1 (molecular) and 6.5 ± 1.7 M⊙yr−1 (ionized). The outflow, driven by the radio jet, has a kinetic power of 5.7% of the jet power - enough to suppress star formation. Our results highlight 3C 293's turbulent post-merger history and JWST's unique capability to probe dust-obscured AGN.
11 Apr 2024
We introduce galmoss, a python-based, torch-powered tool for two-dimensional fitting of galaxy profiles. By seamlessly enabling GPU parallelization, galmoss meets the high computational demands of large-scale galaxy surveys, placing galaxy profile fitting in the LSST-era. It incorporates widely used profiles such as the Sérsic, Exponential disk, Ferrer, King, Gaussian, and Moffat profiles, and allows for the easy integration of more complex models. Tested on 8,289 galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) g-band with a single NVIDIA A100 GPU, galmoss completed classical Sérsic profile fitting in about 10 minutes. Benchmark tests show that galmoss achieves computational speeds that are 6 × faster than those of default implementations.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.