transfer-learning
This research disentangles the causal effects of pre-training, mid-training, and reinforcement learning (RL) on language model reasoning using a controlled synthetic task framework. It establishes that RL extends reasoning capabilities only under specific conditions of pre-training exposure and data calibration, with mid-training playing a crucial role in bridging training stages and improving generalization.
Wan-Move presents a framework for motion-controllable video generation that utilizes latent trajectory guidance to directly edit image condition features within a pre-trained image-to-video model. This method yields superior visual quality and precise motion adherence compared to state-of-the-art academic approaches and rivals commercial solutions, while also establishing MoveBench, a new comprehensive evaluation benchmark.
Apple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
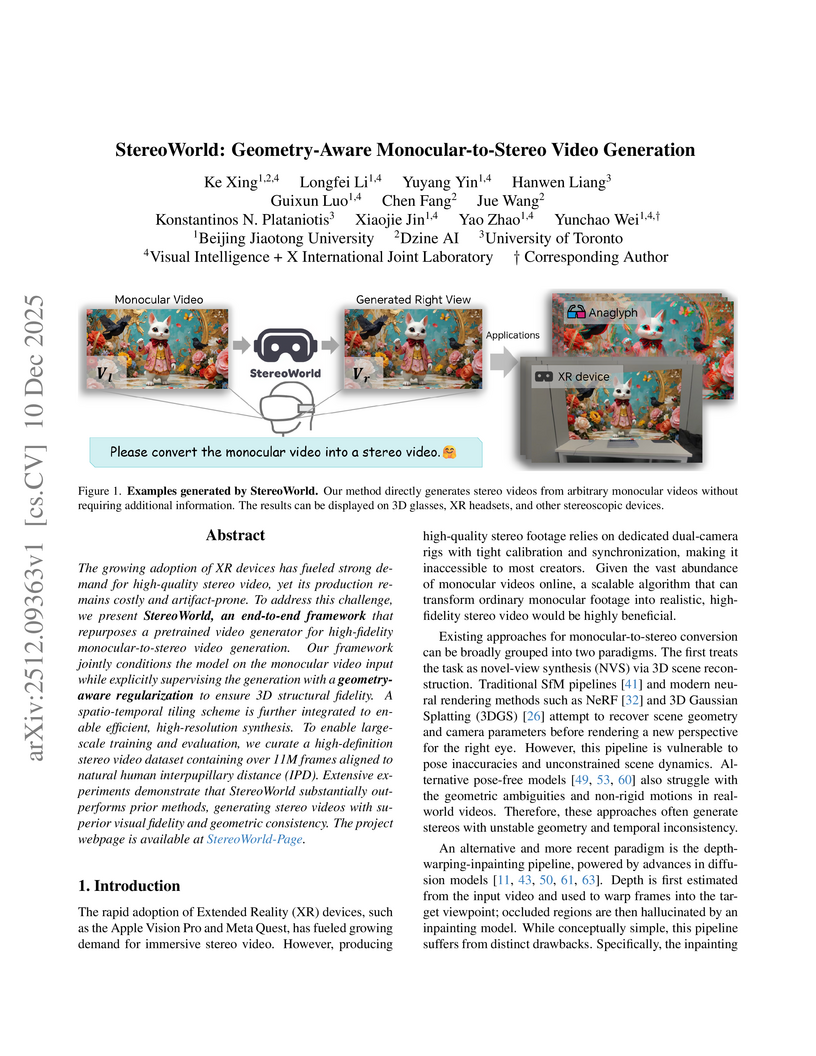
StereoWorld introduces an end-to-end diffusion framework for converting monocular videos into high-fidelity, geometry-aware stereo videos. The method utilizes a novel geometry-aware regularization, integrating disparity and depth supervision, and introduces the large-scale, IPD-aligned StereoWorld-11M dataset, achieving superior visual quality and geometric accuracy, with markedly lower LPIPS and EPE scores compared to prior methods.
10 Dec 2025
The Astribot Team developed Lumo-1, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that explicitly integrates structured reasoning with physical actions to achieve purposeful robotic control on their Astribot S1 bimanual mobile manipulator. This system exhibits superior generalization to novel objects and instructions, improves reasoning-action consistency through reinforcement learning, and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in complex, long-horizon, and dexterous tasks.
Researchers from Microsoft Research Asia, Xi'an Jiaotong University, and Fudan University developed VideoVLA, a robot manipulator that repurposes large pre-trained video generation models. This system jointly predicts future video states and corresponding actions, achieving enhanced generalization capabilities for novel objects and skills in both simulated and real-world environments.
SAM-Body4D introduces a training-free framework for 4D human body mesh recovery from videos, synergistically combining promptable video object segmentation and image-based human mesh recovery models with an occlusion-aware mask refinement module. The system produces temporally consistent and robust mesh trajectories, effectively handling occlusions and maintaining identity across frames.
Researchers at Zhejiang University developed LIVINGSWAP, a high-fidelity video face swapping framework designed for cinematic quality by directly leveraging complete source video attributes and employing keyframe conditioning. The system outperforms existing methods on new cinematic benchmarks and reduces manual editing effort by approximately 40 times.
09 Dec 2025
Lightweight reinforcement learning policies were trained to automate the unmasking process for Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs), improving inference efficiency without sacrificing generation quality. These policies consistently outperformed heuristic methods, particularly in full-diffusion generation settings, and demonstrated transferability across different dLLM architectures and sequence lengths.
Researchers from Meta AI and the University of Copenhagen developed OneStory, a framework for coherent multi-shot video generation that utilizes adaptive memory modules to model long-range cross-shot context. The method consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving higher inter-shot coherence scores (e.g., 0.5813 average inter-shot coherence in text-to-multi-shot video tasks) and enhanced shot-level quality.
The H2R-Grounder framework enables the translation of human interaction videos into physically grounded robot manipulation videos without requiring paired human-robot demonstration data. Researchers at the National University of Singapore's Show Lab developed this approach, which utilizes a simple 2D pose representation and fine-tunes a video diffusion model on unpaired robot videos, achieving higher human preference for motion consistency (54.5%), physical plausibility (63.6%), and visual quality (61.4%) compared to baseline methods.
Splatent introduces a two-stage framework for novel view synthesis that enhances 3D Gaussian Splatting by addressing multi-view inconsistencies in VAE latent spaces. The method achieves state-of-the-art visual quality and detail recovery by refining rendered latent features with a single-step diffusion model conditioned on multiple reference views, leading to substantial quantitative improvements across various datasets.
RETAIN, developed at UC Berkeley, introduces a parameter merging strategy for generalist robot policies, interpolating pre-trained and finetuned weights to enable robust adaptation to new tasks. This approach enhances out-of-distribution generalization by approximately 40% on real-world robotic tasks while preserving the policy's existing broad capabilities in low-data scenarios.
09 Dec 2025
Fed-SE introduces a federated self-evolution framework enabling large language model (LLM) agents to collaboratively improve across diverse, privacy-constrained environments. It achieved an average task success rate of 0.66 across five complex tasks, outperforming centralized and local baselines, by leveraging local success filtering and global low-rank adapter aggregation.
DynaIP introduces a dynamic image prompt adapter for Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiT) that enhances personalized text-to-image generation by achieving superior concept preservation, prompt following, and scalability for multi-subject compositions. The method, developed by Huawei, leverages dynamic decoupling and hierarchical feature fusion, significantly outperforming baselines in qualitative and quantitative evaluations on single and multi-subject tasks.
Researchers from Peking University and Huawei Technologies developed a principled framework for adapting pre-trained autoregressive (AR) models into Block-Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). The adapted 7B-class model, NBDIFF-7B, achieved state-of-the-art performance among diffusion LLMs, with a macro average of 64.3 for its base version and 78.8 for its instruct version across diverse benchmarks.
09 Dec 2025
OSMO is an open-source tactile glove platform designed to capture both shear and normal forces from human demonstrations, facilitating direct transfer of these skills to robots. Policies trained using OSMO achieved 71.69% success in a wiping task, outperforming vision-only baselines (55.75%) by eliminating contact-related failures.
An independent research team secured 1st place in the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge, achieving a 26% q-score by enhancing a Vision-Language-Action model (Pi0.5) with innovations like correlated noise for flow matching, "System 2" stage tracking, and practical inference-time heuristics. The approach demonstrated emergent recovery behaviors and addressed challenges in long-horizon, complex manipulation tasks.
10 Dec 2025
Long-term planning in complex, text-based environments presents significant challenges due to open-ended action spaces, ambiguous observations, and sparse feedback. Recent research suggests that large language models (LLMs) encode rich semantic knowledge about the world, which can be valuable for guiding agents in high-level reasoning and planning across both embodied and purely textual settings. However, existing approaches often depend heavily on querying LLMs during training and inference, making them computationally expensive and difficult to deploy efficiently. In addition, these methods typically employ a pretrained, unaltered LLM whose parameters remain fixed throughout training, providing no opportunity for adaptation to the target task. To address these limitations, we introduce SCOPE (Subgoal-COnditioned Pretraining for Efficient planning), a one-shot hierarchical planner that leverages LLM-generated subgoals only at initialization to pretrain a lightweight student model. Unlike prior approaches that distill LLM knowledge by repeatedly prompting the model to adaptively generate subgoals during training, our method derives subgoals directly from example trajectories. This design removes the need for repeated LLM queries, significantly improving efficiency, though at the cost of reduced explainability and potentially suboptimal subgoals. Despite their suboptimality, our results on the TextCraft environment show that LLM-generated subgoals can still serve as a strong starting point for hierarchical goal decomposition in text-based planning tasks. Compared to the LLM-based hierarchical agent ADaPT (Prasad et al., 2024), which achieves a 0.52 success rate, our method reaches 0.56 and reduces inference time from 164.4 seconds to just 3.0 seconds.
This research provides theoretical and empirical evidence that generative models are essential for achieving data-efficient compositional generalization in visual perception, demonstrating that enforcing necessary inductive biases is feasible for decoders but largely infeasible for encoders without knowledge of out-of-domain data. Generative methods, through techniques like replay and gradient-based search, significantly improve out-of-domain accuracy compared to non-generative counterparts.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.