Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz
Reservoir Computing simplifies neural network training by utilizing a fixed, high-dimensional dynamical system (the reservoir) and only training a linear readout layer. This approach enables leveraging the inherent computational capabilities of diverse physical systems, from electronics and photonics to mechanical and quantum systems, offering a practical path for physical artificial intelligence implementations.
We investigate the behaviour of elliptic Feynman integrals under modular
transformations. This has a practical motivation: Through a suitable modular
transformation we can achieve that the nome squared is a small quantity,
leading to fast numerical evaluations. Contrary to the case of multiple
polylogarithms, where it is sufficient to consider just variable
transformations for the numerical evaluations of multiple polylogarithms, it is
more natural in the elliptic case to consider a combination of a variable
transformation (i.e. a modular transformation) together with a redefinition of
the master integrals. Thus we combine a coordinate transformation on the base
manifold with a basis transformation in the fibre. Only in the combination of
the two transformations we stay within the same class of functions.
Researchers developed a systematic procedure to convert high-performance bivariate bicycle (BB) codes, originally defined on a torus, into fully planar quantum low-density parity-check (qLDPC) codes with open boundaries. This approach resulted in codes that maintain excellent resource efficiency, achieving a kd²/n metric of up to 8.34, an order of magnitude higher than the surface code, while being compatible with two-dimensional hardware.
13 Jan 2013
We show that optically encoded two-qubit Bell states can be unambiguously discriminated with a success probability of more than 50% in both single-rail and dual-rail encodings by using active linear-optical resources that include Gaussian squeezing operations. These results are in contrast to the well-known upper bound of 50% for unambiguous discrimination of dual-rail Bell states using passive, static linear optics and arbitrarily many vacuum modes. We present experimentally feasible schemes that improve the success probability to 64.3% in dual-rail and to 62.5% in single-rail for a uniform random distribution of Bell states. Conceptually, this demonstrates that neither interactions that induce nonlinear mode transformations (such as Kerr interactions) nor auxiliary entangled photons are required to go beyond the one-half limit. We discuss the optimality of our single-rail scheme, and talk about an application of our dual-rail scheme in quantum communication.
30 Aug 2023
Quantum error correction codes based on continuous variables play an important role for the implementation of quantum communication systems. A natural application of such codes occurs within quantum repeater systems which are used to combat severe channel losses and local gate errors. In particular, channel loss drastically reduces the distance of communication between remote users. Here we consider a cavity-QED based repeater scheme to address the losses in the quantum channel. This repeater scheme relies on the transmission of a specific class of rotationally invariant error-correcting codes. We compare several rotation-symmetric bosonic codes (RSBCs) being used to encode the initial states of two remote users connected by a quantum repeater network against the convention of the cat codes and we quantify the performance of the system using the secret key rate. In particular, we determine the number of stations required to exchange a secret key over a fixed distance and establish the resource overhead.
12 Apr 2025
We introduce tile codes, a simple yet powerful way of constructing quantum
codes that are local on a planar 2D-lattice. Tile codes generalize the usual
surface code by allowing for a bit more flexibility in terms of locality and
stabilizer weight. Our construction does not compromise on the fact that the
codes are local on a lattice with open boundary conditions. Despite its
simplicity, we use our construction to find codes with parameters $[[288, 8,
12]]usingweight−6stabilizersand[[288, 8, 14]]$ using weight-8
stabilizers, outperforming all previously known constructions in this
direction. Allowing for a slightly higher non-locality, we find a $[[512, 18,
19]]$ code using weight-8 stabilizers, which outperforms the rotated surface
code by a factor of more than 12. Our approach provides a unified framework for
understanding the structure of codes that are local on a 2D planar lattice and
offers a systematic way to explore the space of possible code parameters. In
particular, due to its simplicity, the construction naturally accommodates
various types of boundary conditions and stabilizer configurations, making it a
versatile tool for quantum error correction code design.
A pedagogical review by a team including D. Budker, F. Schmidt-Kaler, and A. Imamoglu critically re-examines the validity of the Lindblad quantum master equation, detailing the limitations of its Born, Markov, and Rotating Wave approximations. It offers a refined understanding, illustrated with examples such as the Kondo model and photonic crystals, to guide its application in emerging fields like open quantum many-body systems and quantum simulation.
We report on three improvements in the context of Feynman integral reduction
and ε-factorised differential equations: Firstly, we show that with
a specific choice of prefactors, we trivialise the ε-dependence of
the integration-by-parts identities. Secondly, we observe that with a specific
choice of order relation in the Laporta algorithm, we directly obtain a basis
of master integrals, whose differential equation on the maximal cut is in
Laurent polynomial form with respect to ε and compatible with a
particular filtration. Thirdly, we prove that such a differential equation can
always be transformed to an ε-factorised form. This provides a
systematic algorithm to obtain an ε-factorised differential
equation for any Feynman integral. Furthermore, the choices for the prefactors
and the order relation significantly improve the efficiency of the reduction
algorithm.
As the study of active matter has developed into one of the most rapidly growing subfields of condensed matter physics, more and more kinds of physical systems have been included in this framework. While the word 'active' is often thought of as referring to self-propelled particles, it is also applied to a large variety of other systems such as non-polar active nematics or certain particles with non-reciprocal interactions. Developing novel forms of active matter, as attempted, e.g., in the framework of quantum active matter, requires a clear idea of what active matter is. Here, we critically discuss how the understanding of active matter has changed over time, what precisely a definition of 'active matter' can look like, and to what extent it is (still) possible to define active matter in a way that covers all systems that are commonly understood as active matter while distinguishing them from other driven systems. Moreover, we discuss the definition of an 'active field theory', where 'active' is used as an attribute of a theoretical model rather than of a physical system. We show that the usage of the term 'active' requires agreement on a coarse-grained viewpoint. We discuss the meaning of 'active' both in general terms and via the specific examples of chemically driven particles, ultrasound-driven particles, active nematics, particles with non-reciprocal interactions, intracellular phase separation, and quantum active matter.
16 Sep 2024
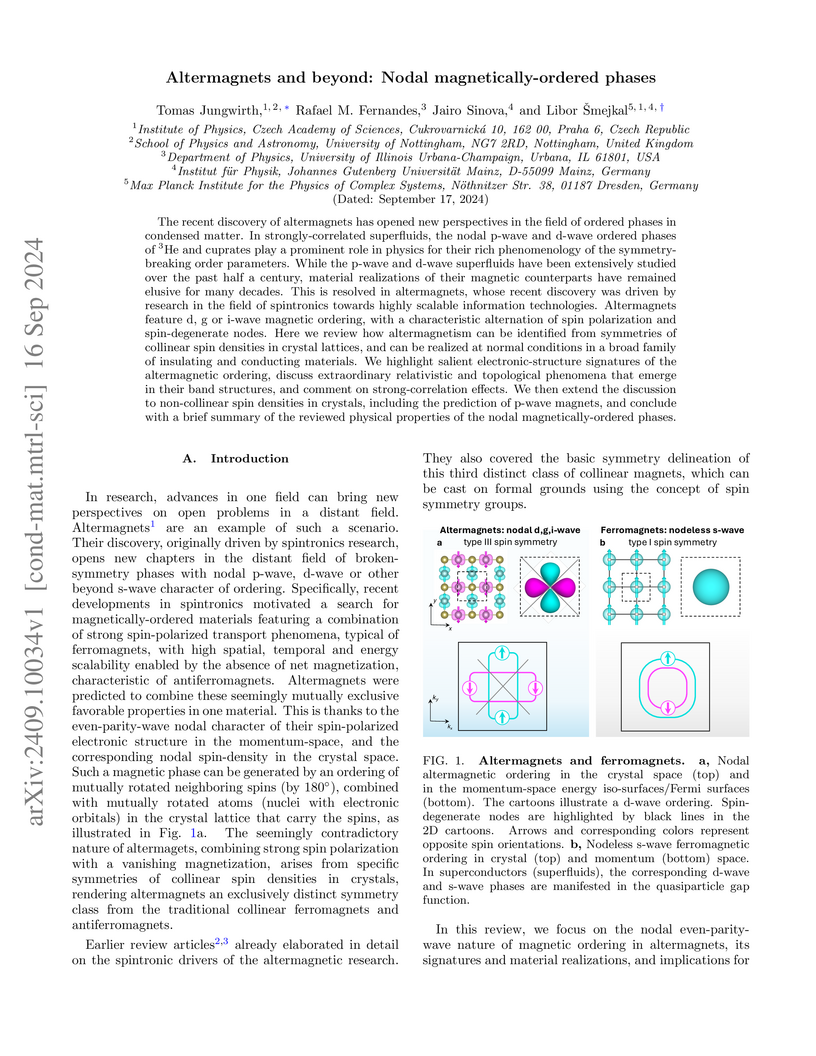
The recent discovery of altermagnets has opened new perspectives in the field of ordered phases in condensed matter. In strongly-correlated superfluids, the nodal p-wave and d-wave ordered phases of 3He and cuprates play a prominent role in physics for their rich phenomenology of the symmetry-breaking order parameters. While the p-wave and d-wave superfluids have been extensively studied over the past half a century, material realizations of their magnetic counterparts have remained elusive for many decades. This is resolved in altermagnets, whose recent discovery was driven by research in the field of spintronics towards highly scalable information technologies. Altermagnets feature d, g or i-wave magnetic ordering, with a characteristic alternation of spin polarization and spin-degenerate nodes. Here we review how altermagnetism can be identified from symmetries of collinear spin densities in crystal lattices, and can be realized at normal conditions in a broad family of insulating and conducting materials. We highlight salient electronic-structure signatures of the altermagnetic ordering, discuss extraordinary relativistic and topological phenomena that emerge in their band structures, and comment on strong-correlation effects. We then extend the discussion to non-collinear spin densities in crystals, including the prediction of p-wave magnets, and conclude with a brief summary of the reviewed physical properties of the nodal magnetically-ordered phases.
Exotic hadrons are a new class of hadronic states whose properties do not
allow them to be classified as conventional quark-antiquark mesons or three
quark baryons. Finding new and understanding established exotic states is the
most important topic in today's hadron spectroscopy and a promising avenue to
advance our knowledge on Quantum Chromodynamics in the non-perturbative regime.
While several high-quality reviews on the topic exist, they are all at an
advanced level. The present article aims to address new-comers to the field
with a simple introduction to exotic hadrons with an emphasis on the
experimental studies.
We show that under mild assumptions, the Fano surfaces of lines on smooth
cubic threefolds are the only smooth subvarieties of abelian varieties whose
Tannaka group for the convolution of perverse sheaves is an exceptional simple
group. This in particular leads to a considerable strengthening of our previous
work on the Shafarevich conjecture. A key idea is to control the Hodge
decomposition on cohomology by a cocharacter of the Tannaka group of Hodge
modules, and to play this off against an improvement of the Hodge number
estimates for irregular varieties by Lazarsfeld-Popa and Lombardi.
 CNRS
CNRS University of AmsterdamUniversity of Zurich
University of AmsterdamUniversity of Zurich New York University
New York University University of ChicagoNikhef
University of ChicagoNikhef Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science
Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Stockholm UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute
Stockholm UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Bologna
Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Bologna Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of Torino
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of Torino University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaIMT AtlantiqueMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikUniversity of CoimbraUniversität FreiburgINFN-TorinoINFN-BolognaWestfälische Wilhelms-Universität MünsterUniversit
de Nantes
University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaIMT AtlantiqueMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikUniversity of CoimbraUniversität FreiburgINFN-TorinoINFN-BolognaWestfälische Wilhelms-Universität MünsterUniversit
de NantesThe XENON Collaboration presents the detailed analysis framework for signal reconstruction, calibration, and event selection from XENONnT's first science run. This work established an ultra-low background level of (15.8 1 1.3) events/(tonne7year7keV) in the (1, 30) keV energy region, marking a five-fold reduction compared to XENON1T.
Quasiparticles are central to condensed matter physics, but their stability can be undermined by quantum many-body interactions. Magnons, quasiparticles in quantum magnets, are particularly intriguing because their properties are governed by both real and spin space. While crystal symmetries may be low, spin interactions often remain approximately isotropic, limiting spontaneous magnon decay. Textbook wisdom holds that collinear Heisenberg magnets follow a dichotomy: ferromagnets host stable magnons, while antiferromagnetic magnons may decay depending on dispersion curvature. Up to now, relativistic spin-orbit coupling and noncollinear order that connect spin space to real space, were shown to introduce more complex magnon instability mechanisms. Here, we show that even in nonrelativistic isotropic collinear systems, this conventional dichotomy is disrupted in altermagnets. Altermagnets, a newly identified class of collinear magnets, exhibit compensated spin order with nonrelativistic time-reversal symmetry breaking and even-parity band splitting. Using kinematic analysis, nonlinear spin-wave theory, and quantum simulations, we reveal that even weak band splitting opens a decay phase space, driving quasiparticle breakdown. Additionally, d-wave altermagnets form a rare ``island of stability'' at the Brillouin zone center. Our findings establish a quasiparticle stability trichotomy in collinear Heisenberg magnets and position altermagnets as a promising platform for unconventional spin dynamics.
First Indication of Solar 8B Neutrinos via Coherent Elastic Neutrino-Nucleus Scattering with XENONnT
First Indication of Solar 8B Neutrinos via Coherent Elastic Neutrino-Nucleus Scattering with XENONnT
 CNRS
CNRS University of AmsterdamUniversity of Zurich
University of AmsterdamUniversity of Zurich New York University
New York University University of ChicagoNikhef
University of ChicagoNikhef Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University INFN
INFN Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science
Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Stockholm UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute
Stockholm UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of BolognaUniversity of Torino
Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of BolognaUniversity of Torino University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaIMT AtlantiqueUniversity of CoimbraUniversität FreiburgUniversity of M̈unsterUniversit
de NantesMax-Planck-Institut f ür Kernphysik
University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaIMT AtlantiqueUniversity of CoimbraUniversität FreiburgUniversity of M̈unsterUniversit
de NantesMax-Planck-Institut f ür KernphysikWe present the first measurement of nuclear recoils from solar 8B neutrinos via coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering with the XENONnT dark matter experiment. The central detector of XENONnT is a low-background, two-phase time projection chamber with a 5.9 t sensitive liquid xenon target. A blind analysis with an exposure of 3.51 t×yr resulted in 37 observed events above 0.5 keV, with (26.4−1.3+1.4) events expected from backgrounds. The background-only hypothesis is rejected with a statistical significance of 2.73 σ. The measured 8B solar neutrino flux of (4.7−2.3+3.6)×106cm−2s−1 is consistent with results from the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory. The measured neutrino flux-weighted CEνNS cross section on Xe of (1.1−0.5+0.8)×10−39cm2 is consistent with the Standard Model prediction. This is the first direct measurement of nuclear recoils from solar neutrinos with a dark matter detector.
11 Oct 2021
We propose two schemes to obtain Gottesman-Kitaev-Preskill (GKP) error syndromes by means of linear optical operations, homodyne measurements and GKP ancillae. This includes showing that for a concatenation of GKP codes with a [n,k,d] stabilizer code only 2n measurements are needed in order to obtain the complete syndrome information, significantly reducing the number of measurements in comparison to the canonical concatenated measurement scheme and at the same time generalizing linear-optics-based syndrome detections to higher GKP codes. Furthermore, we analyze the possibility of building the required ancilla states from single-mode states and linear optics. We find that for simple GKP codes this is possible, whereas for concatenations with qubit Calderbank-Shor-Steane (CSS) codes of distance d≥3 it is not. We also consider the canonical concatenated syndrome measurements and propose methods for avoiding crosstalk between ancillae. In addition, we make use of the observation that the concatenation of a GKP code with a stabilizer code forms a lattice in order to see the analog information decoding of such codes from a different perspective allowing for semi-analytic calculations of the logical error rates.
 University of Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam New York University
New York University University of ChicagoNikhef
University of ChicagoNikhef Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science
Columbia UniversityWeizmann Institute of Science Rice University
Rice University University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Stockholm University
Stockholm University Purdue UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute
Purdue UniversityGran Sasso Science Institute Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Bologna
Sorbonne UniversitéUniversity of Bologna Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of TorinoJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaUniversity of ZürichIMT AtlantiqueCNRS/IN2P3Max-Planck-Institut für KernphysikUniversity of CoimbraINFN NapoliUniversität FreiburgINFN-TorinoINFN-BolognaUniversity of NapoliWestfälische Wilhelms-Universität MünsterUniversit
de NantesUniversit
de Paris
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of TorinoJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzINFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Gran SassoUniversity of L’AquilaUniversity of ZürichIMT AtlantiqueCNRS/IN2P3Max-Planck-Institut für KernphysikUniversity of CoimbraINFN NapoliUniversität FreiburgINFN-TorinoINFN-BolognaUniversity of NapoliWestfälische Wilhelms-Universität MünsterUniversit
de NantesUniversit
de ParisDelayed single- and few-electron emissions plague dual-phase time projection chambers, limiting their potential to search for light-mass dark matter. This paper examines the origins of these events in the XENON1T experiment. Characterization of the intensity of delayed electron backgrounds shows that the resulting emissions are correlated, in time and position, with high-energy events and can effectively be vetoed. In this work we extend previous S2-only analyses down to a single electron. From this analysis, after removing the correlated backgrounds, we observe rates < 30 events/(electron*kg*day) in the region of interest spanning 1 to 5 electrons. We derive 90% confidence upper limits for dark matter-electron scattering, first direct limits on the electric dipole, magnetic dipole, and anapole interactions, and bosonic dark matter models, where we exclude new parameter space for dark photons and solar dark photons.
05 Feb 2025
 CNRS
CNRS University of Maryland
University of Maryland Sorbonne UniversitéÉcole Normale SupérieureJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzUniversity of CaliforniaThe Barcelona Institute of Science and TechnologyICFO - Institut de Ciències FotòniquesGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHJagiellonian University in KrakówHelmholtz-Institut MainzInstitute for Bioengineering of Catalonia
Sorbonne UniversitéÉcole Normale SupérieureJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzUniversity of CaliforniaThe Barcelona Institute of Science and TechnologyICFO - Institut de Ciències FotòniquesGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHJagiellonian University in KrakówHelmholtz-Institut MainzInstitute for Bioengineering of CataloniaZero and ultralow-field nuclear magnetic resonance (ZULF NMR) is an NMR
modality where experiments are performed in fields at which spin-spin
interactions within molecules and materials are stronger than Zeeman
interactions. This typically occurs at external fields of microtesla strength
or below, considerably smaller than Earth's field. In ZULF NMR, the measurement
of spin-spin couplings and spin relaxation rates provides a nondestructive
means for identifying chemicals and chemical fragments, and for conducting
sample or process analyses. The absence of the symmetry imposed by a strong
external magnetic field enables experiments that exploit terms in the nuclear
spin Hamiltonian that are suppressed in high-field NMR, which in turn opens up
new capabilities in a broad range of fields, from the search for dark matter to
the preparation of hyperpolarized contrast agents for clinical imaging.
Furthermore, as in ZULF NMR the Larmor frequencies are typically in the audio
band, the nuclear spins can be manipulated with d.c. magnetic field pulses, and
highly sensitive magnetometers are used for detection. In contrast to
high-field NMR, the low-frequency signals readily pass through conductive
materials such as metals, and heterogeneous samples do not lead to resonance
line broadening, meaning that high-resolution spectroscopy is possible. Notable
practical advantages of ZULF NMR spectroscopy are the low cost and relative
simplicity and portability of the spectrometer system. In recent years ZULF NMR
has become more accessible, thanks to improvements in magnetometer sensitivity
and their commercial availability, and the development of hyperpolarization
methods that provide a simple means to boost signal strengths by several orders
of magnitude. These topics are reviewed and a perspective on potential future
avenues of ZULF-NMR research is presented.
We revisit the extraction of the ∣Vud∣ CKM matrix element from the superallowed transition decay rate of 26mAl→26Mg, focusing on finite nuclear size effects. The decay rate dependence on the 26mAl charge radius is found to be four times higher than previously believed, necessitating precise determination. However, for a short-lived isotope of an odd Z element such as 26mAl, radius extraction relies on challenging many-body atomic calculations. We performed the needed calculations, finding an excellent agreement with previous ones, which used a different methodology. This sets a new standard for the reliability of isotope shift factor calculations in many-electron systems. The Ft value obtained from our analysis is lower by 2.2σ than the corresponding value in the previous critical survey, resulting in an increase in ∣Vud∣2 by 0.9σ. Adopting ∣Vud∣ from this decay alone reduces the CKM unitarity deficit by one standard deviation, irrespective of the choice of ∣Vus∣.
18 Jun 2022
Non-Gaussian states are essential for many optical quantum technologies. The
so-called optical quantum state synthesizer (OQSS), consisting of Gaussian
input states, linear optics, and photon-number resolving detectors, is a
promising method for non-Gaussian state preparation. However, an inevitable and
crucial problem is the complexity of the numerical simulation of the state
preparation on a classical computer. This problem makes it very challenging to
generate important non-Gaussian states required for advanced quantum
information processing. Thus, an efficient method to design OQSS circuits is
highly desirable. To circumvent the problem, we offer a scheme employing a
backcasting approach, where the circuit of OQSS is divided into some sublayers,
and we simulate the OQSS backwards from final to first layers. Moreover, our
results show that the detected photon number by each detector is at most 2,
which can significantly reduce the requirements for the photon-number resolving
detector. By virtue of the potential for the preparation of a wide variety of
non-Gaussian states, the proposed OQSS can be a key ingredient in general
optical quantum information processing.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.