PhiGent Robotics
PhiGent Robotics introduces BEVDet, a multi-camera 3D object detection framework operating entirely in Bird-Eye-View, setting new performance records on the nuScenes benchmark for vision-only methods. It achieves a 39.3% mAP and 47.2% NDS on the nuScenes validation set, surpassing prior state-of-the-art while maintaining high inference efficiency.
SurroundOcc introduces a multi-camera, vision-only method for dense 3D occupancy prediction, achieving state-of-the-art results on nuScenes and SemanticKITTI by accurately reconstructing detailed and occluded scene geometries. A novel pipeline generates dense 3D occupancy ground truth by stitching multi-frame LiDAR data and applying Poisson reconstruction, addressing the critical data annotation bottleneck.
GaussianFormer, developed by Huang et al., predicts 3D semantic occupancy from multi-view images by representing scenes as adaptive 3D Gaussian distributions. This approach significantly reduces memory consumption by 75-82% compared to state-of-the-art voxel-based methods while maintaining comparable performance on the nuScenes dataset, achieving an mIoU of 32.5%.
GaussianFormer-2 introduces a probabilistic Gaussian superposition model for efficient 3D semantic occupancy prediction in autonomous driving, achieving state-of-the-art performance on nuScenes and KITTI-360 datasets while using significantly fewer Gaussians—as low as 8.9% of its predecessor—and reducing memory consumption.
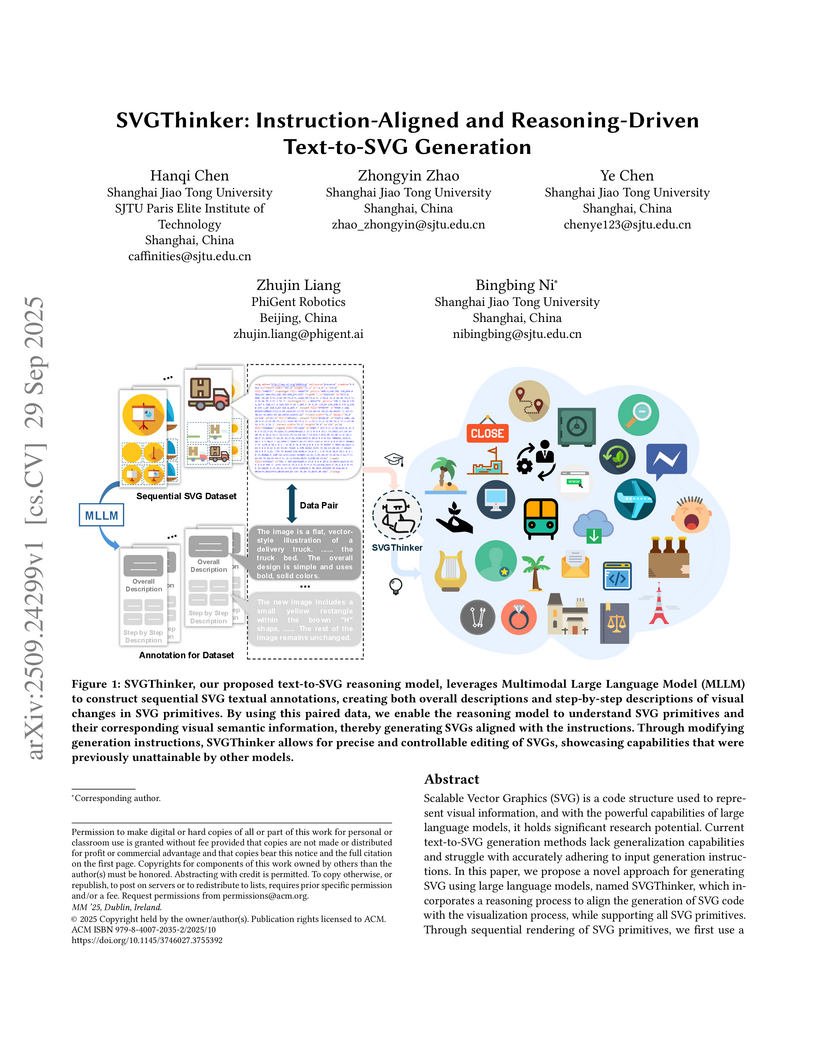
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is a code-based representation for 2D visuals. Leveraging recent advances in large language models (LLMs), we study text-to-SVG generation and address two persistent gaps: weak generalization and poor adherence to input instructions. We present SVGThinker, a reasoning-driven framework that aligns the production of SVG code with the visualization process and supports the full set of SVG primitives. Our pipeline first renders each primitive in sequence and uses a multimodal model to annotate the image and code; we then build stepwise updates that mirror the incremental addition of primitives. On this data, we train an LLM with supervised fine-tuning that exposes its chain-of-thought as intermediate reasoning, improving robustness and reducing errors and hallucinations. Experiments against state-of-the-art baselines show that SVGThinker produces more stable, editable, and higher-quality SVGs while preserving the structural advantages of vector graphics. Unlike image-based methods, our outputs enable precise and hierarchical editing, opening new directions for design, content creation, and automated graphics generation.
PhiGent Robotics researchers developed BEVDet4D, a multi-camera 3D object detection framework that integrates temporal cues from adjacent frames, demonstrating highly accurate velocity estimation that is competitive with LiDAR-based systems. The method achieves a 62.9% reduction in velocity error and sets new state-of-the-art NDS on the nuScenes benchmark.
DrivingRecon is the first feed-forward 4D Gaussian reconstruction model specifically for surround-view driving scenes, enabling rapid, photorealistic generation of dynamic environments for autonomous driving. It achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis and reconstruction for both static and dynamic elements, while also demonstrating utility for unsupervised pre-training, vehicle adaptation, and scene editing capabilities.
OccScene introduces a mutual learning paradigm that unifies text-driven 3D scene generation and semantic occupancy prediction within a single diffusion framework, leading to improved perceptual accuracy and higher-fidelity, consistent 3D scene outputs for both indoor and outdoor environments.
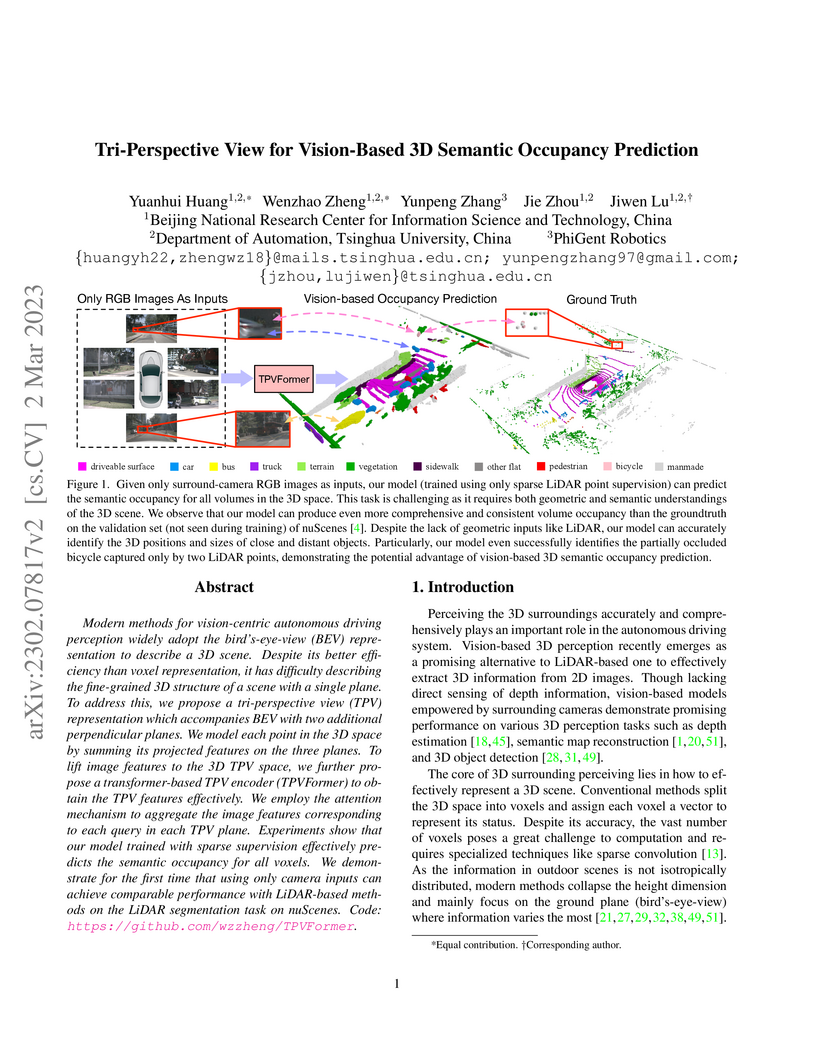
Modern methods for vision-centric autonomous driving perception widely adopt
the bird's-eye-view (BEV) representation to describe a 3D scene. Despite its
better efficiency than voxel representation, it has difficulty describing the
fine-grained 3D structure of a scene with a single plane. To address this, we
propose a tri-perspective view (TPV) representation which accompanies BEV with
two additional perpendicular planes. We model each point in the 3D space by
summing its projected features on the three planes. To lift image features to
the 3D TPV space, we further propose a transformer-based TPV encoder
(TPVFormer) to obtain the TPV features effectively. We employ the attention
mechanism to aggregate the image features corresponding to each query in each
TPV plane. Experiments show that our model trained with sparse supervision
effectively predicts the semantic occupancy for all voxels. We demonstrate for
the first time that using only camera inputs can achieve comparable performance
with LiDAR-based methods on the LiDAR segmentation task on nuScenes. Code:
https://github.com/wzzheng/TPVFormer.
Tsinghua University and industry researchers introduce G²Editor, a framework that leverages a hybrid approach of diffusion models and 3D Gaussian Splatting for realistic and controllable 3D object editing in driving videos. It achieves precise 3D object pose control and high visual fidelity across repositioning, insertion, and deletion tasks, improving downstream autonomous driving perception model performance.
Researchers introduce OpenOccupancy, a large-scale, multi-modal benchmark for surrounding semantic occupancy perception in autonomous driving, which extends the nuScenes dataset with dense annotations. They also propose the Cascade Occupancy Network (CONet), an efficient coarse-to-fine architecture that achieves high-resolution 3D predictions by refining only relevant occupied regions.
4D driving simulation is essential for developing realistic autonomous driving simulators. Despite advancements in existing methods for generating driving scenes, significant challenges remain in view transformation and spatial-temporal dynamic modeling. To address these limitations, we propose a Spatial-Temporal simulAtion for drivinG (Stag-1) model to reconstruct real-world scenes and design a controllable generative network to achieve 4D simulation. Stag-1 constructs continuous 4D point cloud scenes using surround-view data from autonomous vehicles. It decouples spatial-temporal relationships and produces coherent keyframe videos. Additionally, Stag-1 leverages video generation models to obtain photo-realistic and controllable 4D driving simulation videos from any perspective. To expand the range of view generation, we train vehicle motion videos based on decomposed camera poses, enhancing modeling capabilities for distant scenes. Furthermore, we reconstruct vehicle camera trajectories to integrate 3D points across consecutive views, enabling comprehensive scene understanding along the temporal dimension. Following extensive multi-level scene training, Stag-1 can simulate from any desired viewpoint and achieve a deep understanding of scene evolution under static spatial-temporal conditions. Compared to existing methods, our approach shows promising performance in multi-view scene consistency, background coherence, and accuracy, and contributes to the ongoing advancements in realistic autonomous driving simulation. Code: this https URL.
Remarkable advances in recent 2D image and 3D shape generation have induced a significant focus on dynamic 4D content generation. However, previous 4D generation methods commonly struggle to maintain spatial-temporal consistency and adapt poorly to rapid temporal variations, due to the lack of effective spatial-temporal modeling. To address these problems, we propose a novel 4D generation network called 4DSTR, which modulates generative 4D Gaussian Splatting with spatial-temporal rectification. Specifically, temporal correlation across generated 4D sequences is designed to rectify deformable scales and rotations and guarantee temporal consistency. Furthermore, an adaptive spatial densification and pruning strategy is proposed to address significant temporal variations by dynamically adding or deleting Gaussian points with the awareness of their pre-frame movements. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our 4DSTR achieves state-of-the-art performance in video-to-4D generation, excelling in reconstruction quality, spatial-temporal consistency, and adaptation to rapid temporal movements.
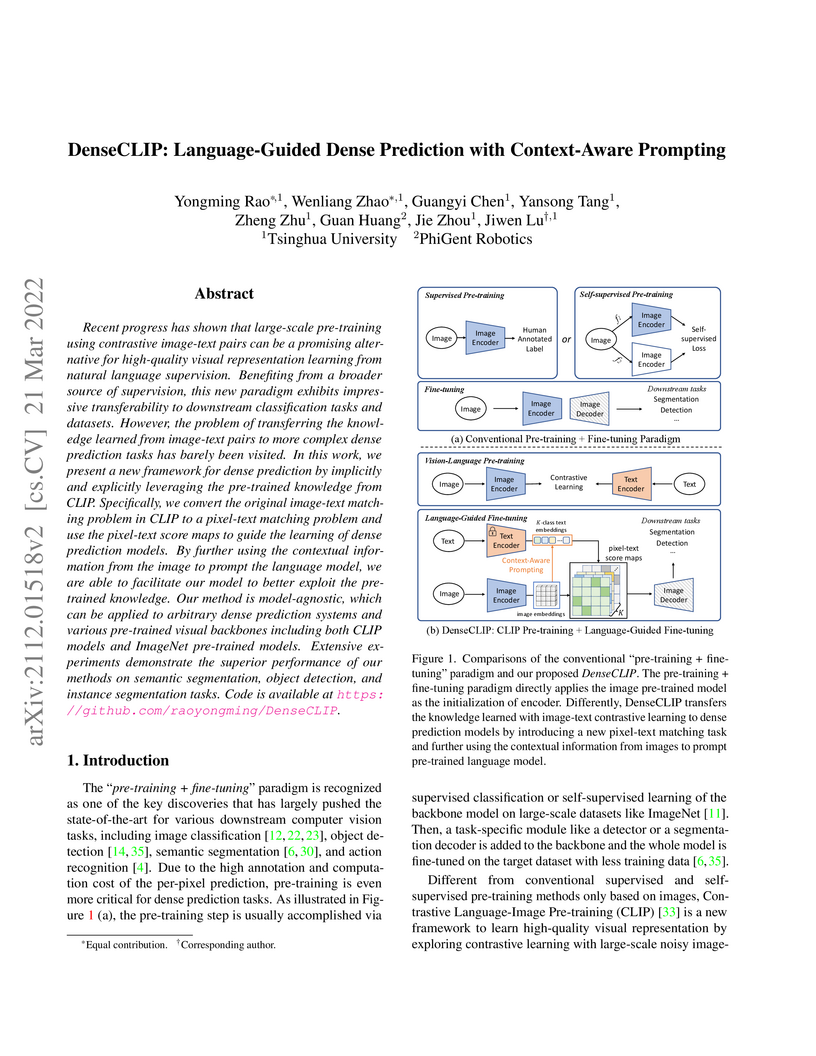
Recent progress has shown that large-scale pre-training using contrastive image-text pairs can be a promising alternative for high-quality visual representation learning from natural language supervision. Benefiting from a broader source of supervision, this new paradigm exhibits impressive transferability to downstream classification tasks and datasets. However, the problem of transferring the knowledge learned from image-text pairs to more complex dense prediction tasks has barely been visited. In this work, we present a new framework for dense prediction by implicitly and explicitly leveraging the pre-trained knowledge from CLIP. Specifically, we convert the original image-text matching problem in CLIP to a pixel-text matching problem and use the pixel-text score maps to guide the learning of dense prediction models. By further using the contextual information from the image to prompt the language model, we are able to facilitate our model to better exploit the pre-trained knowledge. Our method is model-agnostic, which can be applied to arbitrary dense prediction systems and various pre-trained visual backbones including both CLIP models and ImageNet pre-trained models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our methods on semantic segmentation, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks. Code is available at this https URL
Depth estimation from images serves as the fundamental step of 3D perception for autonomous driving and is an economical alternative to expensive depth sensors like LiDAR. The temporal photometric constraints enables self-supervised depth estimation without labels, further facilitating its application. However, most existing methods predict the depth solely based on each monocular image and ignore the correlations among multiple surrounding cameras, which are typically available for modern self-driving vehicles. In this paper, we propose a SurroundDepth method to incorporate the information from multiple surrounding views to predict depth maps across cameras. Specifically, we employ a joint network to process all the surrounding views and propose a cross-view transformer to effectively fuse the information from multiple views. We apply cross-view self-attention to efficiently enable the global interactions between multi-camera feature maps. Different from self-supervised monocular depth estimation, we are able to predict real-world scales given multi-camera extrinsic matrices. To achieve this goal, we adopt the two-frame structure-from-motion to extract scale-aware pseudo depths to pretrain the models. Further, instead of predicting the ego-motion of each individual camera, we estimate a universal ego-motion of the vehicle and transfer it to each view to achieve multi-view ego-motion consistency. In experiments, our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the challenging multi-camera depth estimation datasets DDAD and nuScenes.
BEVerse introduces a unified framework for vision-centric autonomous driving, integrating 3D perception and motion prediction from multi-camera inputs within a Birds-Eye-View representation. The system yields performance improvements on tasks like 3D object detection, semantic map construction, and motion prediction on the nuScenes dataset, alongside notable gains in computational efficiency compared to sequential approaches.
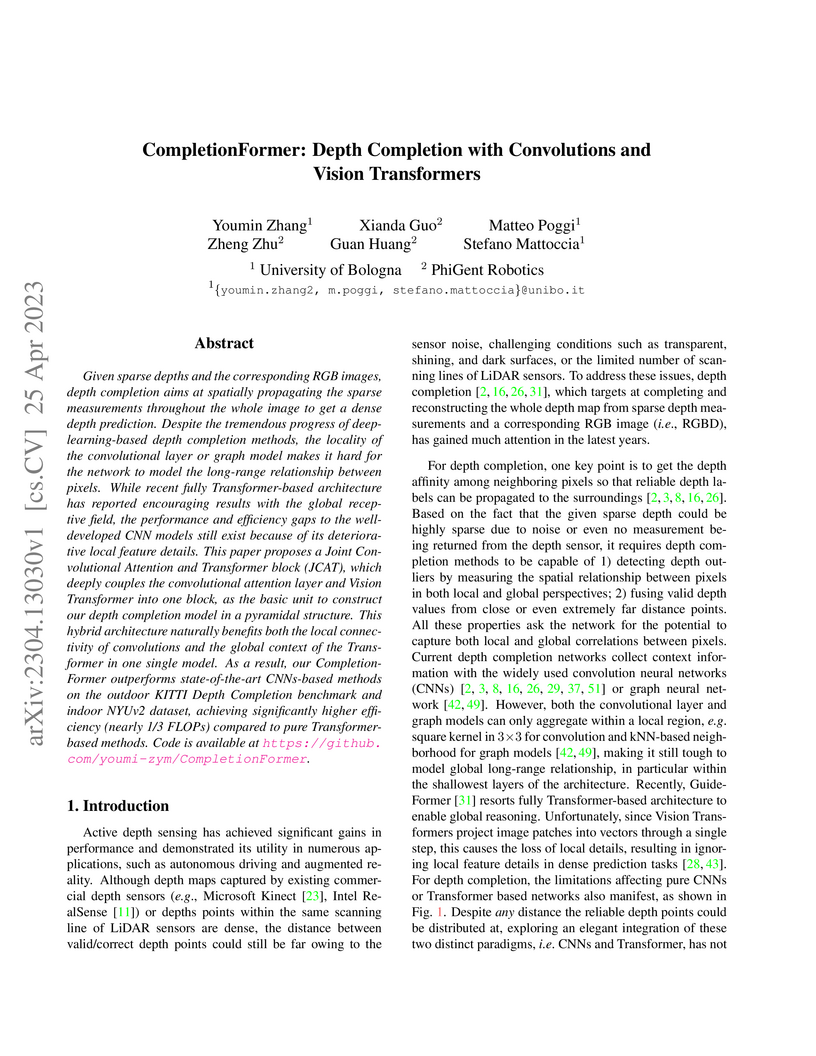
CompletionFormer presents a single-branch, hybrid convolutional and Vision Transformer architecture for dense depth map prediction from sparse measurements. This model effectively integrates local feature extraction with global context reasoning, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the KITTI Depth Completion and NYUv2 datasets while demonstrating improved computational efficiency.
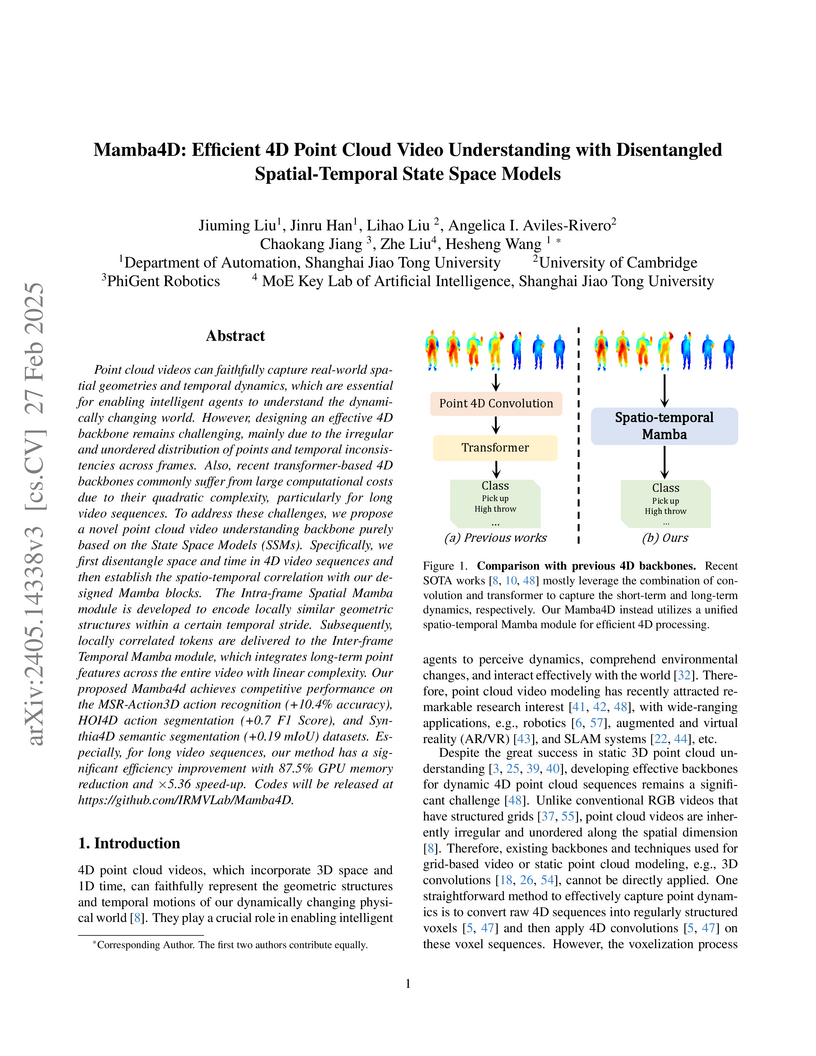
Point cloud videos can faithfully capture real-world spatial geometries and
temporal dynamics, which are essential for enabling intelligent agents to
understand the dynamically changing world. However, designing an effective 4D
backbone remains challenging, mainly due to the irregular and unordered
distribution of points and temporal inconsistencies across frames. Also, recent
transformer-based 4D backbones commonly suffer from large computational costs
due to their quadratic complexity, particularly for long video sequences. To
address these challenges, we propose a novel point cloud video understanding
backbone purely based on the State Space Models (SSMs). Specifically, we first
disentangle space and time in 4D video sequences and then establish the
spatio-temporal correlation with our designed Mamba blocks. The Intra-frame
Spatial Mamba module is developed to encode locally similar geometric
structures within a certain temporal stride. Subsequently, locally correlated
tokens are delivered to the Inter-frame Temporal Mamba module, which integrates
long-term point features across the entire video with linear complexity. Our
proposed Mamba4d achieves competitive performance on the MSR-Action3D action
recognition (+10.4% accuracy), HOI4D action segmentation (+0.7 F1 Score), and
Synthia4D semantic segmentation (+0.19 mIoU) datasets. Especially, for long
video sequences, our method has a significant efficiency improvement with 87.5%
GPU memory reduction and 5.36 times speed-up. Codes will be released at
this https URL
Dataset condensation aims at reducing the network training effort through condensing a cumbersome training set into a compact synthetic one. State-of-the-art approaches largely rely on learning the synthetic data by matching the gradients between the real and synthetic data batches. Despite the intuitive motivation and promising results, such gradient-based methods, by nature, easily overfit to a biased set of samples that produce dominant gradients, and thus lack global supervision of data distribution. In this paper, we propose a novel scheme to Condense dataset by Aligning FEatures (CAFE), which explicitly attempts to preserve the real-feature distribution as well as the discriminant power of the resulting synthetic set, lending itself to strong generalization capability to various architectures. At the heart of our approach is an effective strategy to align features from the real and synthetic data across various scales, while accounting for the classification of real samples. Our scheme is further backed up by a novel dynamic bi-level optimization, which adaptively adjusts parameter updates to prevent over-/under-fitting. We validate the proposed CAFE across various datasets, and demonstrate that it generally outperforms the state of the art: on the SVHN dataset, for example, the performance gain is up to 11%. Extensive experiments and analyses verify the effectiveness and necessity of proposed designs.
GraphAD introduces an Interaction Scene Graph (ISG) into an end-to-end autonomous driving framework to explicitly model complex, heterogeneous interactions between agents and map elements. This approach achieved state-of-the-art results on the nuScenes benchmark, notably reducing the collision rate by 42.9% and improving motion prediction (minADE 0.68m) and object tracking (AMOTA 0.397).
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.