knowledge-distillation
08 Dec 2025
The Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) framework allows Large Language Models to autonomously acquire and deploy genuine parallel reasoning capabilities, without relying on external teacher models. Experiments show NPR improves accuracy by up to 24.5% over baselines and delivers up to 4.6 times faster inference, maintaining 100% parallel execution across various benchmarks.
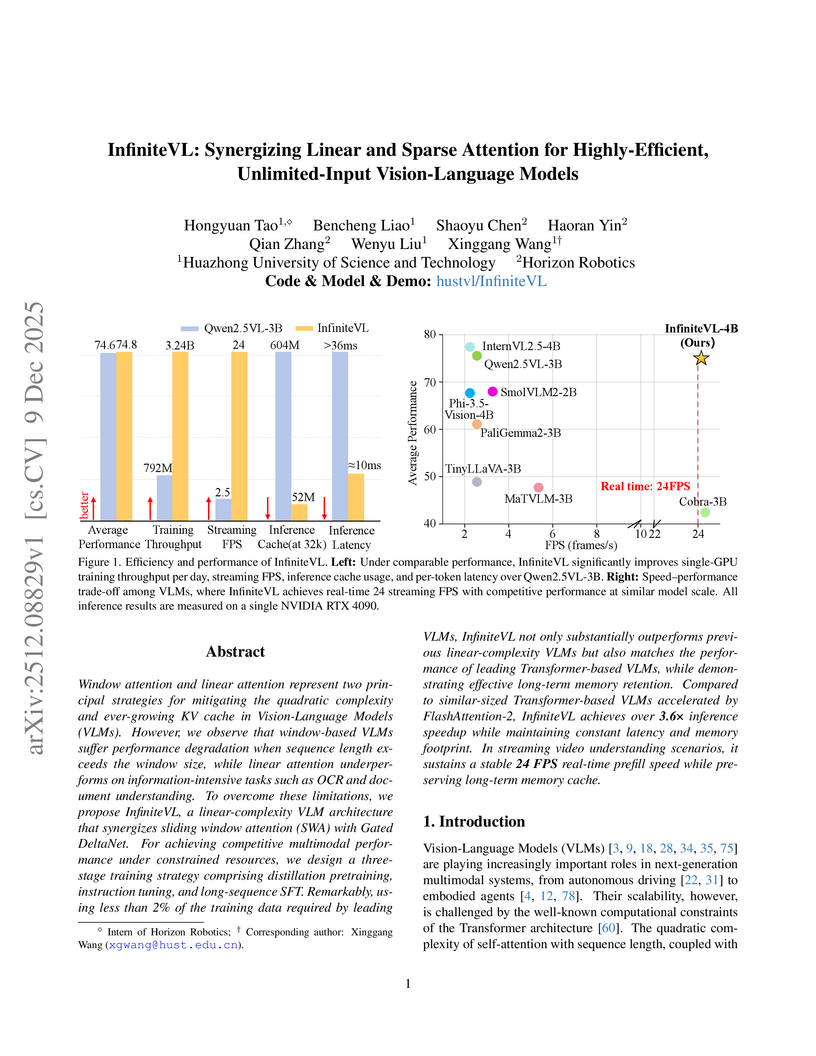
InfiniteVL, a collaboration between Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Horizon Robotics, introduces a hybrid Vision-Language Model that synergizes linear and sparse attention to enable unlimited multimodal input processing with constant latency and memory footprint. The model achieves performance competitive with Transformer-based VLMs on diverse benchmarks, including information-intensive tasks, while demonstrating significant inference speedups and robust real-time streaming capabilities.
Researchers from Cornell University, Google, and UC Berkeley developed Selfi, a framework that refines pre-trained 3D Vision Foundation Model features through self-supervised geometric alignment. It achieves state-of-the-art pose-free novel view synthesis quality and robust camera pose estimation, often rivaling methods requiring ground-truth camera parameters.
Fast-ARDiff introduces an entropy-informed acceleration framework for continuous-space AR-Diffusion hybrid generative models. This framework achieves up to a 4.88x speedup in inference latency with minimal quality degradation by addressing challenges like entropy mismatch in visual speculative decoding and instability in diffusion distillation.
Frontier language model quality increasingly hinges on our ability to organize web-scale text corpora for training. Today's dominant tools trade off speed and flexibility: lexical classifiers (e.g., FastText) are fast but limited to producing classification output scores, while the vector-valued outputs of transformer text embedding models flexibly support numerous workflows (e.g., clustering, classification, and retrieval) but are computationally expensive to produce. We introduce Luxical, a library for high-speed "lexical-dense" text embeddings that aims to recover the best properties of both approaches for web-scale text organization. Luxical combines sparse TF--IDF features, a small ReLU network, and a knowledge distillation training regimen to approximate large transformer embedding models at a fraction of their operational cost. In this technical report, we describe the Luxical architecture and training objective and evaluate a concrete Luxical model in two disparate applications: a targeted webcrawl document retrieval test and an end-to-end language model data curation task grounded in text classification. In these tasks we demonstrate speedups ranging from 3x to 100x over varying-sized neural baselines, and comparable to FastText model inference during the data curation task. On these evaluations, the tested Luxical model illustrates favorable compute/quality trade-offs for large-scale text organization, matching the quality of neural baselines. Luxical is available as open-source software at this https URL.
The Nanbeige4-3B model family from the Nanbeige LLM Lab at Boss Zhipin introduces a 3-billion-parameter language model that consistently outperforms much larger open-source models, setting new state-of-the-art averages in mathematical and scientific reasoning. This performance is achieved through a multi-stage training pipeline incorporating advanced data filtering, a fine-grained learning rate scheduler, dual-level preference distillation, and multi-stage reinforcement learning.
RELIC, an interactive video world model from researchers including those at Adobe Research, enables real-time, memory-aware exploration of diverse scenes for extended durations (up to 20 seconds) from a single image and text prompt. It demonstrates superior visual quality and precise action control compared to state-of-the-art baselines, generalizing across various artistic styles.
Z-Image, a 6-billion parameter image generation foundation model from Alibaba Group, demonstrates high-fidelity image generation, robust bilingual text rendering, and precise image editing while significantly reducing computational costs compared to much larger models. It achieves this by challenging the prevalent 'scale-at-all-costs' paradigm through optimized data, architecture, training, and inference strategies.
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Peking University introduce Fast Flow Joint Distillation (F2D2), a framework that simultaneously achieves accurate, few-step log-likelihood evaluation and efficient sampling in flow-based generative models. F2D2 produces calibrated negative log-likelihoods with as few as 1-8 neural function evaluations (NFEs) while maintaining high sample quality and can even improve FID over high-NFE teacher models through maximum likelihood self-guidance.
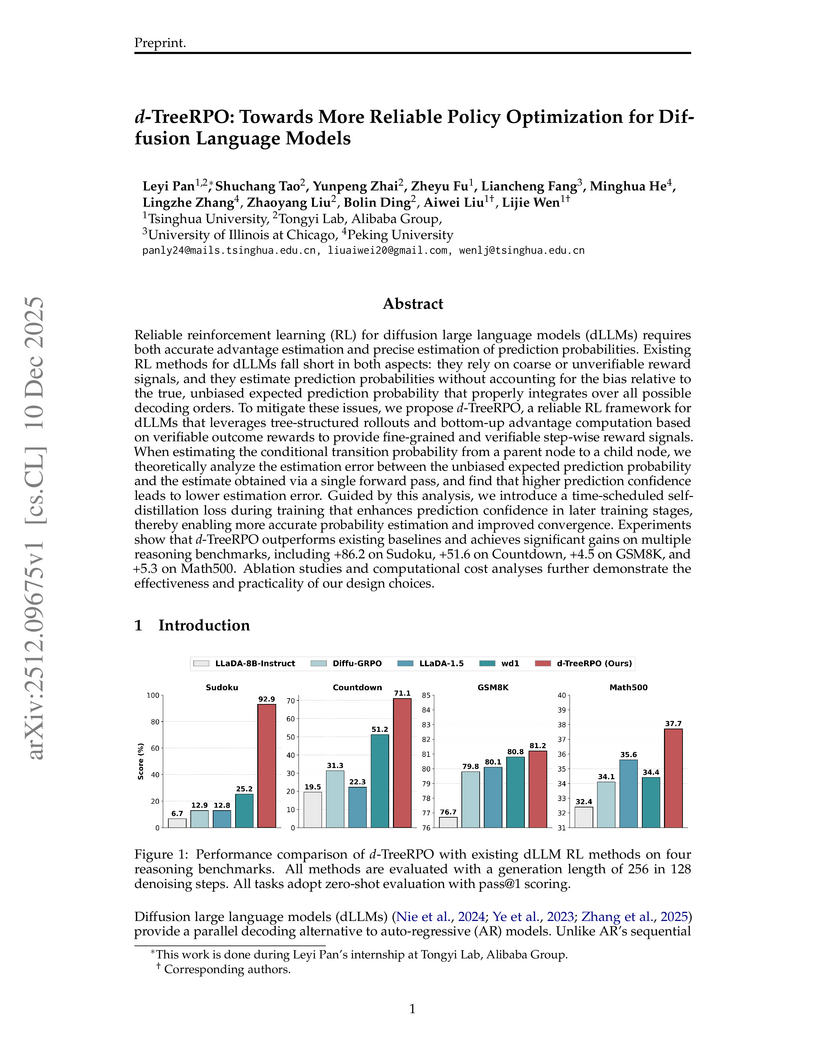
Reliable reinforcement learning (RL) for diffusion large language models (dLLMs) requires both accurate advantage estimation and precise estimation of prediction probabilities. Existing RL methods for dLLMs fall short in both aspects: they rely on coarse or unverifiable reward signals, and they estimate prediction probabilities without accounting for the bias relative to the true, unbiased expected prediction probability that properly integrates over all possible decoding orders. To mitigate these issues, we propose \emph{d}-TreeRPO, a reliable RL framework for dLLMs that leverages tree-structured rollouts and bottom-up advantage computation based on verifiable outcome rewards to provide fine-grained and verifiable step-wise reward signals. When estimating the conditional transition probability from a parent node to a child node, we theoretically analyze the estimation error between the unbiased expected prediction probability and the estimate obtained via a single forward pass, and find that higher prediction confidence leads to lower estimation error. Guided by this analysis, we introduce a time-scheduled self-distillation loss during training that enhances prediction confidence in later training stages, thereby enabling more accurate probability estimation and improved convergence. Experiments show that \emph{d}-TreeRPO outperforms existing baselines and achieves significant gains on multiple reasoning benchmarks, including +86.2 on Sudoku, +51.6 on Countdown, +4.5 on GSM8K, and +5.3 on Math500. Ablation studies and computational cost analyses further demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of our design choices.
Reward Forcing introduces EMA-Sink and Rewarded Distribution Matching Distillation (Re-DMD) to enable efficient, real-time streaming video generation. This framework achieves an overall VBench score of 84.13 and a generation speed of 23.1 FPS, while significantly enhancing motion dynamics and maintaining long-horizon consistency.
TWINFLOW introduces a self-adversarial flow framework that enables competitive one-step image generation on large multi-modal models like Qwen-Image-20B. The method reduces inference computational cost by up to 100x while maintaining image quality and diversity, bypassing the need for external discriminators or frozen teacher models.
Turbulent flows posses broadband, power-law spectra in which multiscale interactions couple high-wavenumber fluctuations to large-scale dynamics. Although diffusion-based generative models offer a principled probabilistic forecasting framework, we show that standard DDPMs induce a fundamental \emph{spectral collapse}: a Fourier-space analysis of the forward SDE reveals a closed-form, mode-wise signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that decays monotonically in wavenumber, ∣k∣ for spectra S(k)∝∣k∣−λ, rendering high-wavenumber modes indistinguishable from noise and producing an intrinsic spectral bias. We reinterpret the noise schedule as a spectral regularizer and introduce power-law schedules β(τ)∝τγ that preserve fine-scale structure deeper into diffusion time, along with \emph{Lazy Diffusion}, a one-step distillation method that leverages the learned score geometry to bypass long reverse-time trajectories and prevent high-k degradation. Applied to high-Reynolds-number 2D Kolmogorov turbulence and 1/12∘ Gulf of Mexico ocean reanalysis, these methods resolve spectral collapse, stabilize long-horizon autoregression, and restore physically realistic inertial-range scaling. Together, they show that naïve Gaussian scheduling is structurally incompatible with power-law physics and that physics-aware diffusion processes can yield accurate, efficient, and fully probabilistic surrogates for multiscale dynamical systems.
Camera-based temporal 3D object detection has shown impressive results in autonomous driving, with offline models improving accuracy by using future frames. Knowledge distillation (KD) can be an appealing framework for transferring rich information from offline models to online models. However, existing KD methods overlook future frames, as they mainly focus on spatial feature distillation under strict frame alignment or on temporal relational distillation, thereby making it challenging for online models to effectively learn future knowledge. To this end, we propose a sparse query-based approach, Future Temporal Knowledge Distillation (FTKD), which effectively transfers future frame knowledge from an offline teacher model to an online student model. Specifically, we present a future-aware feature reconstruction strategy to encourage the student model to capture future features without strict frame alignment. In addition, we further introduce future-guided logit distillation to leverage the teacher's stable foreground and background context. FTKD is applied to two high-performing 3D object detection baselines, achieving up to 1.3 mAP and 1.3 NDS gains on the nuScenes dataset, as well as the most accurate velocity estimation, without increasing inference cost.
Researchers from Alibaba Group and USTC developed Live Avatar, an algorithm-system co-designed framework for real-time, high-fidelity, and infinite-length audio-driven avatar generation using a 14-billion-parameter diffusion model. The system achieves 20.88 FPS and demonstrates visual consistency for over 10,000 seconds, significantly advancing practical applications.
FreeGen introduces a feed-forward reconstruction-generation co-training framework that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting with geometry-aware diffusion models for free-viewpoint driving scene synthesis. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes dataset, with an FID of 11.34 and FVD of 44.98 at a 12m lateral shift, outperforming previous methods without requiring auxiliary LiDAR or 3D bounding box annotations.
Semantic Soft Bootstrapping (SSB), an RL-free self-distillation framework developed at the University of Maryland, enhances large language model reasoning by having the model act as both teacher and student. It boosted pass@1 accuracy on the MATH500 benchmark by 10.6% and on AIME2024 by 10% over a GRPO baseline, while utilizing a smaller dataset and maintaining concise response lengths.
03 Dec 2025
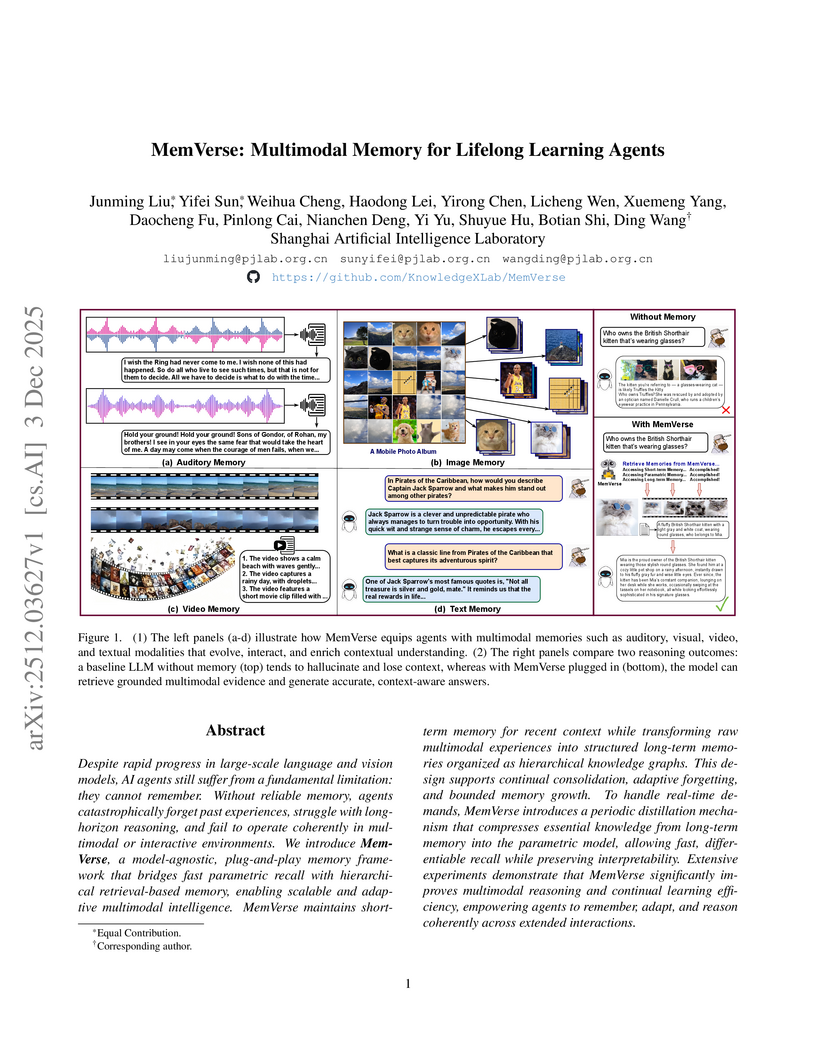
MemVerse, a multimodal memory framework from Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, enables lifelong learning agents to integrate explicit, structured knowledge graphs with fast, distilled parametric memory. It achieved 85.48% accuracy on ScienceQA, improving GPT-4o-mini's baseline by nearly 9 percentage points, and boosted text-to-video retrieval R@1 by over 60 percentage points on MSR-VTT, while accelerating knowledge recall by 89% compared to RAG.
The rapid development of generative models has significantly advanced image and video applications. Among these, video creation, aimed at generating videos under various conditions, has gained substantial attention. However, existing video creation models either focus solely on a few specific conditions or suffer from excessively long generation times due to complex model inference, making them impractical for real-world applications. To mitigate these issues, we propose an efficient unified video creation model, named VDOT. Concretely, we model the training process with the distribution matching distillation (DMD) paradigm. Instead of using the Kullback-Leibler (KL) minimization, we additionally employ a novel computational optimal transport (OT) technique to optimize the discrepancy between the real and fake score distributions. The OT distance inherently imposes geometric constraints, mitigating potential zero-forcing or gradient collapse issues that may arise during KL-based distillation within the few-step generation scenario, and thus, enhances the efficiency and stability of the distillation process. Further, we integrate a discriminator to enable the model to perceive real video data, thereby enhancing the quality of generated videos. To support training unified video creation models, we propose a fully automated pipeline for video data annotation and filtering that accommodates multiple video creation tasks. Meanwhile, we curate a unified testing benchmark, UVCBench, to standardize evaluation. Experiments demonstrate that our 4-step VDOT outperforms or matches other baselines with 100 denoising steps.
Modern Large Language Models achieve impressive reasoning capabilities with long Chain of Thoughts, but they incur substantial computational cost during inference, and this motivates techniques to improve the performance-cost ratio. Among these techniques, Speculative Decoding accelerates inference by employing a fast but inaccurate draft model to autoregressively propose tokens, which are then verified in parallel by a more capable target model. However, due to unnecessary rejections caused by token mismatches in semantically equivalent steps, traditional token-level Speculative Decoding struggles in reasoning tasks. Although recent works have shifted to step-level semantic verification, which improve efficiency by accepting or rejecting entire reasoning steps, existing step-level methods still regenerate many rejected steps with little improvement, wasting valuable target compute. To address this challenge, we propose Arbitrage, a novel step-level speculative generation framework that routes generation dynamically based on the relative advantage between draft and target models. Instead of applying a fixed acceptance threshold, Arbitrage uses a lightweight router trained to predict when the target model is likely to produce a meaningfully better step. This routing approximates an ideal Arbitrage Oracle that always chooses the higher-quality step, achieving near-optimal efficiency-accuracy trade-offs. Across multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks, Arbitrage consistently surpasses prior step-level Speculative Decoding baselines, reducing inference latency by up to ∼2× at matched accuracy.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.