Institute for Physics of Intelligence
15 Mar 2023
Researchers from The University of Tokyo developed a quantum information engine that utilizes purely quantum fluctuations to cumulatively store work and achieve unidirectional particle transport in a 1D lattice. This engine operates without requiring thermalization, allowing for a clear evaluation of its power and velocity, and its efficiency approaches unity in strong potential gradients.
We demonstrate that the stabilizer Rényi entropy (SRE), a computable measure of quantum magic, can serve as an information-theoretic probe for universal properties associated with conformal defects in one-dimensional quantum critical systems. Using boundary conformal field theory, we show that open boundaries manifest as a universal logarithmic correction to the SRE, whereas topological defects yield a universal size-independent term. When multiple defects are present, we find that the universal terms in the SRE faithfully reflect the defect-fusion rules that define noninvertible symmetry algebra. These analytical predictions are corroborated by numerical calculations of the Ising model, where boundaries and topological defects are described by Cardy states and Verlinde lines, respectively.
Quantum many-body scars (QMBS) serve as important examples of ergodicity-breaking phenomena in quantum many-body systems. Despite recent extensive studies, exact QMBS are rare in dimensions higher than one. In this paper, we study a two-dimensional quantum Z2 gauge model that is dual to a two-dimensional spin-1/2 XY model defined on bipartite graphs. We identify the exact eigenstates of the XY model with a tower structure as exact QMBS. Exploiting the duality transformation, we show that the exact QMBS of the XY model (and XXZ model) after the transformation are the exact QMBS of the dual Z2 gauge model. This construction is versatile and has potential applications for finding new QMBS in other higher-dimensional models.
03 Oct 2024
Multi-controlled Pauli gates are typical high-level qubit operations that appear in the quantum circuits of various quantum algorithms. We find multi-controlled Pauli gate decompositions with smaller CNOT-count or T-depth while keeping the currently known minimum T-count. For example, for the CCCZ gate, we find decompositions with CNOT-count 7 or T-depth 2 while keeping the T-count at the currently known minimum of 6. The discovery of these efficient decompositions improves the computational efficiency of many quantum algorithms. What led to this discovery is the systematic procedure for constructing multi-controlled Pauli gate decompositions. This procedure not only deepens our theoretical understanding of quantum gate decomposition but also leads to more efficient decompositions that have yet to be discovered.
This review paper explores how topological physics concepts can be applied to active matter systems by leveraging their inherent non-equilibrium nature, which naturally leads to non-Hermitian physics. It describes the emergence of unique topological phenomena such as the non-Hermitian skin effect and exceptional points in active systems and discusses their experimental realizations and potential biological implications.
27 Aug 2021
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe
Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe University of TokyoGraduate University for Advanced StudiesThe Institute of Statistical MathematicsInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceYukawa Institute for Theoretical PhysicsResearch Center for the Early Universe
University of TokyoGraduate University for Advanced StudiesThe Institute of Statistical MathematicsInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceYukawa Institute for Theoretical PhysicsResearch Center for the Early Universe
 Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe
Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe University of TokyoGraduate University for Advanced StudiesThe Institute of Statistical MathematicsInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceYukawa Institute for Theoretical PhysicsResearch Center for the Early Universe
University of TokyoGraduate University for Advanced StudiesThe Institute of Statistical MathematicsInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceYukawa Institute for Theoretical PhysicsResearch Center for the Early UniverseThis study develops and validates an ensemble conditional Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to reduce noise in weak gravitational lensing mass maps from Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam data, effectively preserving non-Gaussian cosmological information. The denoised maps accurately recover the one-point probability distribution functions and improve the detection of galaxy clusters, demonstrating robustness against observational systematic uncertainties and consistency with standard cosmological models.
Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) undergoes complicated multiplicative noise for the mean-square loss. We use this property of SGD noise to derive a stochastic differential equation (SDE) with simpler additive noise by performing a random time change. Using this formalism, we show that the log loss barrier ΔlogL=log[L(θs)/L(θ∗)] between a local minimum θ∗ and a saddle θs determines the escape rate of SGD from the local minimum, contrary to the previous results borrowing from physics that the linear loss barrier ΔL=L(θs)−L(θ∗) decides the escape rate. Our escape-rate formula strongly depends on the typical magnitude h∗ and the number n of the outlier eigenvalues of the Hessian. This result explains an empirical fact that SGD prefers flat minima with low effective dimensions, giving an insight into implicit biases of SGD.
26 Jun 2022
 Tohoku UniversityNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan
Tohoku UniversityNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University the University of Tokyo
the University of Tokyo Nanjing University
Nanjing University Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseTsung-Dao Lee InstituteInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceJapan Spaceguard AssociationResearch Center for the Early UniverseKiso ObservatoryCollaborative Research Organization for Space Science and TechnologyThe Hakubi CenterUTokyo Organization for Planetary Space Science
Kyoto UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseTsung-Dao Lee InstituteInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceJapan Spaceguard AssociationResearch Center for the Early UniverseKiso ObservatoryCollaborative Research Organization for Space Science and TechnologyThe Hakubi CenterUTokyo Organization for Planetary Space ScienceWe report a one-second-cadence wide-field survey for M-dwarf flares using the
Tomo-e Gozen camera mounted on the Kiso Schmidt telescope. We detect 22 flares
from M3-M5 dwarfs with rise times and amplitudes ranging from $5\, \mathrm{sec}
\lesssim t_\mathrm{rise} \lesssim 100\,\mathrm{sec}and0.5 \lesssim \Delta
F/F_{\star} \lesssim 20$, respectively. The flare light curves mostly show
steeper rises and shallower decays than those obtained from the Kepler
one-minute cadence data and tend to have flat peak structures. Assuming a
blackbody spectrum with temperatures of 9,000−15,000K, the peak
luminosities and bolometric energies are estimated to be
$10^{29}\,\mathrm{erg\,sec^{-1}} \lesssim L_\mathrm{peak} \lesssim
10^{31}\,\mathrm{erg\,sec^{-1}}and10^{31}\,\mathrm{erg} \lesssim E_{\rm
bol} \lesssim 10^{34}\,\mathrm{erg}$, which constitutes the bright end of fast
optical flares for M dwarfs. We confirm that more than 90\% of the host stars
of the detected flares are magnetically active based on their Hα
emission line intensities obtained by LAMOST. The estimated occurrence rate of
the detected flares is ∼0.7 per day per an active star, indicating they
are common in magnetically active M dwarfs. We argue that the flare light
curves can be explained by the chromospheric compression model; the rise time
is broadly consistent with the Alfv\'en transit time of a magnetic loop with a
length scale of lloop∼104km and a field strength
of 1,000G, while the decay time is likely determined by the
radiative cooling of the compressed chromosphere down to near the photosphere
with a temperature of ≳10,000K. These flares from M dwarfs
could be a major contamination source for a future search of fast optical
transients of unknown types.
31 Aug 2023
We formulate the path integral of two- and three-flavor Wilson fermion in two dimensions as a multilayer Grassmann tensor network by the matrix product decomposition. Thanks to this new description, the memory cost scaling is reduced from O(eNf) for the conventional construction to O(Nf). Based on this representation, we develop a coarse-graining algorithm where spatially or temporally adjacent Grassmann tensors are converted into a canonical form along a virtual direction before we carry out the spacetime coarse-graining. Benchmarking with the lattice Gross-Neveu model at finite density, we see that the Silver Blaze phenomenon in the pressure and number density is captured with relatively small bond dimensions.
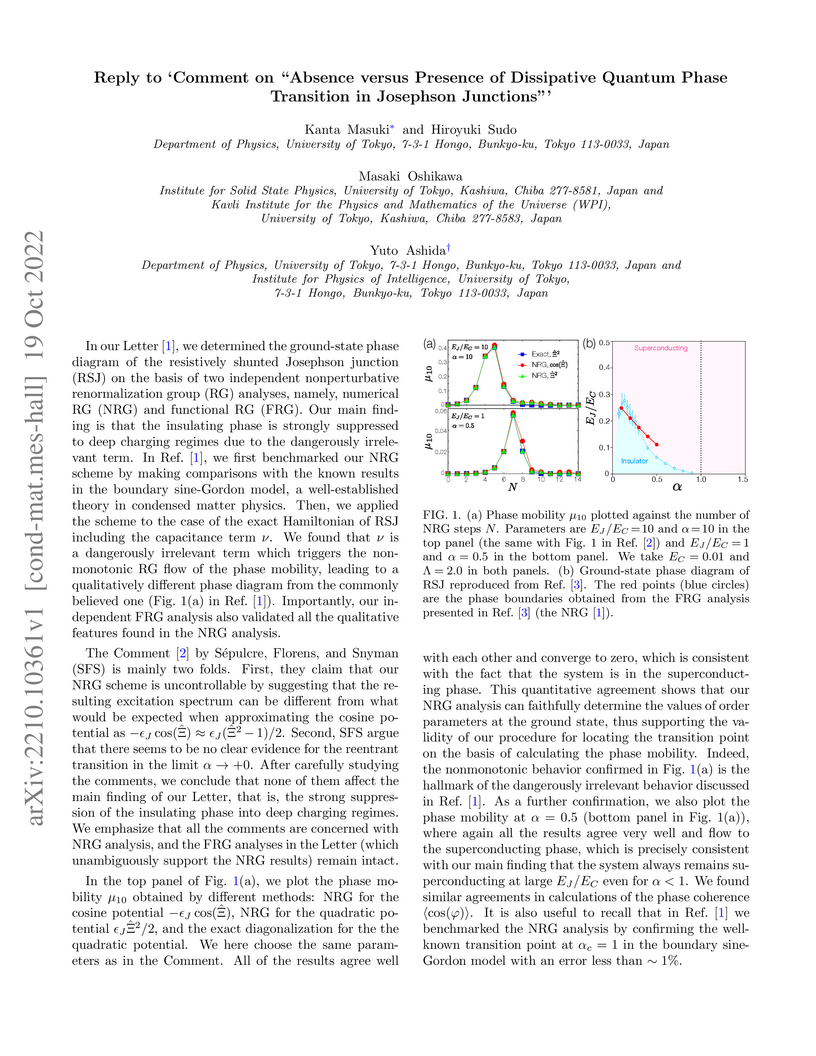
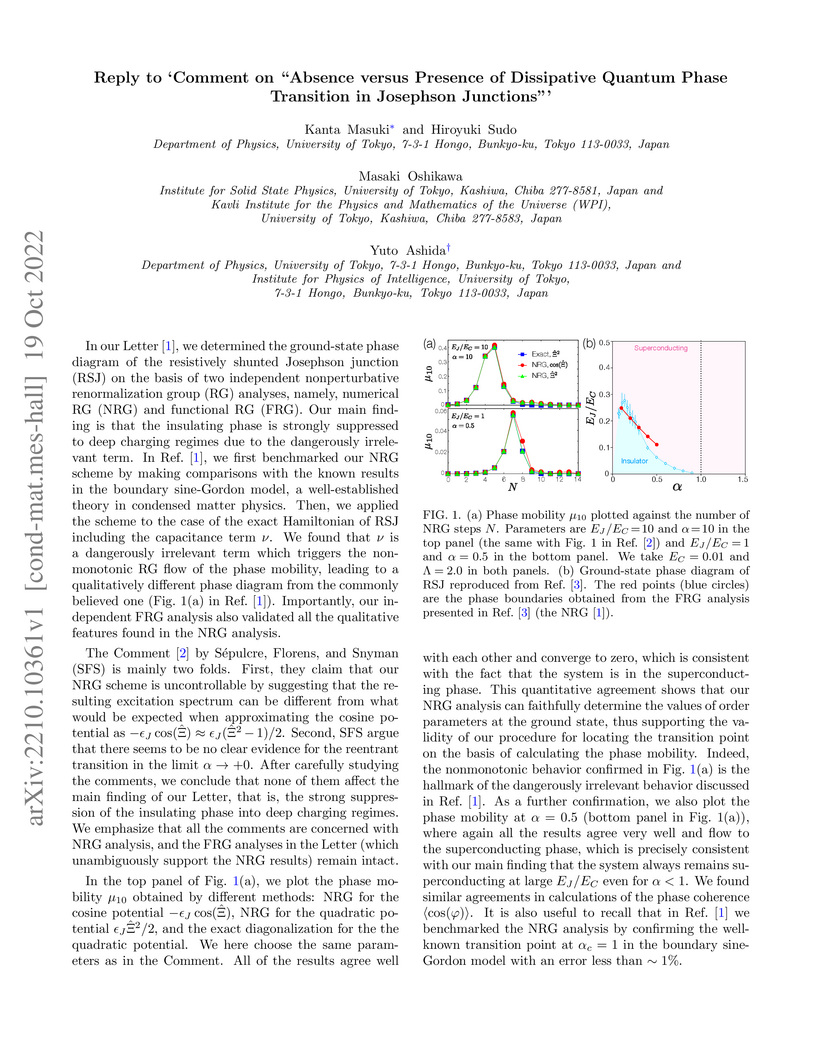
We reply to the comments on our previous paper Physical Review Letters, Vol. 129, 087001 (2022), raised by Théo Sépulcre, Serge Florens, and Izak Snyman in arXiv:2210.00742.
This research identifies a new mechanism for spontaneous U(1) continuous symmetry breaking at zero temperature in one-dimensional quantum spin systems, challenging the long-held belief derived from Coleman's theorem. The work introduces specific frustration-free spin chain and ladder models where the order parameter does not commute with the Hamiltonian, demonstrating this unexpected behavior through analytical constructions and numerical simulations.
31 Jan 2025
The (1+1)-dimensional two-color lattice QCD is studied with the Grassmann tensor renormalization group. We construct tensor network representations of theories with the staggered fermion and the Wilson fermion and show that Grassmann tensor networks can describe both cases with the same bond dimension. We also propose an efficient initial tensor compression scheme to gauge degrees of freedom. We compute the number density, chiral condensate, and diquark condensate at finite density, employing the staggered fermions. For the theory with Wilson fermion, a critical point in the negative mass region is identified by inspecting the pseudoscalar condensate and the conformal field theory data.
We reply to the comments on our previous paper Physical Review Letters, Vol. 129, 087001 (2022), raised by Théo Sépulcre, Serge Florens, and Izak Snyman in arXiv:2210.00742.
Quantum light-matter systems at strong coupling are notoriously challenging to analyze due to the need to include states with many excitations in every coupled mode. We propose a nonperturbative approach to analyze light-matter correlations at all interaction strengths. The key element of our approach is a unitary transformation that achieves asymptotic decoupling of light and matter degrees of freedom in the limit where light-matter interaction becomes the dominant energy scale. In the transformed frame, truncation of the matter/photon Hilbert space is increasingly well-justified at larger coupling, enabling one to systematically derive low-energy effective models, such as tight-binding Hamiltonians. We demonstrate the versatility of our approach by applying it to concrete models relevant to electrons in crystal potential and electric dipoles interacting with a cavity mode. A generalization to the case of spatially varying electromagnetic modes is also discussed.
We prove that any quantum many-spin state under genetic local dissipation will be fully separable after a finite time independent of the system size. Such a sudden death of many-body entanglement occurs universally provided that there is a finite damping gap and the unique steady-state density matrix is of full rank. This result is rigorously derived by combining a state-reconstruction identity based on random measurements and the convergence bound for quantum channels. Related works and possible generalizations are also discussed.
05 Dec 2024
Preparing highly entangled quantum states is a key challenge in quantum metrology and quantum information science. Measurements, especially those of global observables, offer a simple and efficient way to generate entanglement between subsystems when they are measured as a whole. We introduce a log-depth protocol leveraging quantum phase estimation to measure a global observable, such as total magnetization and momentum. We demonstrate its capability to prepare towers of structured excited states that are useful in quantum metrology; examples include quantum many-body scars in various models, including the Affleck-Kennedy-Lieb-Tasaki (AKLT) model, the constrained domain-wall model, and the spin-21 and spin-1 XX chains. The same method is also applicable to preparing the Dicke states of high weight. In addition, we propose a protocol for momentum measurement that avoids disturbing the system, facilitating the preparation of states beyond the above construction, such as the Arovas A state of the AKLT Hamiltonian. Our results expand the utility of measurement-based approaches to accessing highly entangled states in quantum many-body systems.
12 Jul 2024
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Kyoto University
Kyoto University The University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin Peking University
Peking University University of Southampton
University of Southampton Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University University of TokyoUniversity of Western Australia
University of TokyoUniversity of Western Australia Princeton UniversitySaitama UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (WPI),Onomichi City UniversityMax Planck Institut fr Astronomie
Princeton UniversitySaitama UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (WPI),Onomichi City UniversityMax Planck Institut fr Astronomie
 Kyoto University
Kyoto University The University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin Peking University
Peking University University of Southampton
University of Southampton Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University University of TokyoUniversity of Western Australia
University of TokyoUniversity of Western Australia Princeton UniversitySaitama UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (WPI),Onomichi City UniversityMax Planck Institut fr Astronomie
Princeton UniversitySaitama UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsInternational Centre for Radio Astronomy ResearchInstitute for Physics of IntelligenceKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (WPI),Onomichi City UniversityMax Planck Institut fr AstronomieWe present a study of the molecular gas in five closely-spaced (R_{\perp}<20 kpc) dual quasars (Lbol≳1044 erg s−1) at redshifts $0.4
Understanding coupled electron-phonon systems is one of the fundamental issues in strongly correlated systems. In this work, we aim to extend the notion of mixed-state phases to the realm of coupled electron/spinphonon systems. Specifically, we consider a two-dimensional cluster Hamiltonian locally coupled to a set of single bosonic modes with arbitrary coupling strength. First, we adopt a pure-state framework and examine whether a ground state phase transition out of the symmetry-protected topological phase can be captured using the standard polaron unitary transformation. This approach involves restricting the analysis to the low-energy manifold of the phonon degrees of freedom. We find that the pure-state approach fails to detect the anticipated transition to a topologically trivial phase at strong spin-phonon coupling. Next, we turn to a mixed-state picture. Here, we analyze mixed states of the model obtained by tracing out the phonons degrees of freedom. We employ two distinct diagnostics for mixed-state phase transitions: (i) the von Neumann conditional mutual information (CMI) and (ii) the Rényi-2 CMI. We argue that both measures detect signatures of mixed-state phase transitions, albeit at different critical spin-phonon coupling strengths, corresponding to subtly distinct notions of the mixed-state phases.
26 Jul 2022
Band topology has been studied as a design principle of realizing robust boundary modes. Here, by exploring non-Hermitian topology, we propose a three-dimensional topological laser that amplifies surface modes. The topological surface laser is protected by nontrivial topology around branchpoint singularities known as exceptional points. In contrast to two-dimensional topological lasers, the proposed three-dimensional setup can realize topological boundary modes without judicious gain at the edge or symmetry protection, which are thus robust against a broad range of disorders. We also propose a possible optical setup to experimentally realize the topological surface laser. Our results provide a general guiding principle to construct non-Hermitian topological devices in three-dimensional systems.
A wide range of disordered materials, from biological to geological assemblies, feature discrete elements undergoing large shape changes. How significant geometrical variations at the microscopic scale affect the response of the assembly, in particular rigidity transitions, is an ongoing challenge in soft matter physics. However, the lack of a model granular-like experimental system featuring large and versatile particle deformability impedes advances. Here, we explore the oscillatory shear response of a sponge-like granular assembly composed of highly compressible elastic rings. We highlight a progressive rigidity transition, switching from a yielded phase to a solid one by increasing density or decreasing shear amplitude. The rearranging yielded state consists of crystal clusters separated by melted regions; in contrast, the solid state remains amorphous and absorbs all imposed shear elastically. We rationalize this transition by uncovering an effective, attractive shear force between rings that emerges from a friction-geometry interplay. If friction is sufficiently high, the extent of the contacts between rings, captured analytically by elementary geometry, controls the rigidity transition.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.