Islamic Azad University Mashhad Branch
 University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad Branch
University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad BranchEpileptic seizures are one of the most crucial neurological disorders, and their early diagnosis will help the clinicians to provide accurate treatment for the patients. The electroencephalogram (EEG) signals are widely used for epileptic seizures detection, which provides specialists with substantial information about the functioning of the brain. In this paper, a novel diagnostic procedure using fuzzy theory and deep learning techniques is introduced. The proposed method is evaluated on the Bonn University dataset with six classification combinations and also on the Freiburg dataset. The tunable-Q wavelet transform (TQWT) is employed to decompose the EEG signals into different sub-bands. In the feature extraction step, 13 different fuzzy entropies are calculated from different sub-bands of TQWT, and their computational complexities are calculated to help researchers choose the best set for various tasks. In the following, an autoencoder (AE) with six layers is employed for dimensionality reduction. Finally, the standard adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and also its variants with grasshopper optimization algorithm (ANFIS-GOA), particle swarm optimization (ANFIS-PSO), and breeding swarm optimization (ANFIS-BS) methods are used for classification. Using our proposed method, ANFIS-BS method has obtained an accuracy of 99.74% in classifying into two classes and an accuracy of 99.46% in ternary classification on the Bonn dataset and 99.28% on the Freiburg dataset, reaching state-of-the-art performances on both of them.
 University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad Branch
University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad BranchEpileptic seizures are one of the most crucial neurological disorders, and their early diagnosis will help the clinicians to provide accurate treatment for the patients. The electroencephalogram (EEG) signals are widely used for epileptic seizures detection, which provides specialists with substantial information about the functioning of the brain. In this paper, a novel diagnostic procedure using fuzzy theory and deep learning techniques is introduced. The proposed method is evaluated on the Bonn University dataset with six classification combinations and also on the Freiburg dataset. The tunable-Q wavelet transform (TQWT) is employed to decompose the EEG signals into different sub-bands. In the feature extraction step, 13 different fuzzy entropies are calculated from different sub-bands of TQWT, and their computational complexities are calculated to help researchers choose the best set for various tasks. In the following, an autoencoder (AE) with six layers is employed for dimensionality reduction. Finally, the standard adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and also its variants with grasshopper optimization algorithm (ANFIS-GOA), particle swarm optimization (ANFIS-PSO), and breeding swarm optimization (ANFIS-BS) methods are used for classification. Using our proposed method, ANFIS-BS method has obtained an accuracy of 99.74% in classifying into two classes and an accuracy of 99.46% in ternary classification on the Bonn dataset and 99.28% on the Freiburg dataset, reaching state-of-the-art performances on both of them.
20 Nov 2018
Cancer is the main cause of mortality at the developed countries and is the
second cause of mortality at the developing countries and breast cancer is the
most prevalent malignancy and the first cause of mortality among women of the
world. At the US, 28% of new cancer cases and 15% of mortality caused by that
in 2010 was caused by breast cancer. Moreover, breast cancer is the most common
cancer among Iranian women, which includes 24.4% of overall malignancies and
causes 3.3% of mortalities per 1.000 people. The disease is most spread in
Tehran and including 25.5% of all cancers. According to the mentioned, the
study has tried to assess the effect of nanotechnology in form of a review to
diagnose and treat breast cancer. The method applied in this study is
descriptive analytical method and library method has been used for data
collection purpose. In the data collection method, 45 articles relevant to
structure of types of nanoparticles and their uses in diagnosis, imaging and
medicine delivery systems and breast cancer treatment have been used. Although
there are still some challenges and limitations to use nanoparticles in
medication, it is hope that nanoparticles can make wonderful revolution not
only in oncology, but also in medication in near future. The most underlying
headlines of the present study include mineral nanoparticles, antibodies and
tumor imaging methods. Keywords: magnetic nanoparticles, breast cancer,
nanobody.
23 Sep 2023
Mazucheli et al. (2019) introduced the unit-Gompertz (UG) distribution and studied some of its properties. More specifically, they considered the random variable X =exp(-Y), where Y has the Gompertz distribution. In this paper, we consider the lower k-record values from this distribution. We obtain exact explicit expressions as well as several recurrence relations for the single and product moments of lower k-record values and then we use these results to compute the means, variances and the covariances of the lower k-record values. We make use of these calculated moments to find the best linear unbiased estimators (BLUEs) of the location and scale parameters of the UG distribution. Applying the relation between the BLUE and the best linear invariant estimator (BLIE), we obtain the BLIEs of the location and scale parameters, as well. In addition, based on the observed k-records, we investigate how to obtain the best linear unbiased predictor (BLUP) and best linear invariant predictor (BLIP) for a future k-record value. Confidence intervals for the unknown parameters and prediction intervals for future k-records are also discussed. A simulation study is performed to assess the point and interval estimators and predictors proposed in the paper. The results show that the BLIE and BLIP outperform the BLUE and BLIP, in the sense of mean squared error criterion, respectively. Finally, a real data set pertaining to COVID-19 2-records is analyzed.
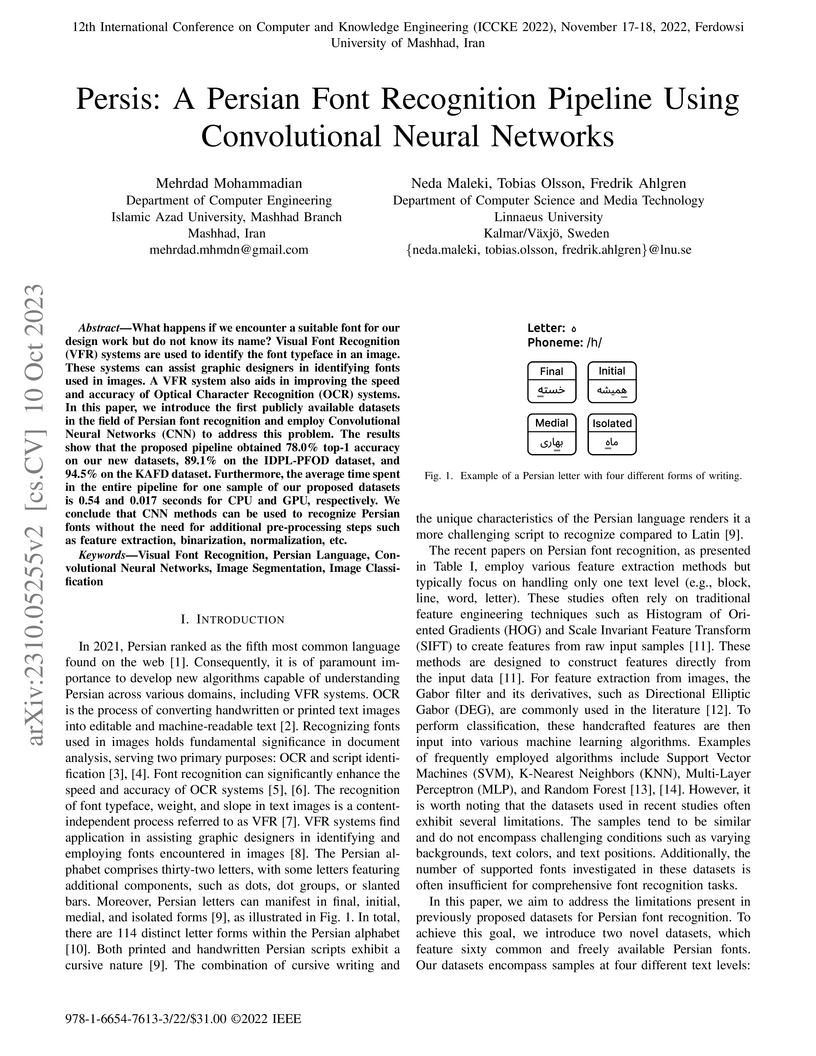
What happens if we encounter a suitable font for our design work but do not
know its name? Visual Font Recognition (VFR) systems are used to identify the
font typeface in an image. These systems can assist graphic designers in
identifying fonts used in images. A VFR system also aids in improving the speed
and accuracy of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems. In this paper, we
introduce the first publicly available datasets in the field of Persian font
recognition and employ Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) to address this
problem. The results show that the proposed pipeline obtained 78.0% top-1
accuracy on our new datasets, 89.1% on the IDPL-PFOD dataset, and 94.5% on the
KAFD dataset. Furthermore, the average time spent in the entire pipeline for
one sample of our proposed datasets is 0.54 and 0.017 seconds for CPU and GPU,
respectively. We conclude that CNN methods can be used to recognize Persian
fonts without the need for additional pre-processing steps such as feature
extraction, binarization, normalization, etc.
Data mining techniques can be used to discover useful patterns by exploring and analyzing data and it's feasible to synergitically combine machine learning tools to discover fuzzy classification this http URL this paper, an adaptive Neuro fuzzy network with TSK fuzzy type and an improved quantum subtractive clustering has been developed. Quantum clustering (QC) is an intuition from quantum mechanics which uses Schrodinger potential and time-consuming gradient descent method. The principle advantage and shortcoming of QC is analyzed and based on its shortcomings, an improved algorithm through a subtractive clustering method is proposed. Cluster centers represent a general model with essential characteristics of data which can be use as premise part of fuzzy this http URL experimental results revealed that proposed Anfis based on quantum subtractive clustering yielded good approximation and generalization capabilities and impressive decrease in the number of fuzzy rules and network output accuracy in comparison with traditional methods.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.