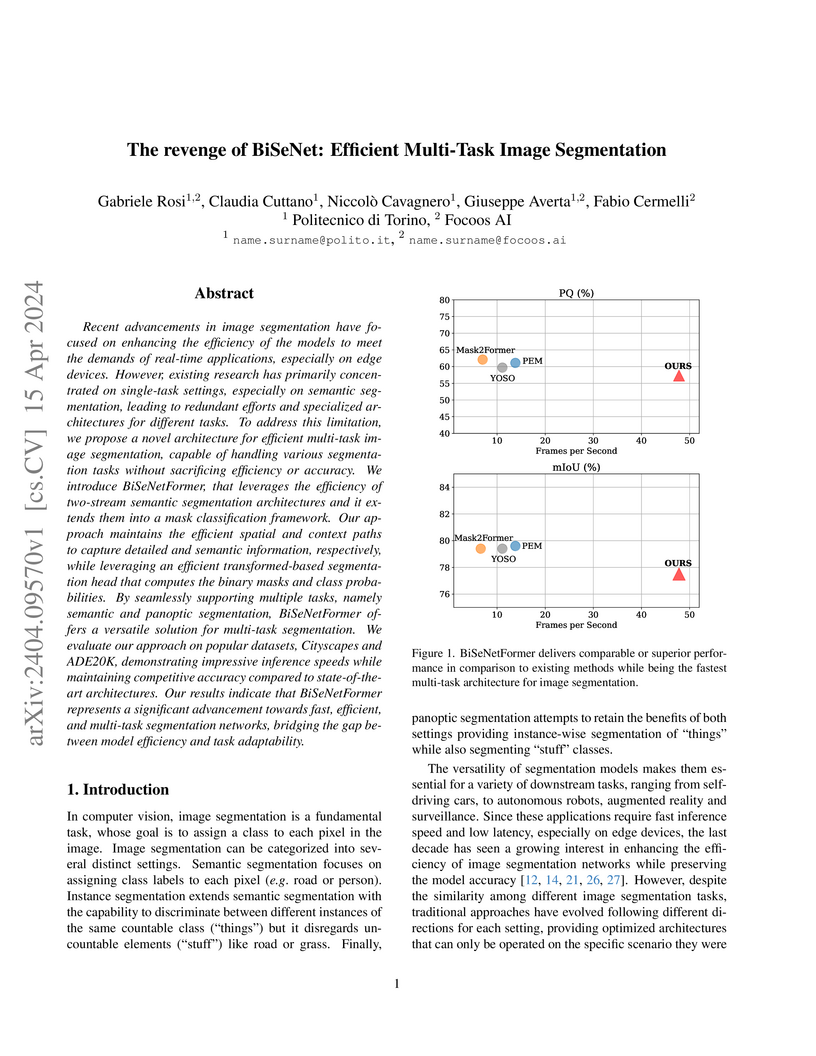
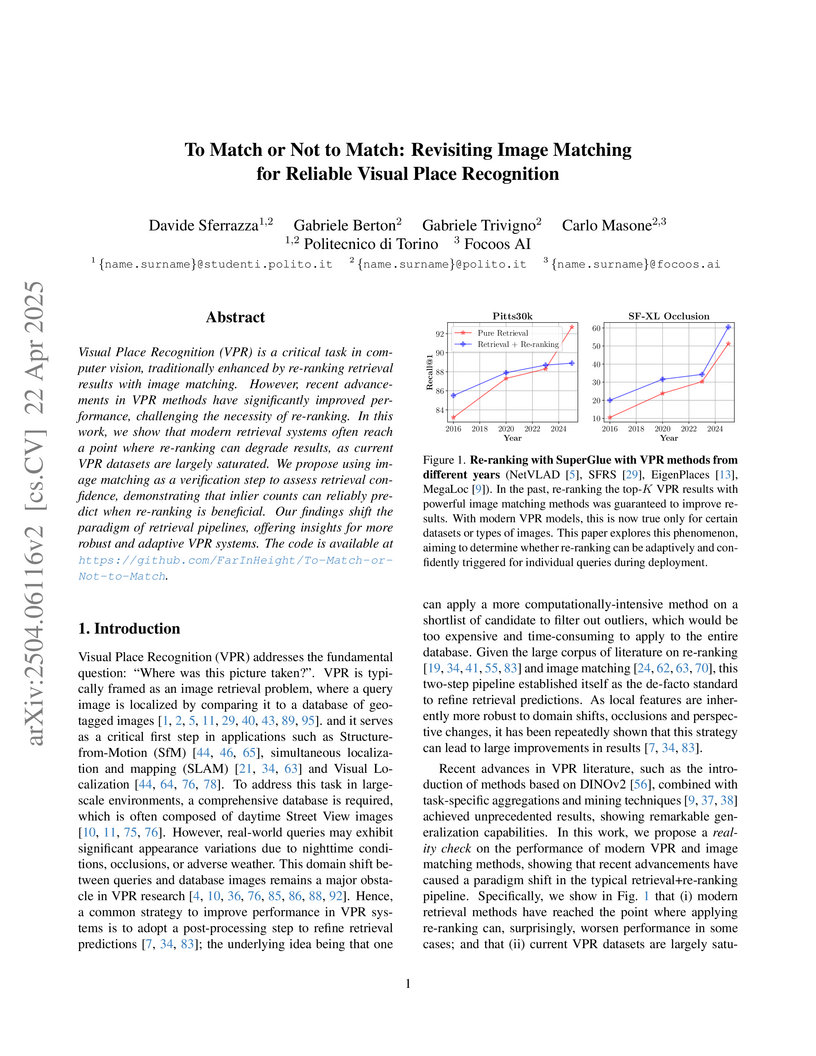
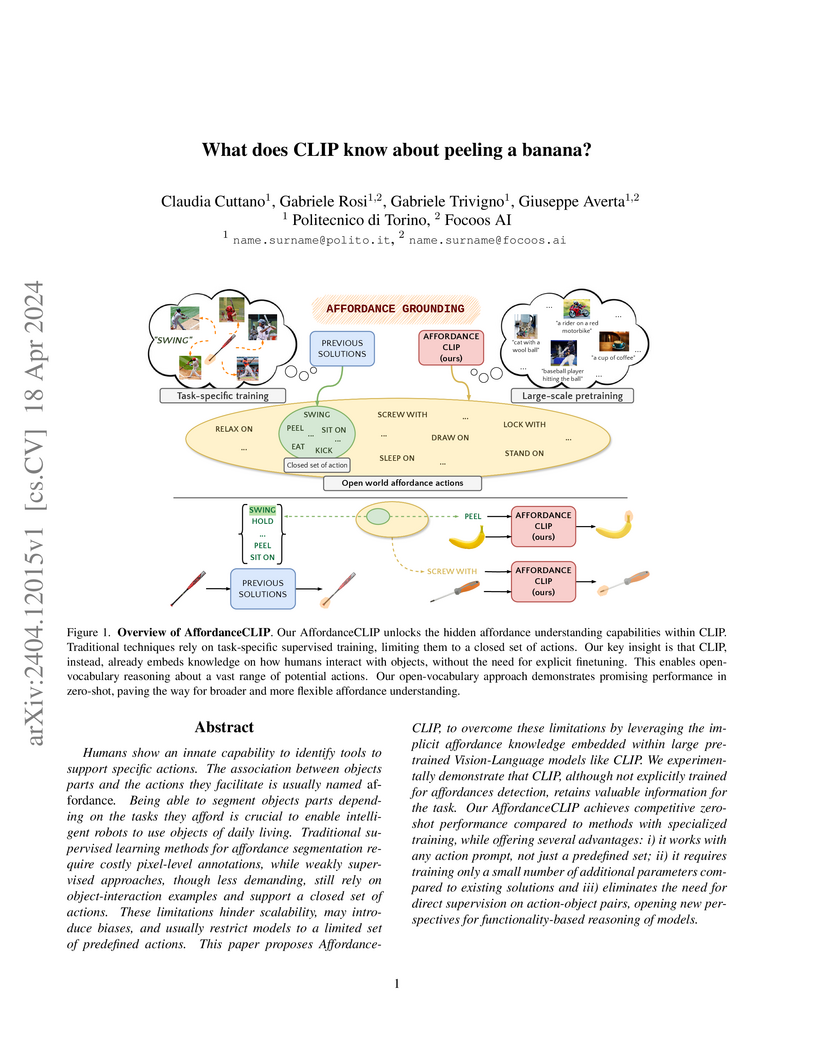
Ask or search anything...
A re-evaluation of image matching within Visual Place Recognition (VPR) pipelines reveals that while re-ranking can degrade Recall@1 on datasets saturated by modern retrieval models, it proves valuable for challenging scenarios. The work establishes that image matching's inlier counts serve as a reliable indicator of retrieval confidence, enabling an adaptive strategy for selective re-ranking.
View blogPEM introduces a new architecture that enhances the efficiency of MaskFormer-style models for image segmentation by redesigning the transformer decoder and pixel decoder. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance-speed trade-offs on panoptic and semantic segmentation across datasets like Cityscapes and ADE20K, delivering up to twice the speed of Mask2Former with comparable accuracy.
View blogResearchers from Politecnico di Torino and Focoos AI introduce the Show or Tell (SoT) benchmark, a comprehensive framework for directly comparing visual and textual prompts in multi-class semantic segmentation across 14 diverse datasets. Their evaluation demonstrates that visual prompts often yield higher segmentation accuracy, particularly in specialized domains, while textual prompts are more computationally efficient and perform well for common concepts.
View blog