Upwork
24 Oct 2025
Generative recommendation is emerging as a transformative paradigm by directly generating recommended items, rather than relying on matching. Building such a system typically involves two key components: (1) optimizing the tokenizer to derive suitable item identifiers, and (2) training the recommender based on those identifiers. Existing approaches often treat these components separately--either sequentially or in alternation--overlooking their interdependence. This separation can lead to misalignment: the tokenizer is trained without direct guidance from the recommendation objective, potentially yielding suboptimal identifiers that degrade recommendation performance.
To address this, we propose BLOGER, a Bi-Level Optimization for GEnerative Recommendation framework, which explicitly models the interdependence between the tokenizer and the recommender in a unified optimization process. The lower level trains the recommender using tokenized sequences, while the upper level optimizes the tokenizer based on both the tokenization loss and recommendation loss. We adopt a meta-learning approach to solve this bi-level optimization efficiently, and introduce gradient surgery to mitigate gradient conflicts in the upper-level updates, thereby ensuring that item identifiers are both informative and recommendation-aligned. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that BLOGER consistently outperforms state-of-the-art generative recommendation methods while maintaining practical efficiency with no significant additional computational overhead, effectively bridging the gap between item tokenization and autoregressive generation.
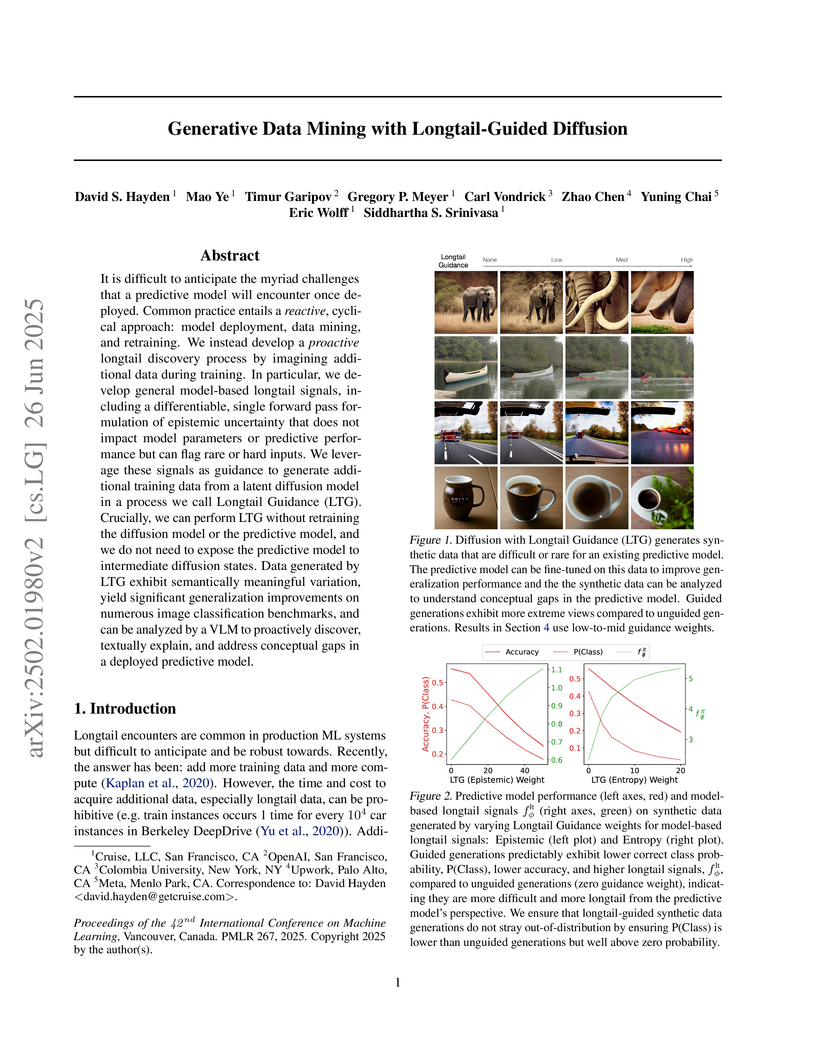
A new framework, Generative Data Mining with Longtail-Guided Diffusion, proactively identifies and addresses "longtail" challenges in deployed machine learning models by using generative models to create synthetic data specifically difficult for existing predictive models, leading to improved generalization and robustness. The method improves rare class accuracy by 10 percentage points (+24%) on ImageNet-LT, using significantly less data than prior approaches.
15 Nov 2025
UpBench is a dynamically evolving framework that uses real, economically verified freelance jobs from Upwork to benchmark AI agents, measuring their performance on authentic tasks through expert human evaluation. It quantifies significant improvements in AI agent completion rates and output quality when human-in-the-loop feedback is integrated.
This paper critically examines the fundamental distinctions between gradient methods applied to non-differentiable functions (NGDMs) and classical gradient descents (GDs) for differentiable functions, revealing significant gaps in current deep learning optimization theory. We demonstrate that NGDMs exhibit markedly different convergence properties compared to GDs, strongly challenging the applicability of extensive neural network convergence literature based on L−smoothness to non-smooth neural networks. Our analysis reveals paradoxical behavior of NDGM solutions for L1-regularized problems, where increasing regularization counterintuitively leads to larger L1 norms of optimal solutions. This finding calls into question widely adopted L1 penalization techniques for network pruning. We further challenge the common assumption that optimization algorithms like RMSProp behave similarly in differentiable and non-differentiable contexts. Expanding on the Edge of Stability phenomenon, we demonstrate its occurrence in a broader class of functions, including Lipschitz continuous convex differentiable functions. This finding raises important questions about its relevance and interpretation in non-convex, non-differentiable neural networks, particularly those using ReLU activations. Our work identifies critical misunderstandings of NDGMs in influential literature, stemming from an overreliance on strong smoothness assumptions. These findings necessitate a reevaluation of optimization dynamics in deep learning, emphasizing the crucial need for more nuanced theoretical foundations in analyzing these complex systems.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.