graphics
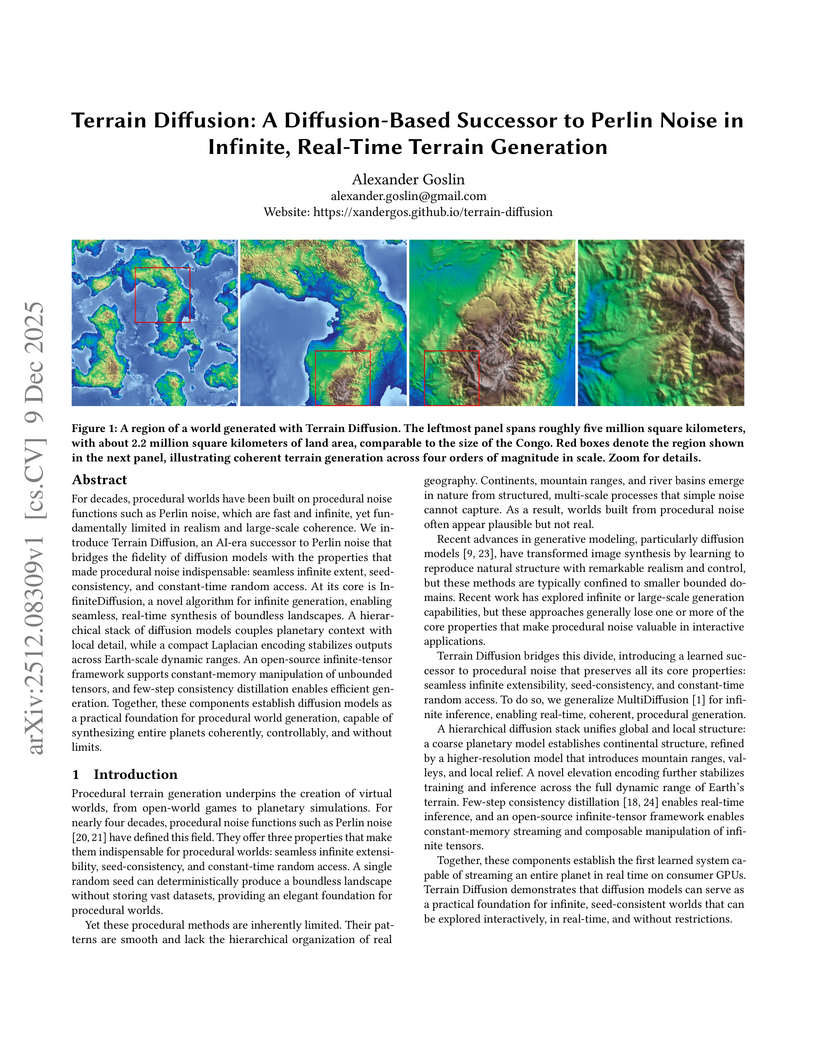
Terrain Diffusion introduces a diffusion-based framework for generating infinite, real-time procedural terrain, delivering highly realistic, boundless virtual worlds with seed-consistency and constant-time random access. The system achieves competitive FID scores and real-time generation latency on consumer hardware, demonstrating its practical applicability.
09 Dec 2025
Visionary introduces a WebGPU-powered platform for 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) that enables real-time, client-side rendering and inference for dynamic and generative 3DGS models. The platform demonstrates up to 135x speedup compared to WebGL-based viewers, while maintaining or improving visual quality and ensuring robust depth-aware composition.
We present WonderZoom, a novel approach to generating 3D scenes with contents across multiple spatial scales from a single image. Existing 3D world generation models remain limited to single-scale synthesis and cannot produce coherent scene contents at varying granularities. The fundamental challenge is the lack of a scale-aware 3D representation capable of generating and rendering content with largely different spatial sizes. WonderZoom addresses this through two key innovations: (1) scale-adaptive Gaussian surfels for generating and real-time rendering of multi-scale 3D scenes, and (2) a progressive detail synthesizer that iteratively generates finer-scale 3D contents. Our approach enables users to "zoom into" a 3D region and auto-regressively synthesize previously non-existent fine details from landscapes to microscopic features. Experiments demonstrate that WonderZoom significantly outperforms state-of-the-art video and 3D models in both quality and alignment, enabling multi-scale 3D world creation from a single image. We show video results and an interactive viewer of generated multi-scale 3D worlds in this https URL
Researchers from Cornell University, Google, and UC Berkeley developed Selfi, a framework that refines pre-trained 3D Vision Foundation Model features through self-supervised geometric alignment. It achieves state-of-the-art pose-free novel view synthesis quality and robust camera pose estimation, often rivaling methods requiring ground-truth camera parameters.
Mimic2DM is a framework that learns to control physically simulated 3D characters from abundant 2D video data, bypassing explicit 3D reconstruction by formulating motion imitation as a physics-based 2D motion tracking problem. The system enables characters to perform complex human-object interactions and animal locomotion, outperforming two-stage methods and exhibiting implicit 3D understanding from diverse 2D viewpoints.
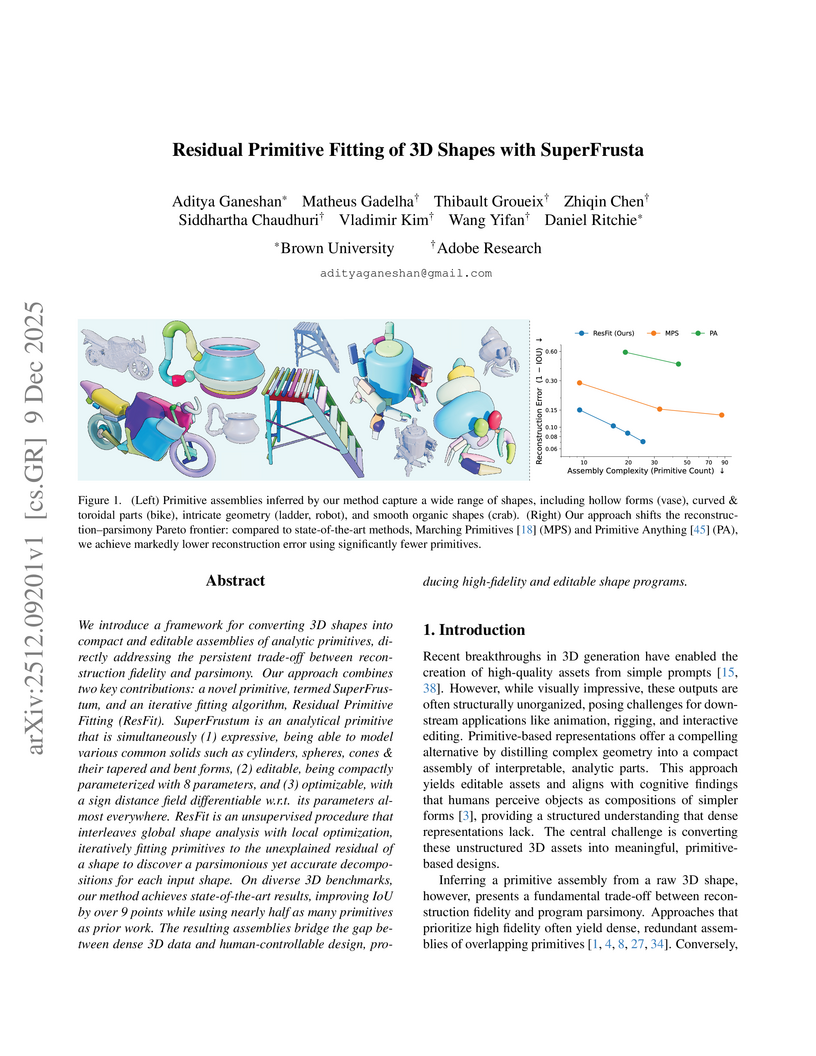
We introduce a framework for converting 3D shapes into compact and editable assemblies of analytic primitives, directly addressing the persistent trade-off between reconstruction fidelity and parsimony. Our approach combines two key contributions: a novel primitive, termed SuperFrustum, and an iterative fiting algorithm, Residual Primitive Fitting (ResFit). SuperFrustum is an analytical primitive that is simultaneously (1) expressive, being able to model various common solids such as cylinders, spheres, cones & their tapered and bent forms, (2) editable, being compactly parameterized with 8 parameters, and (3) optimizable, with a sign distance field differentiable w.r.t. its parameters almost everywhere. ResFit is an unsupervised procedure that interleaves global shape analysis with local optimization, iteratively fitting primitives to the unexplained residual of a shape to discover a parsimonious yet accurate decompositions for each input shape. On diverse 3D benchmarks, our method achieves state-of-the-art results, improving IoU by over 9 points while using nearly half as many primitives as prior work. The resulting assemblies bridge the gap between dense 3D data and human-controllable design, producing high-fidelity and editable shape programs.
Recent advancements in Gaussian Splatting have enabled increasingly accurate reconstruction of photorealistic head avatars, opening the door to numerous applications in visual effects, videoconferencing, and virtual reality. This, however, comes with the lack of intuitive editability offered by traditional triangle mesh-based methods. In contrast, we propose a method that combines the accuracy and fidelity of 2D Gaussian Splatting with the intuitiveness of UV texture mapping. By embedding each canonical Gaussian primitive's local frame into a patch in the UV space of a template mesh in a computationally efficient manner, we reconstruct continuous editable material head textures from a single monocular video on a conventional UV domain. Furthermore, we leverage an efficient physically based reflectance model to enable relighting and editing of these intrinsic material maps. Through extensive comparisons with state-of-the-art methods, we demonstrate the accuracy of our reconstructions, the quality of our relighting results, and the ability to provide intuitive controls for modifying an avatar's appearance and geometry via texture mapping without additional optimization.
Lang3D-XL introduces a method for embedding language features into 3D Gaussian Splatting models of large-scale "in-the-wild" scenes. It enables interactive, text-based semantic understanding, achieving comparable semantic segmentation performance to HaLo-NeRF while accelerating inference speed by orders of magnitude (under 0.1 seconds per query vs. two hours) and outperforming other feature-based methods with an mAP of 0.59 on the HolyScenes dataset.
03 Dec 2025
Researchers introduced Score-Matching Motion Priors (SMP), a framework that leverages pre-trained motion diffusion models as static, reusable reward functions for physics-based character control. This method generates high-quality, naturalistic character movements and supports style adaptation and composition across various tasks, matching or exceeding performance of state-of-the-art adversarial methods while reducing data dependency.
We present FNOpt, a self-supervised cloth simulation framework that formulates time integration as an optimization problem and trains a resolution-agnostic neural optimizer parameterized by a Fourier neural operator (FNO). Prior neural simulators often rely on extensive ground truth data or sacrifice fine-scale detail, and generalize poorly across resolutions and motion patterns. In contrast, FNOpt learns to simulate physically plausible cloth dynamics and achieves stable and accurate rollouts across diverse mesh resolutions and motion patterns without retraining. Trained only on a coarse grid with physics-based losses, FNOpt generalizes to finer resolutions, capturing fine-scale wrinkles and preserving rollout stability. Extensive evaluations on a benchmark cloth simulation dataset demonstrate that FNOpt outperforms prior learning-based approaches in out-of-distribution settings in both accuracy and robustness. These results position FNO-based meta-optimization as a compelling alternative to previous neural simulators for cloth, thus reducing the need for curated data and improving cross-resolution reliability.
A new hybrid 3D scene representation, Radiance Meshes, leverages Delaunay tetrahedral cells and an Instant-NGP backbone to enable real-time, high-quality, and exact volume rendering using standard hardware rasterization. The approach achieves rendering speeds 32% faster than 3D Gaussian Splatting and greater robustness than prior volumetric methods, eliminating temporal popping artifacts while supporting physical simulation.
07 Dec 2025
Inverse design of slender elastic structures underlies a wide range of applications in computer graphics, flexible electronics, biomedical devices, and soft robotics. Traditional optimization-based approaches, however, are often orders of magnitude slower than forward dynamic simulations and typically impose restrictive boundary conditions. In this work, we present an inverse discrete elastic rods (inverse-DER) method that enables efficient and accurate inverse design under general loading and boundary conditions. By reformulating the inverse problem as a static equilibrium in the reference configuration, our method attains computational efficiency comparable to forward simulations while preserving high fidelity. This framework allows rapid determination of undeformed geometries for elastic fabrication structures that naturally deform into desired target shapes upon actuation or loading. We validate the approach through both physical prototypes and forward simulations, demonstrating its accuracy, robustness, and potential for real-world design applications.
Deep learning models have achieved remarkable success across various domains, yet their learned representations and decision-making processes remain largely opaque and hard to interpret. This work introduces HOLE (Homological Observation of Latent Embeddings), a method for analyzing and interpreting deep neural networks through persistent homology. HOLE extracts topological features from neural activations and presents them using a suite of visualization techniques, including Sankey diagrams, heatmaps, dendrograms, and blob graphs. These tools facilitate the examination of representation structure and quality across layers. We evaluate HOLE on standard datasets using a range of discriminative models, focusing on representation quality, interpretability across layers, and robustness to input perturbations and model compression. The results indicate that topological analysis reveals patterns associated with class separation, feature disentanglement, and model robustness, providing a complementary perspective for understanding and improving deep learning systems.
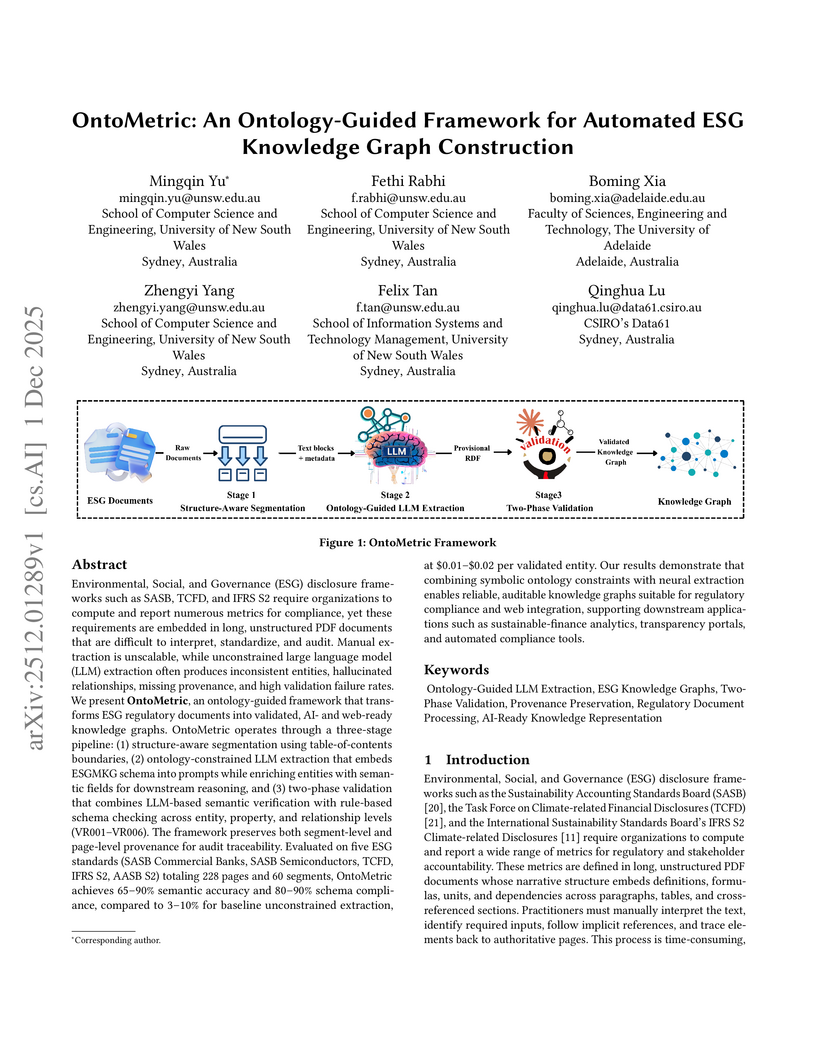
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) disclosure frameworks such as SASB, TCFD, and IFRS S2 require organizations to compute and report numerous metrics for compliance, yet these requirements are embedded in long, unstructured PDF documents that are difficult to interpret, standardize, and audit. Manual extraction is unscalable, while unconstrained large language model (LLM) extraction often produces inconsistent entities, hallucinated relationships, missing provenance, and high validation failure rates. We present OntoMetric, an ontology-guided framework that transforms ESG regulatory documents into validated, AI- and web-ready knowledge graphs. OntoMetric operates through a three-stage pipeline: (1) structure-aware segmentation using table-of-contents boundaries, (2) ontology-constrained LLM extraction that embeds the ESGMKG schema into prompts while enriching entities with semantic fields for downstream reasoning, and (3) two-phase validation that combines LLM-based semantic verification with rule-based schema checking across entity, property, and relationship levels (VR001-VR006). The framework preserves both segment-level and page-level provenance for audit traceability. Evaluated on five ESG standards (SASB Commercial Banks, SASB Semiconductors, TCFD, IFRS S2, AASB S2) totaling 228 pages and 60 segments, OntoMetric achieves 65-90% semantic accuracy and 80-90% schema compliance, compared to 3-10% for baseline unconstrained extraction, at approximately 0.01 to 0.02 USD per validated entity. Our results demonstrate that combining symbolic ontology constraints with neural extraction enables reliable, auditable knowledge graphs suitable for regulatory compliance and web integration, supporting downstream applications such as sustainable-finance analytics, transparency portals, and automated compliance tools.
SplatSuRe, developed by the University of Maryland, College Park, introduces a framework to generate sharp, high-resolution, and multi-view consistent novel views from low-resolution inputs using 3D Gaussian Splatting. The method selectively applies super-resolution based on a per-Gaussian fidelity score, resulting in noticeably sharper reconstructions with reduced blurring and superior performance across various metrics on datasets like Tanks & Temples and Deep Blending.
02 Dec 2025
LumiX, developed by researchers at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology and Huazhong University of Science and Technology, presents a generative model that produces coherent sets of intrinsic maps (RGB, albedo, irradiance, depth, normal) directly from text prompts. It achieves superior cross-map structural consistency, with an alignment score of 8.30 (compared to baselines like 2.40), and demonstrates zero-shot intrinsic image decomposition capabilities.
An empirical study clarifies the impact of motion representations and loss functions on human motion generation using diffusion models, finding that a simple Joint Position representation combined with v-loss and geometric regularization yields superior motion quality and diversity while substantially reducing training time.
We present LATTICE, a new framework for high-fidelity 3D asset generation that bridges the quality and scalability gap between 3D and 2D generative models. While 2D image synthesis benefits from fixed spatial grids and well-established transformer architectures, 3D generation remains fundamentally more challenging due to the need to predict both spatial structure and detailed geometric surfaces from scratch. These challenges are exacerbated by the computational complexity of existing 3D representations and the lack of structured and scalable 3D asset encoding schemes. To address this, we propose VoxSet, a semi-structured representation that compresses 3D assets into a compact set of latent vectors anchored to a coarse voxel grid, enabling efficient and position-aware generation. VoxSet retains the simplicity and compression advantages of prior VecSet methods while introducing explicit structure into the latent space, allowing positional embeddings to guide generation and enabling strong token-level test-time scaling. Built upon this representation, LATTICE adopts a two-stage pipeline: first generating a sparse voxelized geometry anchor, then producing detailed geometry using a rectified flow transformer. Our method is simple at its core, but supports arbitrary resolution decoding, low-cost training, and flexible inference schemes, achieving state-of-the-art performance on various aspects, and offering a significant step toward scalable, high-quality 3D asset creation.
CtrlVDiff unifies video understanding and controllable video generation within a single diffusion model by integrating physically-grounded intrinsic modalities and a flexible control strategy. The framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in both tasks, enabling precise video editing applications like relighting and material changes.
Neural Texture Splatting (NTS), developed at ETH Zurich, enhances 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) by augmenting primitives with neural RGBA texture fields, generated by a global neural network. This method consistently improves view synthesis, geometry, and dynamic reconstruction, particularly in sparse-view settings, resulting in sharper and more accurate scene representations.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.