South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute
Anomaly detection with weakly supervised video-level labels is typically formulated as a multiple instance learning (MIL) problem, in which we aim to identify snippets containing abnormal events, with each video represented as a bag of video snippets. Although current methods show effective detection performance, their recognition of the positive instances, i.e., rare abnormal snippets in the abnormal videos, is largely biased by the dominant negative instances, especially when the abnormal events are subtle anomalies that exhibit only small differences compared with normal events. This issue is exacerbated in many methods that ignore important video temporal dependencies. To address this issue, we introduce a novel and theoretically sound method, named Robust Temporal Feature Magnitude learning (RTFM), which trains a feature magnitude learning function to effectively recognise the positive instances, substantially improving the robustness of the MIL approach to the negative instances from abnormal videos. RTFM also adapts dilated convolutions and self-attention mechanisms to capture long- and short-range temporal dependencies to learn the feature magnitude more faithfully. Extensive experiments show that the RTFM-enabled MIL model (i) outperforms several state-of-the-art methods by a large margin on four benchmark data sets (ShanghaiTech, UCF-Crime, XD-Violence and UCSD-Peds) and (ii) achieves significantly improved subtle anomaly discriminability and sample efficiency. Code is available at this https URL.
A memory-augmented multi-level cross-attentional masked autoencoder (MemMC-MAE) is introduced for unsupervised anomaly detection in medical images, designed to ensure high reconstruction error for anomalous regions. The model achieves state-of-the-art results, including a 10.4% AUC increase on Pneumonia Chest X-ray and 17.1% AUC increase on Covid-X datasets, while also improving anomaly localization by 4.7% IoU on Hyper-Kvasir compared to previous methods.
Contrastive Transformer-based Multiple Instance Learning for Weakly Supervised Polyp Frame Detection
Contrastive Transformer-based Multiple Instance Learning for Weakly Supervised Polyp Frame Detection
Current polyp detection methods from colonoscopy videos use exclusively normal (i.e., healthy) training images, which i) ignore the importance of temporal information in consecutive video frames, and ii) lack knowledge about the polyps. Consequently, they often have high detection errors, especially on challenging polyp cases (e.g., small, flat, or partially visible polyps). In this work, we formulate polyp detection as a weakly-supervised anomaly detection task that uses video-level labelled training data to detect frame-level polyps. In particular, we propose a novel convolutional transformer-based multiple instance learning method designed to identify abnormal frames (i.e., frames with polyps) from anomalous videos (i.e., videos containing at least one frame with polyp). In our method, local and global temporal dependencies are seamlessly captured while we simultaneously optimise video and snippet-level anomaly scores. A contrastive snippet mining method is also proposed to enable an effective modelling of the challenging polyp cases. The resulting method achieves a detection accuracy that is substantially better than current state-of-the-art approaches on a new large-scale colonoscopy video dataset introduced in this work.
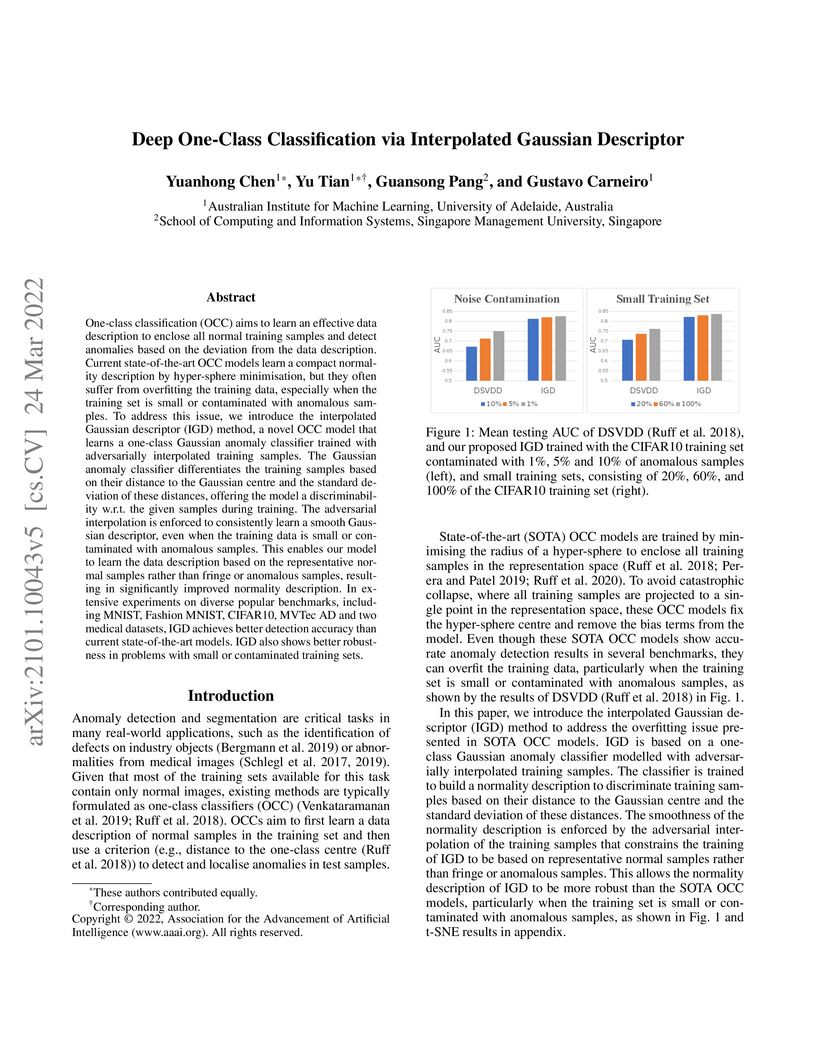
One-class classification (OCC) aims to learn an effective data description to enclose all normal training samples and detect anomalies based on the deviation from the data description. Current state-of-the-art OCC models learn a compact normality description by hyper-sphere minimisation, but they often suffer from overfitting the training data, especially when the training set is small or contaminated with anomalous samples. To address this issue, we introduce the interpolated Gaussian descriptor (IGD) method, a novel OCC model that learns a one-class Gaussian anomaly classifier trained with adversarially interpolated training samples. The Gaussian anomaly classifier differentiates the training samples based on their distance to the Gaussian centre and the standard deviation of these distances, offering the model a discriminability w.r.t. the given samples during training. The adversarial interpolation is enforced to consistently learn a smooth Gaussian descriptor, even when the training data is small or contaminated with anomalous samples. This enables our model to learn the data description based on the representative normal samples rather than fringe or anomalous samples, resulting in significantly improved normality description. In extensive experiments on diverse popular benchmarks, including MNIST, Fashion MNIST, CIFAR10, MVTec AD and two medical datasets, IGD achieves better detection accuracy than current state-of-the-art models. IGD also shows better robustness in problems with small or contaminated training sets. Code is available at this https URL.
Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is used extensively in the diagnosis and
management of cardiovascular disease. Deep learning methods have proven to
deliver segmentation results comparable to human experts in CMR imaging, but
there have been no convincing results for the problem of end-to-end
segmentation and diagnosis from CMR. This is in part due to a lack of
sufficiently large datasets required to train robust diagnosis models. In this
paper, we propose a learning method to train diagnosis models, where our
approach is designed to work with relatively small datasets. In particular, the
optimisation loss is based on multi-task learning that jointly trains for the
tasks of segmentation and diagnosis classification. We hypothesize that
segmentation has a regularizing effect on the learning of features relevant for
diagnosis. Using the 100 training and 50 testing samples available from the
Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) dataset, which has a balanced
distribution of 5 cardiac diagnoses, we observe a reduction of the
classification error from 32% to 22%, and a faster convergence compared to a
baseline without segmentation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the best
diagnosis results from CMR using an end-to-end diagnosis and segmentation
learning method.
The training of deep learning models generally requires a large amount of annotated data for effective convergence and generalisation. However, obtaining high-quality annotations is a laboursome and expensive process due to the need of expert radiologists for the labelling task. The study of semi-supervised learning in medical image analysis is then of crucial importance given that it is much less expensive to obtain unlabelled images than to acquire images labelled by expert radiologists. Essentially, semi-supervised methods leverage large sets of unlabelled data to enable better training convergence and generalisation than using only the small set of labelled images. In this paper, we propose Self-supervised Mean Teacher for Semi-supervised (S2MTS2) learning that combines self-supervised mean-teacher pre-training with semi-supervised fine-tuning. The main innovation of S2MTS2 is the self-supervised mean-teacher pre-training based on the joint contrastive learning, which uses an infinite number of pairs of positive query and key features to improve the mean-teacher representation. The model is then fine-tuned using the exponential moving average teacher framework trained with semi-supervised learning. We validate S2MTS2 on the multi-label classification problems from Chest X-ray14 and CheXpert, and the multi-class classification from ISIC2018, where we show that it outperforms the previous SOTA semi-supervised learning methods by a large margin.
Segmentation of cerebral blood vessels from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an open problem that could be solved with deep learning (DL). However, annotated data for training is often scarce. Due to the absence of open-source tools, we aim to develop a classical segmentation method that generates vessel ground truth from Magnetic Resonance Angiography for DL training of segmentation across a variety of modalities. The method combines size-specific Hessian filters, hysteresis thresholding and connected component correction. The optimal choice of processing steps was evaluated with a blinded scoring by a clinician using 24 3D images. The results show that all method steps are necessary to produce the highest (14.2/15) vessel segmentation quality score. Omitting the connected component correction caused the largest quality loss. The method, which is available on GitHub, can be used to train DL models for vessel segmentation.
Organ at risk (OAR) segmentation is a critical process in radiotherapy treatment planning such as head and neck tumors. Nevertheless, in clinical practice, radiation oncologists predominantly perform OAR segmentations manually on CT scans. This manual process is highly time-consuming and expensive, limiting the number of patients who can receive timely radiotherapy. Additionally, CT scans offer lower soft-tissue contrast compared to MRI. Despite MRI providing superior soft-tissue visualization, its time-consuming nature makes it infeasible for real-time treatment planning. To address these challenges, we propose a method called SegReg, which utilizes Elastic Symmetric Normalization for registering MRI to perform OAR segmentation. SegReg outperforms the CT-only baseline by 16.78% in mDSC and 18.77% in mIoU, showing that it effectively combines the geometric accuracy of CT with the superior soft-tissue contrast of MRI, making accurate automated OAR segmentation for clinical practice become possible. See project website this https URL
Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) methods are trained with normal (or healthy) images only, but during testing, they are able to classify normal and abnormal (or disease) images. UAD is an important medical image analysis (MIA) method to be applied in disease screening problems because the training sets available for those problems usually contain only normal images. However, the exclusive reliance on normal images may result in the learning of ineffective low-dimensional image representations that are not sensitive enough to detect and segment unseen abnormal lesions of varying size, appearance, and shape. Pre-training UAD methods with self-supervised learning, based on computer vision techniques, can mitigate this challenge, but they are sub-optimal because they do not explore domain knowledge for designing the pretext tasks, and their contrastive learning losses do not try to cluster the normal training images, which may result in a sparse distribution of normal images that is ineffective for anomaly detection. In this paper, we propose a new self-supervised pre-training method for MIA UAD applications, named Pseudo Multi-class Strong Augmentation via Contrastive Learning (PMSACL). PMSACL consists of a novel optimisation method that contrasts a normal image class from multiple pseudo classes of synthesised abnormal images, with each class enforced to form a dense cluster in the feature space. In the experiments, we show that our PMSACL pre-training improves the accuracy of SOTA UAD methods on many MIA benchmarks using colonoscopy, fundus screening and Covid-19 Chest X-ray datasets. The code is made publicly available via this https URL.
Gliomas appear with wide variation in their characteristics both in terms of
their appearance and location on brain MR images, which makes robust tumour
segmentation highly challenging, and leads to high inter-rater variability even
in manual segmentations. In this work, we propose a triplanar ensemble network,
with an independent tumour core prediction module, for accurate segmentation of
these tumours and their sub-regions. On evaluating our method on the MICCAI
Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge validation dataset, for tumour
sub-regions, we achieved a Dice similarity coefficient of 0.77 for both
enhancing tumour (ET) and tumour core (TC). In the case of the whole tumour
(WT) region, we achieved a Dice value of 0.89, which is on par with the
top-ranking methods from BraTS'17-19. Our method achieved an evaluation score
that was the equal 5th highest value (with our method ranking in 10th place) in
the BraTS'20 challenge, with mean Dice values of 0.81, 0.89 and 0.84 on ET, WT
and TC regions respectively on the BraTS'20 unseen test dataset.
Many applications in image-guided surgery and therapy require fast and
reliable non-linear, multi-modal image registration. Recently proposed
unsupervised deep learning-based registration methods have demonstrated
superior performance compared to iterative methods in just a fraction of the
time. Most of the learning-based methods have focused on mono-modal image
registration. The extension to multi-modal registration depends on the use of
an appropriate similarity function, such as the mutual information (MI). We
propose guiding the training of a deep learning-based registration method with
MI estimation between an image-pair in an end-to-end trainable network. Our
results show that a small, 2-layer network produces competitive results in both
mono- and multi-modal registration, with sub-second run-times. Comparisons to
both iterative and deep learning-based methods show that our MI-based method
produces topologically and qualitatively superior results with an extremely low
rate of non-diffeomorphic transformations. Real-time clinical application will
benefit from a better visual matching of anatomical structures and less
registration failures/outliers.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.