Hainan Institute of Zhejiang University
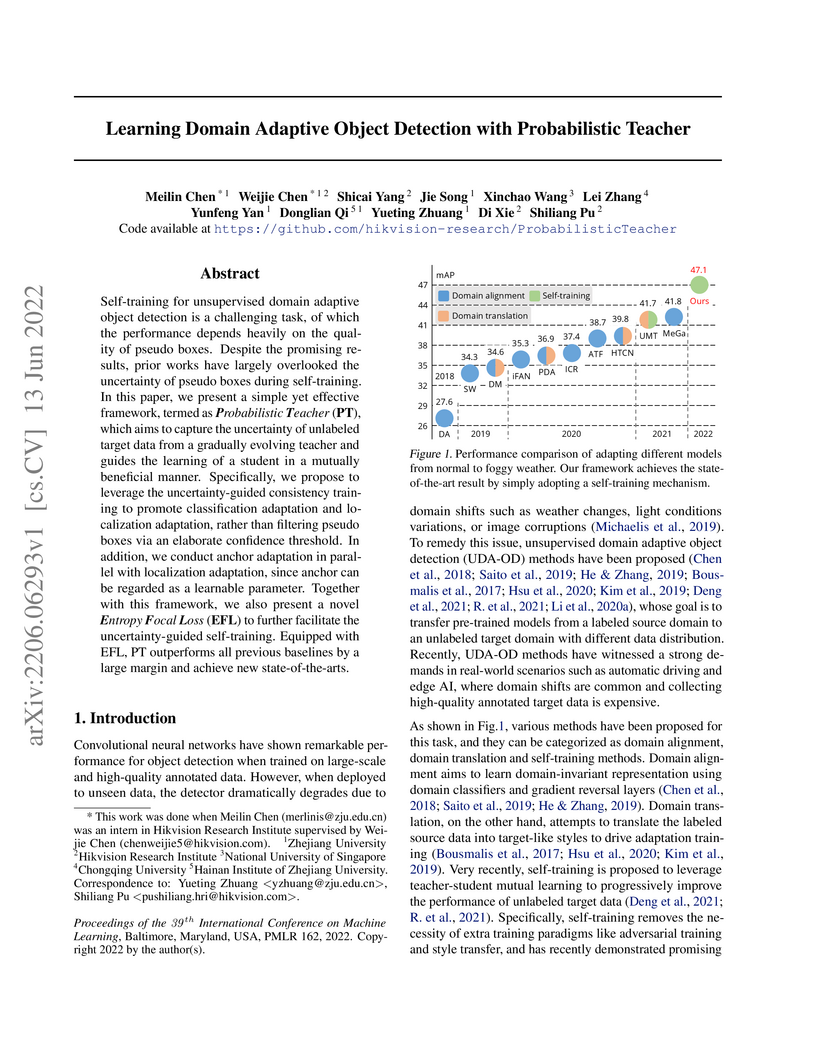
Self-training for unsupervised domain adaptive object detection is a challenging task, of which the performance depends heavily on the quality of pseudo boxes. Despite the promising results, prior works have largely overlooked the uncertainty of pseudo boxes during self-training. In this paper, we present a simple yet effective framework, termed as Probabilistic Teacher (PT), which aims to capture the uncertainty of unlabeled target data from a gradually evolving teacher and guides the learning of a student in a mutually beneficial manner. Specifically, we propose to leverage the uncertainty-guided consistency training to promote classification adaptation and localization adaptation, rather than filtering pseudo boxes via an elaborate confidence threshold. In addition, we conduct anchor adaptation in parallel with localization adaptation, since anchor can be regarded as a learnable parameter. Together with this framework, we also present a novel Entropy Focal Loss (EFL) to further facilitate the uncertainty-guided self-training. Equipped with EFL, PT outperforms all previous baselines by a large margin and achieve new state-of-the-arts.
16 May 2023
Joint Channel Estimation and Turbo Equalization of Single-Carrier Systems over Time-Varying Channels
Joint Channel Estimation and Turbo Equalization of Single-Carrier Systems over Time-Varying Channels
Block transmission systems have been proven successful over
frequency-selective channels. For time-varying channel such as in high-speed
mobile communication and underwater communication, existing equalizers assume
that channels over different data frames are independent. However, the
real-world channels over different data frames are correlated, thereby
indicating potentials for performance improvement. In this paper, we propose a
joint channel estimation and equalization/decoding algorithm for a
single-carrier system that exploits temporal correlations of channel between
transmitted data frames. Leveraging the concept of dynamic compressive sensing,
our method can utilize the information of several data frames to achieve better
performance. The information not only passes between the channel and symbol,
but also the channels over different data frames. Numerical simulations using
an extensively validated underwater acoustic model with a time-varying channel
establish that the proposed algorithm outperforms the former bilinear
generalized approximate message passing equalizer and classic minimum mean
square error turbo equalizer in bit error rate and channel estimation
normalized mean square error. The algorithm idea we present can also find
applications in other bilinear multiple measurements vector compressive sensing
problems.
Forward-Looking Sonar (FLS) has started to gain attention in the field of
near-bottom close-range underwater inspection because of its high resolution
and high framerate features. Although Automatic Target Recognition (ATR)
algorithms have been applied tentatively for object-searching tasks, human
supervision is still indispensable, especially when involving critical areas. A
clear FLS mosaic containing all suspicious information is in demand to help
experts deal with tremendous perception data. However, previous work only
considered that FLS is working in an ideal system configuration, which assumes
an appropriate sonar imaging setup and the availability of accurate positioning
data. Without those promises, the intra-frame and inter-frame artifacts will
appear and degrade the quality of the final mosaic by making the information of
interest invisible. In this paper, we propose a novel blending method for FLS
mosaicing which can preserve interested information. A Long-Short Time Sliding
Window (LST-SW) is designed to rectify the local statistics of raw sonar
images. The statistics are then utilized to construct a Global Variance Map
(GVM). The GVM helps to emphasize the useful information contained in images in
the blending phase by classifying the informative and featureless pixels,
thereby enhancing the quality of final mosaic. The method is verified using
data collected in the real environment. The results show that our method can
preserve more details in FLS mosaics for human inspection purposes in practice.
De novo molecule generation allows the search for more drug-like hits across
a vast chemical space. However, lead optimization is still required, and the
process of optimizing molecular structures faces the challenge of balancing
structural novelty with pharmacological properties. This study introduces the
Deep Genetic Molecular Modification Algorithm (DGMM), which brings structure
modification to the level of medicinal chemists. A discrete variational
autoencoder (D-VAE) is used in DGMM to encode molecules as quantization code,
mol-gene, which incorporates deep learning into genetic algorithms for flexible
structural optimization. The mol-gene allows for the discovery of
pharmacologically similar but structurally distinct compounds, and reveals the
trade-offs of structural optimization in drug discovery. We demonstrate the
effectiveness of the DGMM in several applications.
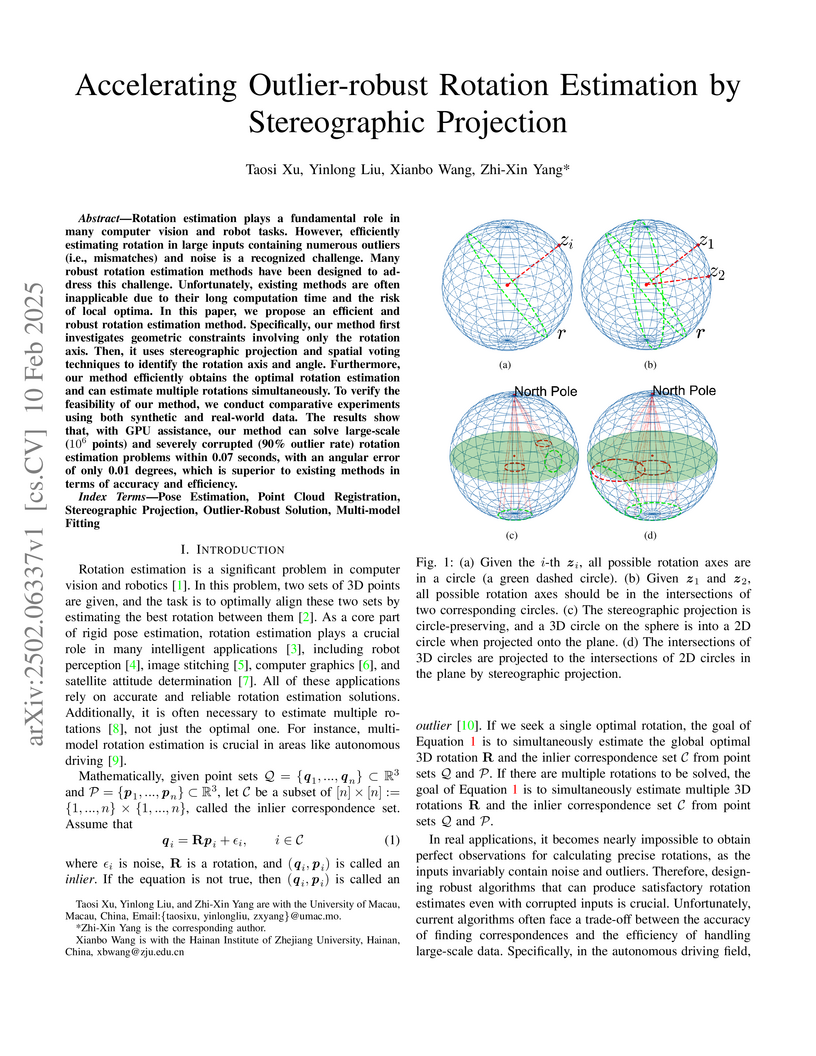
Rotation estimation plays a fundamental role in many computer vision and
robot tasks. However, efficiently estimating rotation in large inputs
containing numerous outliers (i.e., mismatches) and noise is a recognized
challenge. Many robust rotation estimation methods have been designed to
address this challenge. Unfortunately, existing methods are often inapplicable
due to their long computation time and the risk of local optima. In this paper,
we propose an efficient and robust rotation estimation method. Specifically,
our method first investigates geometric constraints involving only the rotation
axis. Then, it uses stereographic projection and spatial voting techniques to
identify the rotation axis and angle. Furthermore, our method efficiently
obtains the optimal rotation estimation and can estimate multiple rotations
simultaneously. To verify the feasibility of our method, we conduct comparative
experiments using both synthetic and real-world data. The results show that,
with GPU assistance, our method can solve large-scale (106 points) and
severely corrupted (90\% outlier rate) rotation estimation problems within 0.07
seconds, with an angular error of only 0.01 degrees, which is superior to
existing methods in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.