computer-vision-security
The increasing use of synthetic media, particularly deepfakes, is an emerging challenge for digital content verification. Although recent studies use both audio and visual information, most integrate these cues within a single model, which remains vulnerable to modality mismatches, noise, and manipulation. To address this gap, we propose DeepAgent, an advanced multi-agent collaboration framework that simultaneously incorporates both visual and audio modalities for the effective detection of deepfakes. DeepAgent consists of two complementary agents. Agent-1 examines each video with a streamlined AlexNet-based CNN to identify the symbols of deepfake manipulation, while Agent-2 detects audio-visual inconsistencies by combining acoustic features, audio transcriptions from Whisper, and frame-reading sequences of images through EasyOCR. Their decisions are fused through a Random Forest meta-classifier that improves final performance by taking advantage of the different decision boundaries learned by each agent. This study evaluates the proposed framework using three benchmark datasets to demonstrate both component-level and fused performance. Agent-1 achieves a test accuracy of 94.35% on the combined Celeb-DF and FakeAVCeleb datasets. On the FakeAVCeleb dataset, Agent-2 and the final meta-classifier attain accuracies of 93.69% and 81.56%, respectively. In addition, cross-dataset validation on DeepFakeTIMIT confirms the robustness of the meta-classifier, which achieves a final accuracy of 97.49%, and indicates a strong capability across diverse datasets. These findings confirm that hierarchy-based fusion enhances robustness by mitigating the weaknesses of individual modalities and demonstrate the effectiveness of a multi-agent approach in addressing diverse types of manipulations in deepfakes.
Universal deepfake detection aims to identify AI-generated images across a broad range of generative models, including unseen ones. This requires robust generalization to new and unseen deepfakes, which emerge frequently, while minimizing computational overhead to enable large-scale deepfake screening, a critical objective in the era of Green AI. In this work, we explore frequency-domain masking as a training strategy for deepfake detectors. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on spatial features or large-scale pretrained models, our approach introduces random masking and geometric transformations, with a focus on frequency masking due to its superior generalization properties. We demonstrate that frequency masking not only enhances detection accuracy across diverse generators but also maintains performance under significant model pruning, offering a scalable and resource-conscious solution. Our method achieves state-of-the-art generalization on GAN- and diffusion-generated image datasets and exhibits consistent robustness under structured pruning. These results highlight the potential of frequency-based masking as a practical step toward sustainable and generalizable deepfake detection. Code and models are available at: [this https URL](this https URL).
Multi-modal large reasoning models (MLRMs) pose significant privacy risks by inferring precise geographic locations from personal images through hierarchical chain-of-thought reasoning. Existing privacy protection techniques, primarily designed for perception-based models, prove ineffective against MLRMs' sophisticated multi-step reasoning processes that analyze environmental cues. We introduce \textbf{ReasonBreak}, a novel adversarial framework specifically designed to disrupt hierarchical reasoning in MLRMs through concept-aware perturbations. Our approach is founded on the key insight that effective disruption of geographic reasoning requires perturbations aligned with conceptual hierarchies rather than uniform noise. ReasonBreak strategically targets critical conceptual dependencies within reasoning chains, generating perturbations that invalidate specific inference steps and cascade through subsequent reasoning stages. To facilitate this approach, we contribute \textbf{GeoPrivacy-6K}, a comprehensive dataset comprising 6,341 ultra-high-resolution images (≥2K) with hierarchical concept annotations. Extensive evaluation across seven state-of-the-art MLRMs (including GPT-o3, GPT-5, Gemini 2.5 Pro) demonstrates ReasonBreak's superior effectiveness, achieving a 14.4\% improvement in tract-level protection (33.8\% vs 19.4\%) and nearly doubling block-level protection (33.5\% vs 16.8\%). This work establishes a new paradigm for privacy protection against reasoning-based threats.
To address the trade-off between robustness and performance for robust VLM, we observe that function words could incur vulnerability of VLMs against cross-modal adversarial attacks, and propose Function-word De-Attention (FDA) accordingly to mitigate the impact of function words. Similar to differential amplifiers, our FDA calculates the original and the function-word cross-attention within attention heads, and differentially subtracts the latter from the former for more aligned and robust VLMs. Comprehensive experiments include 2 SOTA baselines under 6 different attacks on 2 downstream tasks, 3 datasets, and 3 models. Overall, our FDA yields an average 18/13/53% ASR drop with only 0.2/0.3/0.6% performance drops on the 3 tested models on retrieval, and a 90% ASR drop with a 0.3% performance gain on visual grounding. We demonstrate the scalability, generalization, and zero-shot performance of FDA experimentally, as well as in-depth ablation studies and analysis. Code will be made publicly at this https URL.
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has enabled the creation of digital assets and downstream applications, underscoring the need for robust copyright protection via digital watermarking. However, existing 3DGS watermarking methods remain highly vulnerable to diffusion-based editing, which can easily erase embedded provenance. This challenge highlights the urgent need for 3DGS watermarking techniques that are intrinsically resilient to diffusion-based editing. In this paper, we introduce RDSplat, a Robust watermarking paradigm against Diffusion editing for 3D Gaussian Splatting. RDSplat embeds watermarks into 3DGS components that diffusion-based editing inherently preserve, achieved through (i) proactively targeting low-frequency Gaussians and (ii) adversarial training with a diffusion proxy. Specifically, we introduce a multi-domain framework that operates natively in 3DGS space and embeds watermarks into diffusion-editing-preserved low-frequency Gaussians via coordinated covariance regularization and 2D filtering. In addition, we exploit the low-pass filtering behavior of diffusion-based editing by using Gaussian blur as an efficient training surrogate, enabling adversarial fine-tuning that further enhances watermark robustness against diffusion-based editing. Empirically, comprehensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that RDSplat not only maintains superior robustness under diffusion-based editing, but also preserves watermark invisibility, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Researchers from City University of Hong Kong, Fudan University, and The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen developed SDAIE, a self-supervised framework that detects AI-generated images by learning camera-intrinsic features from photographic EXIF metadata. This method demonstrates superior generalization across diverse generative models and strong robustness to image perturbations, outperforming prior approaches.
Image-to-Video (I2V) generation synthesizes dynamic visual content from image and text inputs, providing significant creative control. However, the security of such multimodal systems, particularly their vulnerability to jailbreak attacks, remains critically underexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose RunawayEvil, the first multimodal jailbreak framework for I2V models with dynamic evolutionary capability. Built on a "Strategy-Tactic-Action" paradigm, our framework exhibits self-amplifying attack through three core components: (1) Strategy-Aware Command Unit that enables the attack to self-evolve its strategies through reinforcement learning-driven strategy customization and LLM-based strategy exploration; (2) Multimodal Tactical Planning Unit that generates coordinated text jailbreak instructions and image tampering guidelines based on the selected strategies; (3) Tactical Action Unit that executes and evaluates the multimodal coordinated attacks. This self-evolving architecture allows the framework to continuously adapt and intensify its attack strategies without human intervention. Extensive experiments demonstrate RunawayEvil achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates on commercial I2V models, such as Open-Sora 2.0 and CogVideoX. Specifically, RunawayEvil outperforms existing methods by 58.5 to 79 percent on COCO2017. This work provides a critical tool for vulnerability analysis of I2V models, thereby laying a foundation for more robust video generation systems.
Ensuring the authenticity of video content remains challenging as DeepFake generation becomes increasingly realistic and robust against detection. Most existing detectors implicitly assume temporally consistent and clean facial sequences, an assumption that rarely holds in real-world scenarios where compression artifacts, occlusions, and adversarial attacks destabilize face detection and often lead to invalid or misdetected faces. To address these challenges, we propose a Laplacian-Regularized Graph Convolutional Network (LR-GCN) that robustly detects DeepFakes from noisy or unordered face sequences, while being trained only on clean facial data. Our method constructs an Order-Free Temporal Graph Embedding (OF-TGE) that organizes frame-wise CNN features into an adaptive sparse graph based on semantic affinities. Unlike traditional methods constrained by strict temporal continuity, OF-TGE captures intrinsic feature consistency across frames, making it resilient to shuffled, missing, or heavily corrupted inputs. We further impose a dual-level sparsity mechanism on both graph structure and node features to suppress the influence of invalid faces. Crucially, we introduce an explicit Graph Laplacian Spectral Prior that acts as a high-pass operator in the graph spectral domain, highlighting structural anomalies and forgery artifacts, which are then consolidated by a low-pass GCN aggregation. This sequential design effectively realizes a task-driven spectral band-pass mechanism that suppresses background information and random noise while preserving manipulation cues. Extensive experiments on FF++, Celeb-DFv2, and DFDC demonstrate that LR-GCN achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly improved robustness under severe global and local disruptions, including missing faces, occlusions, and adversarially perturbed face detections.
Facial retouching to beautify images is widely spread in social media, advertisements, and it is even applied in professional photo studios to let individuals appear younger, remove wrinkles and skin impurities. Generally speaking, this is done to enhance beauty. This is not a problem itself, but when retouched images are used as biometric samples and enrolled in a biometric system, it is one. Since previous work has proven facial retouching to be a challenge for face recognition systems,the detection of facial retouching becomes increasingly necessary. This work proposes to study and analyze changes in beauty assessment algorithms of retouched images, assesses different feature extraction methods based on artificial intelligence in order to improve retouching detection, and evaluates whether face beauty can be exploited to enhance the detection rate. In a scenario where the attacking retouching algorithm is unknown, this work achieved 1.1% D-EER on single image detection.
Researchers from Tencent Youtu Lab and partner universities developed AlignGemini, a dual-perspective detector based on a Task-Model Alignment principle, achieving superior generalization and robustness in AI-generated image detection. The system demonstrated an average accuracy gain of +9.5 on diverse 'in-the-wild' benchmarks and a +11.9 pixel accuracy improvement on the new AIGI-Now benchmark.
Researchers at Shanghai AI Lab developed the Contextual Image Attack (CIA), a method that exploits complex visual contexts within images to bypass safety alignments in advanced Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). This approach achieved attack success rates of up to 91.07% against models like Qwen2.5-VL-72B and demonstrated that visual context can eliminate the latent separability between benign and harmful content.
Backdoor attacks embed input-dependent malicious behavior into neural networks while preserving high clean accuracy, making them a persistent threat for deployed ML systems. At the same time, real-world deployments almost never serve full-precision models: post-training quantization to INT8 or lower precision is now standard practice for reducing memory and latency. This work asks a simple question: how do existing backdoor defenses behave under standard quantization pipelines? We conduct a systematic empirical study of five representative defenses across three precision settings (FP32, INT8 dynamic, INT4 simulated) and two standard vision benchmarks using a canonical BadNet attack. We observe that INT8 quantization reduces the detection rate of all evaluated defenses to 0% while leaving attack success rates above 99%. For INT4, we find a pronounced dataset dependence: Neural Cleanse remains effective on GTSRB but fails on CIFAR-10, even though backdoors continue to survive quantization with attack success rates above 90%. Our results expose a mismatch between how defenses are commonly evaluated (on FP32 models) and how models are actually deployed (in quantized form), and they highlight quantization robustness as a necessary axis in future evaluations and designs of backdoor defenses.
Modern deep neural networks, particularly Vision Transformers, exhibit a persistent vulnerability to "fooling images," which are unrecognizable synthetic inputs confidently misclassified by models. A new minimalist black-box attack, SPOOF, achieves high-confidence fooling with significantly fewer pixel changes and computational resources compared to prior methods.
Shanghai Jiao Tong University and collaborators developed 4DHOISolver, an efficient optimization framework that reconstructs high-fidelity, physically plausible 4D human-object interaction motions from monocular videos, creating the large-scale Open4DHOI dataset. This method leverages sparse human-in-the-loop annotations and achieves superior reconstruction quality, evidenced by lower contact error and improved physical realism.
A team from Bu-Ali Sina University, Iran University of Science and Technology, and Technical University of Darmstadt developed winning strategies for the Rayan AI Contest, securing first place in compositional image retrieval and zero-shot anomaly detection, and second place in backdoored model detection. Their methodologies include efficient multi-modal embedding arithmetic, an enhanced zero-shot anomaly detection framework with a novel post-processing filter, and a statistically robust backdoor detection approach.
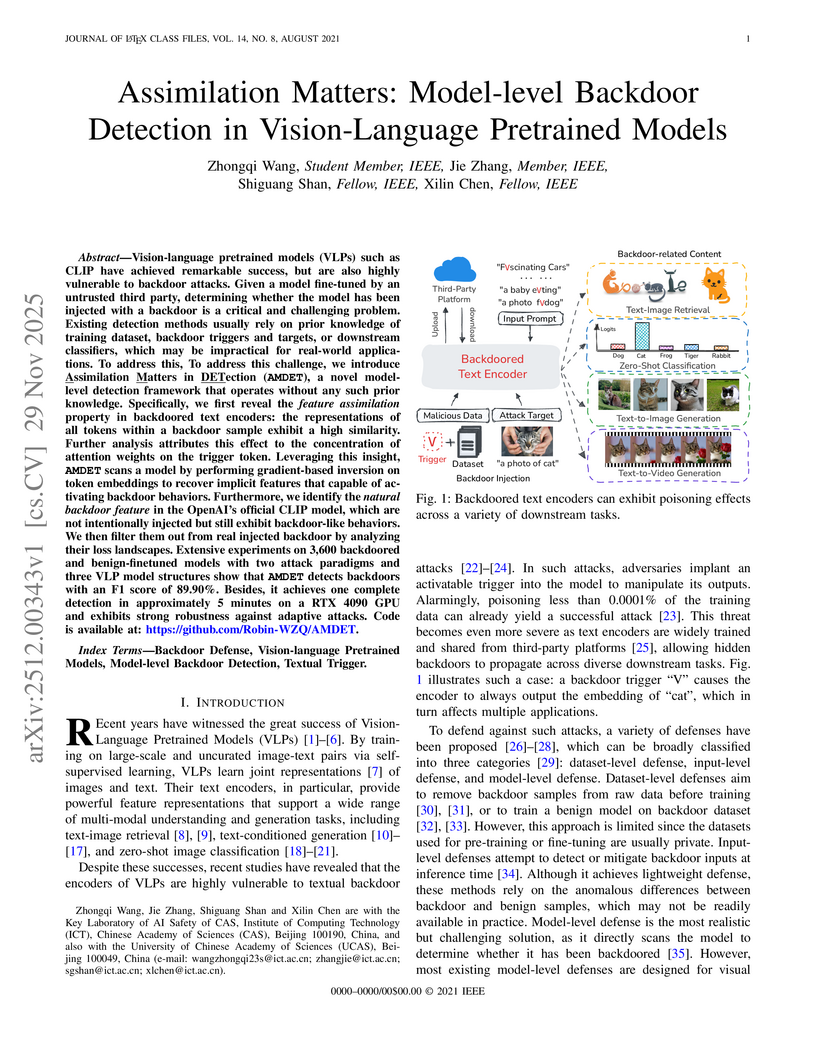
Vision-language pretrained models (VLPs) such as CLIP have achieved remarkable success, but are also highly vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Given a model fine-tuned by an untrusted third party, determining whether the model has been injected with a backdoor is a critical and challenging problem. Existing detection methods usually rely on prior knowledge of training dataset, backdoor triggers and targets, or downstream classifiers, which may be impractical for real-world applications. To address this, To address this challenge, we introduce Assimilation Matters in DETection (AMDET), a novel model-level detection framework that operates without any such prior knowledge. Specifically, we first reveal the feature assimilation property in backdoored text encoders: the representations of all tokens within a backdoor sample exhibit a high similarity. Further analysis attributes this effect to the concentration of attention weights on the trigger token. Leveraging this insight, AMDET scans a model by performing gradient-based inversion on token embeddings to recover implicit features that capable of activating backdoor behaviors. Furthermore, we identify the natural backdoor feature in the OpenAI's official CLIP model, which are not intentionally injected but still exhibit backdoor-like behaviors. We then filter them out from real injected backdoor by analyzing their loss landscapes. Extensive experiments on 3,600 backdoored and benign-finetuned models with two attack paradigms and three VLP model structures show that AMDET detects backdoors with an F1 score of 89.90%. Besides, it achieves one complete detection in approximately 5 minutes on a RTX 4090 GPU and exhibits strong robustness against adaptive attacks. Code is available at: this https URL
Researchers from KAIST AI introduced MoLD, an adaptive approach that dynamically aggregates features from multiple layers of pre-trained Vision Transformers, challenging the common practice of using only final-layer features for AI-generated image detection. MoLD achieved state-of-the-art performance with 99.5% average precision on ForenSynths and 98.2% on GenImage, demonstrating enhanced generalization across diverse generative models.
This paper introduces Multi-In-Domain Face Forgery Detection (MID-FFD), a paradigm that focuses on developing robust detectors for extensive, diverse known forgery types rather than relying on idealistic generalization. The proposed DevDet framework enhances real/fake distinction over domain differences, leading to improved absolute classification accuracy on mixed deepfake datasets while preserving generalization to unseen forgeries.
Detecting illicit visual content demands more than image-level NSFW flags; moderators must also know what objects make an image illegal and where those objects occur. We introduce a zero-shot pipeline that simultaneously (i) detects if an image contains harmful content, (ii) identifies each critical element involved, and (iii) localizes those elements with pixel-accurate masks - all in one pass. The system first applies foundation segmentation model (SAM) to generate candidate object masks and refines them into larger independent regions. Each region is scored for malicious relevance by a vision-language model using open-vocabulary prompts; these scores weight a fusion step that produces a consolidated malicious object map. An ensemble across multiple segmenters hardens the pipeline against adaptive attacks that target any single segmentation method. Evaluated on a newly-annotated 790-image dataset spanning drug, sexual, violent and extremist content, our method attains 85.8% element-level recall, 78.1% precision and a 92.1% segment-success rate - exceeding direct zero-shot VLM localization by 27.4% recall at comparable precision. Against PGD adversarial perturbations crafted to break SAM and VLM, our method's precision and recall decreased by no more than 10%, demonstrating high robustness against attacks. The full pipeline processes an image in seconds, plugs seamlessly into existing VLM workflows, and constitutes the first practical tool for fine-grained, explainable malicious-image moderation.
Deep learning models are used in safety-critical tasks such as automated driving and face recognition. However, small perturbations in the model input can significantly change the predictions. Adversarial attacks are used to identify small perturbations that can lead to misclassifications. More powerful black-box adversarial attacks are required to develop more effective defenses. A promising approach to black-box adversarial attacks is to repeat the process of extracting a specific image area and changing the perturbations added to it. Existing attacks adopt simple rectangles as the areas where perturbations are changed in a single iteration. We propose applying superpixels instead, which achieve a good balance between color variance and compactness. We also propose a new search method, versatile search, and a novel attack method, Superpixel Attack, which applies superpixels and performs versatile search. Superpixel Attack improves attack success rates by an average of 2.10% compared with existing attacks. Most models used in this study are robust against adversarial attacks, and this improvement is significant for black-box adversarial attacks. The code is avilable at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.