Ask or search anything...
Lightweight reinforcement learning policies were trained to automate the unmasking process for Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs), improving inference efficiency without sacrificing generation quality. These policies consistently outperformed heuristic methods, particularly in full-diffusion generation settings, and demonstrated transferability across different dLLM architectures and sequence lengths.
View blogResearchers from Yandex and academic partners introduce AsyncReasoning, a training-free framework that enables existing Large Language Models to concurrently reason, process new inputs, and generate responses. This method drastically reduces user-perceived delays by 6-11x (Time to First Token from minutes to seconds) while preserving most of the reasoning accuracy and allowing for real-time safety checks.
View blogSegEarth-OV3 introduces a training-free adaptation of the Segment Anything Model 3 (SAM 3) for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation in remote sensing images. The method establishes a new state-of-the-art for training-free approaches, achieving a 53.4% average mIoU across eight remote sensing benchmarks, an improvement of 12.7% mIoU over previous methods.
View blogSAM-Body4D introduces a training-free framework for 4D human body mesh recovery from videos, synergistically combining promptable video object segmentation and image-based human mesh recovery models with an occlusion-aware mask refinement module. The system produces temporally consistent and robust mesh trajectories, effectively handling occlusions and maintaining identity across frames.
View blogResearchers from Google, NYU, ETH Zurich, and Stanford present a theoretical framework to formalize how large language models perform complex, iterative reasoning. The framework characterizes reasoning "oracles" and algorithms, proving that branching and genetic algorithms can achieve optimal success probabilities for models where oracle accuracy can decay with context size, and explains phenomena like "overthinking."
View blogSIMPACT introduces a framework that enables Vision-Language Models to perform zero-shot, physics-aware robotic manipulation by integrating an automatically constructed multi-physics simulator into the planning loop. This approach achieves success rates up to 90% on tasks such as shaping rope and Play-Doh, significantly outperforming geometric and VLM-based baselines.
View blogThis research quantifies the 'short-context dominance' in natural language, revealing that 75-80% of next-token predictions in large language models depend on local contexts of 32-96 tokens. It introduces a ground-truth-independent method, Long-Short Distribution Shift (LSDS), to detect when longer contexts are truly needed, and a targeted decoding algorithm, TaBoo, that consistently improves performance on long-range reasoning tasks.
View blogSplatPainter, a framework developed by researchers from Stanford University and Adobe Research, enables interactive, high-fidelity editing of 3D Gaussian Splatting assets directly from 2D inputs. It achieves identity-preserving local and global modifications at sub-second speeds, bridging a critical gap in 3D content creation workflows.
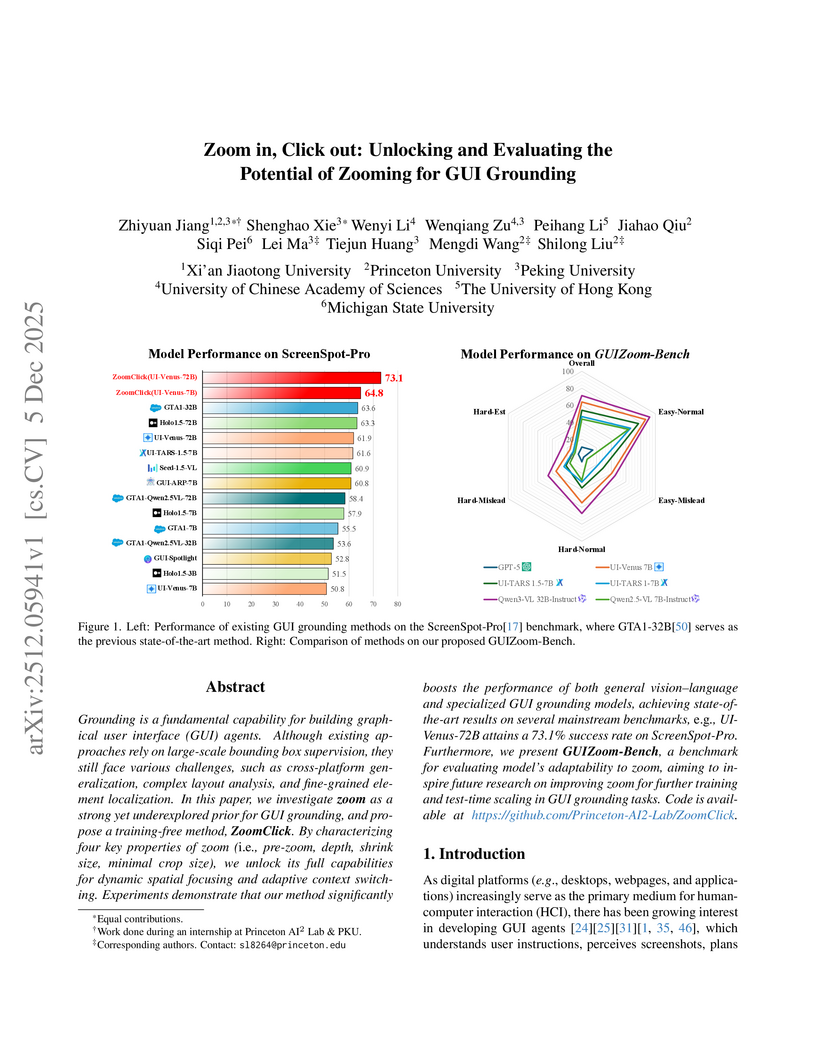
View blogResearchers from Peking University, Princeton University, and other institutions developed ZoomClick, a training-free inference strategy that enhances GUI grounding accuracy by dynamically zooming into relevant regions, and GUIZoom-Bench, a diagnostic benchmark for evaluating zoom behaviors. ZoomClick achieved a new state-of-the-art of 73.1% accuracy on ScreenSpot-Pro and a 66.7% relative improvement on UI-Vision, enabling smaller models to outperform larger unaugmented counterparts.
View blogResearchers introduce ReJump, a dual tree-jump representation that models LLM reasoning by capturing hierarchical problem-solving steps and dynamic action flows, including backtracking. This framework enables diagnosing reasoning inefficiencies and improving model performance on complex tasks through guided test-time selection.
View blogThis study from Generative AI Labs at The Wharton School empirically demonstrates that assigning expert personas to large language models generally does not improve their factual accuracy on challenging objective questions from benchmarks like GPQA Diamond and MMLU-Pro. The research found that most persona conditions yielded performance statistically similar to a baseline without personas, with low-knowledge personas often decreasing accuracy and some mismatched expert roles causing models to refuse to answer.
View blogMetacognitive Test-time Reasoning (MCTR) imbues Vision-Language Models with human-like fluid intelligence through a dual-level metacognitive architecture and test-time reinforcement learning. This framework achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot adaptation, securing 9 out of 12 top-1 results on unseen Atari games and improving average unseen performance by 275% over the SFT baseline.
View blogGoogle DeepMind's Plantain framework enables large language models to interleave planning with intermediate answers, addressing user experience issues in reasoning tasks. This approach reduces the time-to-first-response by over 60% and maintains or improves task accuracy across various benchmarks by allowing early user intervention.
View blog



 Mila - Quebec AI Institute
Mila - Quebec AI Institute McGill University
McGill University

 University of Maryland
University of Maryland

 Stanford University
Stanford University Adobe
Adobe


 Seoul National University
Seoul National University




