agentic-frameworks
07 Dec 2025
WisPaper introduces an AI-powered scholar search engine that unifies academic literature discovery, management, and continuous tracking within a single platform. Its core Deep Search component, powered by the WisModel agent, achieved 94.8% semantic similarity in query understanding and 93.70% overall accuracy in paper-criteria matching, demonstrating superior performance over leading commercial LLMs, especially in nuanced judgments.
08 Dec 2025
Researchers from Harvard University and Perplexity conducted a large-scale field study on the real-world adoption and usage of general-purpose AI agents, leveraging hundreds of millions of user interactions with Perplexity's Comet AI-powered browser and its integrated Comet Assistant. The study provides foundational evidence on who uses these agents, their usage intensity, and a detailed breakdown of use cases via a novel hierarchical taxonomy.
09 Dec 2025
The paper empirically investigates the performance of multi-agent LLM systems across diverse agentic tasks and architectures, revealing that benefits are highly contingent on task structure rather than universal. It establishes a quantitative scaling principle, achieving 87% accuracy in predicting optimal agent architectures for unseen tasks based on model capability, task properties, and measured coordination dynamics.
04 Dec 2025
Researchers from Google, NYU, ETH Zurich, and Stanford present a theoretical framework to formalize how large language models perform complex, iterative reasoning. The framework characterizes reasoning "oracles" and algorithms, proving that branching and genetic algorithms can achieve optimal success probabilities for models where oracle accuracy can decay with context size, and explains phenomena like "overthinking."
Edward Y. Chang from Stanford University proposes a "Substrate plus Coordination" framework for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that Large Language Models (LLMs) provide a necessary System-1 pattern-matching substrate that requires a System-2 coordination layer to achieve reliable, goal-directed reasoning. This work formalizes semantic anchoring through the Unified Contextual Control Theory (UCCT) and introduces the Multi-Agent Collaborative Intelligence (MACI) architecture to implement this missing layer.
09 Dec 2025
Large language model (LLM)-based multi-agent systems are challenging to debug because failures often arise from long, branching interaction traces. The prevailing practice is to leverage LLMs for log-based failure localization, attributing errors to a specific agent and step. However, this paradigm has two key limitations: (i) log-only debugging lacks validation, producing untested hypotheses, and (ii) single-step or single-agent attribution is often ill-posed, as we find that multiple distinct interventions can independently repair the failed task. To address the first limitation, we introduce DoVer, an intervention-driven debugging framework, which augments hypothesis generation with active verification through targeted interventions (e.g., editing messages, altering plans). For the second limitation, rather than evaluating on attribution accuracy, we focus on measuring whether the system resolves the failure or makes quantifiable progress toward task success, reflecting a more outcome-oriented view of debugging. Within the Magnetic-One agent framework, on the datasets derived from GAIA and AssistantBench, DoVer flips 18-28% of failed trials into successes, achieves up to 16% milestone progress, and validates or refutes 30-60% of failure hypotheses. DoVer also performs effectively on a different dataset (GSMPlus) and agent framework (AG2), where it recovers 49% of failed trials. These results highlight intervention as a practical mechanism for improving reliability in agentic systems and open opportunities for more robust, scalable debugging methods for LLM-based multi-agent systems. Project website and code will be available at this https URL.
02 Dec 2025
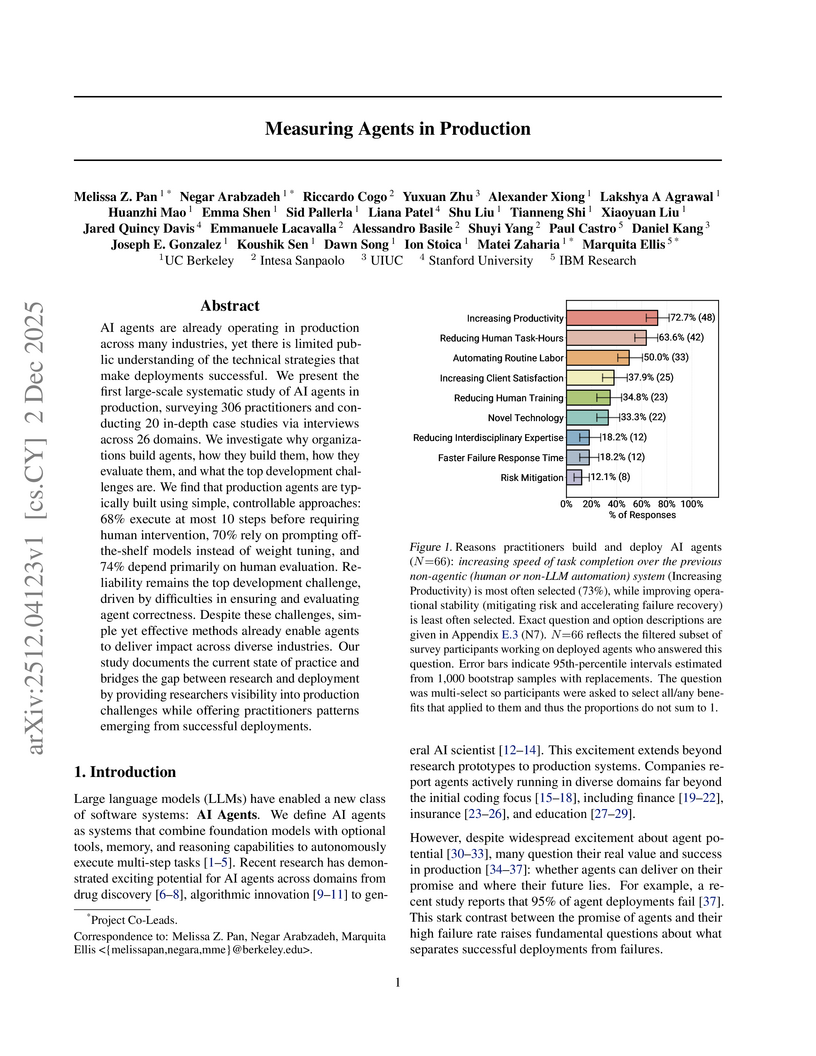
An empirical study surveyed 306 AI agent practitioners and conducted 20 in-depth case studies to analyze the technical strategies, architectural patterns, and challenges of successfully deployed AI agents. The research reveals how real-world production agents prioritize reliability and controlled autonomy to achieve productivity gains across diverse industries.
08 Dec 2025
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have given rise to powerful coding agents, making it possible for code assistants to evolve into code engineers. However, existing methods still face significant challenges in achieving high-fidelity document-to-codebase synthesis--such as scientific papers to code--primarily due to a fundamental conflict between information overload and the context bottlenecks of LLMs. In this work, we introduce DeepCode, a fully autonomous framework that fundamentally addresses this challenge through principled information-flow management. By treating repository synthesis as a channel optimization problem, DeepCode seamlessly orchestrates four information operations to maximize task-relevant signals under finite context budgets: source compression via blueprint distillation, structured indexing using stateful code memory, conditional knowledge injection via retrieval-augmented generation, and closed-loop error correction. Extensive evaluations on the PaperBench benchmark demonstrate that DeepCode achieves state-of-the-art performance, decisively outperforming leading commercial agents such as Cursor and Claude Code, and crucially, surpassing PhD-level human experts from top institutes on key reproduction metrics. By systematically transforming paper specifications into production-grade implementations comparable to human expert quality, this work establishes new foundations for autonomous scientific reproduction that can accelerate research evaluation and discovery.
07 Dec 2025
This research introduces PersonaMem-v2, a dataset designed for implicit user persona learning, and an agentic memory framework, enabling smaller LLMs to achieve state-of-the-art personalization performance. The agentic memory system processes long conversational histories into a compact 2k-token memory, resulting in a 16x efficiency improvement while outperforming frontier models like GPT-5 variants.
05 Dec 2025
Researchers at FAIR at Meta propose a strategic shift from developing autonomous self-improving AI to fostering human-AI co-improvement, aiming for a safer "co-superintelligence" that leverages complementary human and AI strengths. Their framework outlines eleven key collaborative development activities, emphasizing joint research to accelerate discovery while ensuring alignment and safety.
05 Dec 2025
Salesforce AI Research and UNC Chapel Hill developed Active Video Perception (AVP), an iterative evidence-seeking framework for long video understanding that leverages MLLMs in a "Plan–Observe–Reflect" loop. AVP achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across five benchmarks while dramatically reducing inference time by 81.6% and token usage by 87.6% compared to prior agentic methods.
08 Dec 2025
Recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs) have enabled agentic search systems to perform complex multi-step reasoning across multiple sources. However, most studies focus on general information retrieval and rarely explores vertical domains with unique challenges. In this work, we focus on local life services and introduce LocalSearchBench, which encompass diverse and complex business scenarios. Real-world queries in this domain are often ambiguous and require multi-hop reasoning across merchants and products, remaining challenging and not fully addressed. As the first comprehensive benchmark for agentic search in local life services, LocalSearchBench includes over 150,000 high-quality entries from various cities and business types. We construct 300 multi-hop QA tasks based on real user queries, challenging agents to understand questions and retrieve information in multiple steps. We also developed LocalPlayground, a unified environment integrating multiple tools for agent interaction. Experiments show that even state-of-the-art LRMs struggle on LocalSearchBench: the best model (DeepSeek-V3.1) achieves only 34.34% correctness, and most models have issues with completeness (average 77.33%) and faithfulness (average 61.99%). This highlights the need for specialized benchmarks and domain-specific agent training in local life services. Code, Benchmark, and Leaderboard are available at this http URL.
09 Dec 2025
Agentic AI marks a major shift in how autonomous systems reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks. Unlike traditional single model prompting, agentic workflows integrate multiple specialized agents with different Large Language Models(LLMs), tool-augmented capabilities, orchestration logic, and external system interactions to form dynamic pipelines capable of autonomous decision-making and action. As adoption accelerates across industry and research, organizations face a central challenge: how to design, engineer, and operate production-grade agentic AI workflows that are reliable, observable, maintainable, and aligned with safety and governance requirements. This paper provides a practical, end-to-end guide for designing, developing, and deploying production-quality agentic AI systems. We introduce a structured engineering lifecycle encompassing workflow decomposition, multi-agent design patterns, Model Context Protocol(MCP), and tool integration, deterministic orchestration, Responsible-AI considerations, and environment-aware deployment strategies. We then present nine core best practices for engineering production-grade agentic AI workflows, including tool-first design over MCP, pure-function invocation, single-tool and single-responsibility agents, externalized prompt management, Responsible-AI-aligned model-consortium design, clean separation between workflow logic and MCP servers, containerized deployment for scalable operations, and adherence to the Keep it Simple, Stupid (KISS) principle to maintain simplicity and robustness. To demonstrate these principles in practice, we present a comprehensive case study: a multimodal news-analysis and media-generation workflow. By combining architectural guidance, operational patterns, and practical implementation insights, this paper offers a foundational reference to build robust, extensible, and production-ready agentic AI workflows.
09 Dec 2025
Foundation agents have rapidly advanced in their ability to reason and interact with real environments, making the evaluation of their core capabilities increasingly important. While many benchmarks have been developed to assess agent performance, most concentrate on academic settings or artificially designed scenarios while overlooking the challenges that arise in real applications. To address this issue, we focus on a highly practical real-world setting, the e-commerce domain, which involves a large volume of diverse user interactions, dynamic market conditions, and tasks directly tied to real decision-making processes. To this end, we introduce EcomBench, a holistic E-commerce Benchmark designed to evaluate agent performance in realistic e-commerce environments. EcomBench is built from genuine user demands embedded in leading global e-commerce ecosystems and is carefully curated and annotated through human experts to ensure clarity, accuracy, and domain relevance. It covers multiple task categories within e-commerce scenarios and defines three difficulty levels that evaluate agents on key capabilities such as deep information retrieval, multi-step reasoning, and cross-source knowledge integration. By grounding evaluation in real e-commerce contexts, EcomBench provides a rigorous and dynamic testbed for measuring the practical capabilities of agents in modern e-commerce.
08 Dec 2025
Despite impressive advances in agent systems, multi-turn tool-use scenarios remain challenging. It is mainly because intent is clarified progressively and the environment evolves with each tool call. While reusing past experience is natural, current LLM agents either treat entire trajectories or pre-defined subtasks as indivisible units, or solely exploit tool-to-tool dependencies, hindering adaptation as states and information evolve across turns. In this paper, we propose a State Integrated Tool Graph (SIT-Graph), which enhances multi-turn tool use by exploiting partially overlapping experience. Inspired by human decision-making that integrates episodic and procedural memory, SIT-Graph captures both compact state representations (episodic-like fragments) and tool-to-tool dependencies (procedural-like routines) from historical trajectories. Specifically, we first build a tool graph from accumulated tool-use sequences, and then augment each edge with a compact state summary of the dialog and tool history that may shape the next action. At inference time, SIT-Graph enables a human-like balance between episodic recall and procedural execution: when the next decision requires recalling prior context, the agent retrieves the state summaries stored on relevant edges and uses them to guide its next action; when the step is routine, it follows high-confidence tool dependencies without explicit recall. Experiments across multiple stateful multi-turn tool-use benchmarks show that SIT-Graph consistently outperforms strong memory- and graph-based baselines, delivering more robust tool selection and more effective experience transfer.
The Nex-AGI Team developed a unified ecosystem, Nex, for constructing large-scale, diverse, and realistically grounded interactive environments to train autonomous AI agents. Their Nex-N1 models, trained using this infrastructure, demonstrate competitive to superior performance on complex agentic tasks, including coding and deep research, across various benchmarks and real-world evaluations.
08 Dec 2025
Specialized visual tools can augment large language models or vision language models with expert knowledge (e.g., grounding, spatial reasoning, medical knowledge, etc.), but knowing which tools to call (and when to call them) can be challenging. We introduce DART, a multi-agent framework that uses disagreements between multiple debating visual agents to identify useful visual tools (e.g., object detection, OCR, spatial reasoning, etc.) that can resolve inter-agent disagreement. These tools allow for fruitful multi-agent discussion by introducing new information, and by providing tool-aligned agreement scores that highlight agents in agreement with expert tools, thereby facilitating discussion. We utilize an aggregator agent to select the best answer by providing the agent outputs and tool information. We test DART on four diverse benchmarks and show that our approach improves over multi-agent debate as well as over single agent tool-calling frameworks, beating the next-strongest baseline (multi-agent debate with a judge model) by 3.4% and 2.4% on A-OKVQA and MMMU respectively. We also find that DART adapts well to new tools in applied domains, with a 1.3% improvement on the M3D medical dataset over other strong tool-calling, single agent, and multi-agent baselines. Additionally, we measure text overlap across rounds to highlight the rich discussion in DART compared to existing multi-agent methods. Finally, we study the tool call distribution, finding that diverse tools are reliably used to help resolve disagreement.
03 Dec 2025
A new benchmark, DAComp, evaluates large language model (LLM) agents across the full data intelligence lifecycle, integrating repository-level data engineering and open-ended data analysis. Experiments reveal state-of-the-art LLMs struggle with holistic pipeline orchestration and strategic insight synthesis, achieving an aggregated data engineering score of 43.45% and a data analysis score of 50.84% with top models.
08 Dec 2025
Fliggy Alibaba researchers developed Progressive Reward Shaping (PRS) and Value-based Sampling Policy Optimization (VSPO) to improve large language model agents performing Tool-Integrated Reasoning. Their methods provide dense, stage-wise feedback and enhance policy optimization, leading to superior performance on short-form QA (0.419 average EM score with VSPO+PRS) and significant gains on long-form QA, particularly for multi-query tasks.
09 Dec 2025
Modern businesses are increasingly challenged by the time and expense required to generate and assess high-quality content. Human writers face time constraints, and extrinsic evaluations can be costly. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer potential in content creation, concerns about the quality of AI-generated content persist. Traditional evaluation methods, like human surveys, further add operational costs, highlighting the need for efficient, automated solutions. This research introduces Generative Agents as a means to tackle these challenges. These agents can rapidly and cost-effectively evaluate AI-generated content, simulating human judgment by rating aspects such as coherence, interestingness, clarity, fairness, and relevance. By incorporating these agents, businesses can streamline content generation and ensure consistent, high-quality output while minimizing reliance on costly human evaluations. The study provides critical insights into enhancing LLMs for producing business-aligned, high-quality content, offering significant advancements in automated content generation and evaluation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.