Apple
AppleATOKEN presents a unified tokenizer for vision that integrates high-fidelity reconstruction and rich semantic understanding across images, videos, and 3D assets within a single transformer-based framework. This approach achieves competitive performance in both tasks across diverse modalities, serving as a foundation for general multimodal AI.
Manzano, a unified multimodal model developed by Apple, successfully integrates visual understanding (Image-to-Text) and generation (Text-to-Image) capabilities without performance trade-offs by employing a hybrid vision tokenizer and a scalable autoregressive LLM. The model achieved state-of-the-art results among unified models, particularly excelling in text-rich understanding tasks and demonstrating high-fidelity image generation.
Apple researchers introduce SimpleFold, a protein folding model that solely uses general-purpose transformer blocks and a flow-matching objective, moving away from complex domain-specific architectures. The model achieves competitive accuracy on benchmarks like CAMEO22 and CASP14, often outperforming ESMFold, while also demonstrating enhanced capabilities for generating diverse protein ensembles and significantly improving computational efficiency.
Step-by-step decision planning with large language models (LLMs) is gaining
attention in AI agent development. This paper focuses on decision planning with
uncertainty estimation to address the hallucination problem in language models.
Existing approaches are either white-box or computationally demanding, limiting
use of black-box proprietary LLMs within budgets. The paper's first
contribution is a non-parametric uncertainty quantification method for LLMs,
efficiently estimating point-wise dependencies between input-decision on the
fly with a single inference, without access to token logits. This estimator
informs the statistical interpretation of decision trustworthiness. The second
contribution outlines a systematic design for a decision-making agent,
generating actions like ``turn on the bathroom light'' based on user prompts
such as ``take a bath''. Users will be asked to provide preferences when more
than one action has high estimated point-wise dependencies. In conclusion, our
uncertainty estimation and decision-making agent design offer a cost-efficient
approach for AI agent development.
The CodeAct framework unifies LLM agent actions into executable Python code, enabling dynamic interaction, self-correction, and leveraging the Python ecosystem. This approach significantly improves task success rates and efficiency for LLM agents on complex multi-tool tasks, with the open-source CodeActAgent demonstrating strong performance on agentic benchmarks while retaining general LLM capabilities.
This tutorial, authored by researchers from Apple and Mila, offers an accessible first course on diffusion models and flow matching, simplifying their complex mathematical foundations. It systematically derives the algorithms for stochastic (DDPM) and deterministic (DDIM) sampling, unifying them under the general framework of Flow Matching.
Apple researchers investigated the "thinking" mechanisms of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) using controlled puzzle environments, revealing that these models consistently fail beyond a specific complexity threshold and often exhibit "overthinking" on simpler tasks. The study identified three performance regimes where LRMs either matched, outperformed, or collapsed alongside standard LLMs, while also demonstrating limitations in executing explicit algorithms and maintaining consistent reasoning.
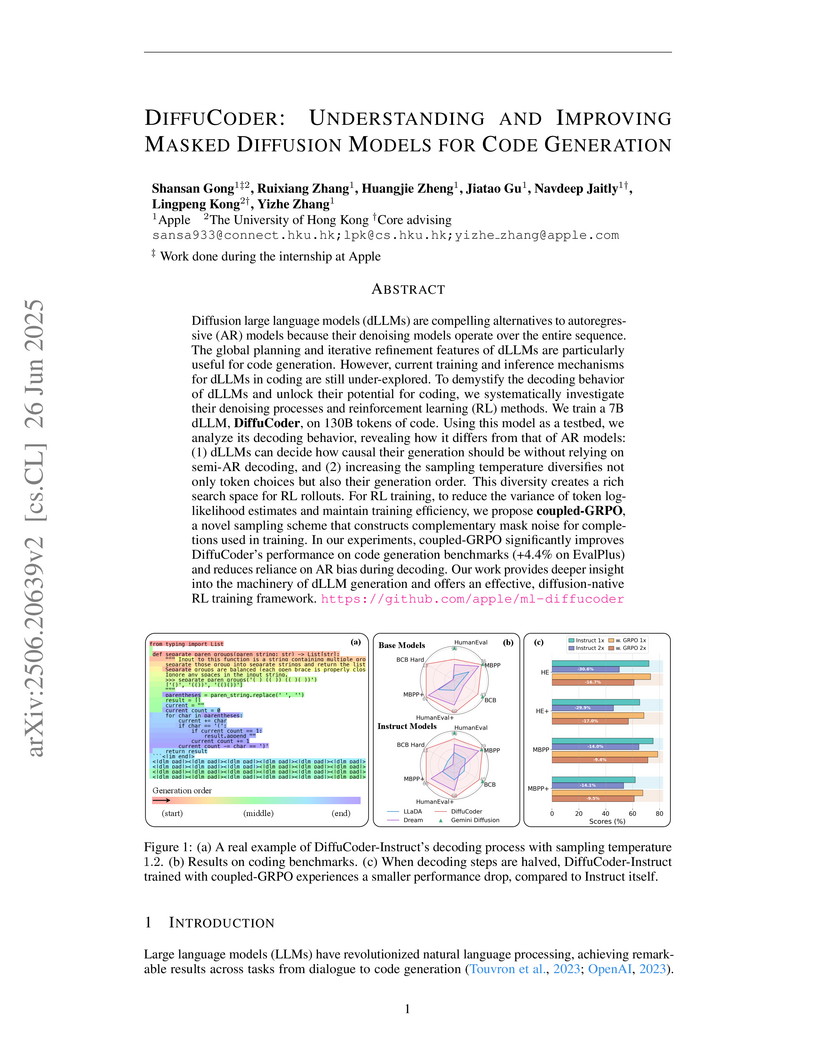
Researchers from Apple and The University of Hong Kong present DiffuCoder, an open-source 7B masked diffusion model for code generation, demonstrating performance competitive with autoregressive models. They introduce Coupled-GRPO, a 'diffusion-native' reinforcement learning algorithm that improves DiffuCoder's performance by 4.4% on EvalPlus, while also enhancing the model's non-autoregressive generation and parallelism.
Apple researchers introduced a hierarchical memory architecture for large language models, separating general reasoning from specific long-tail knowledge, to enhance efficiency for on-device deployment. This approach allowed smaller anchor models augmented with parametric memories to achieve performance comparable to significantly larger monolithic models while drastically reducing runtime memory and improving knowledge control.
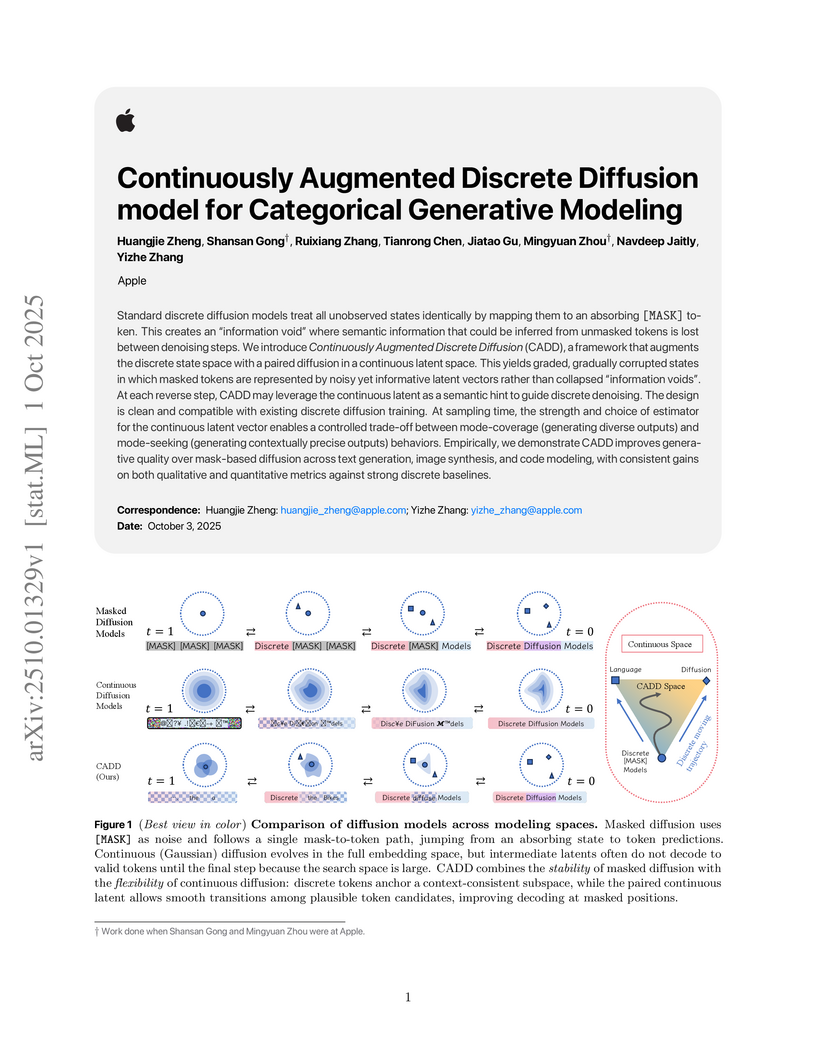
The Continuously Augmented Discrete Diffusion (CADD) model, developed by Apple researchers, introduces a hybrid approach to categorical generative modeling that combines discrete masking with continuous semantic guidance. It achieves new state-of-the-art results in text, image, and code generation, often surpassing existing discrete and continuous diffusion models by notable margins.
Modern large language models (LLMs) extend context lengths to millions of tokens, enabling coherent, personalized responses grounded in long conversational histories. This ability, however, hinges on Key-Value (KV) caching, whose memory grows linearly with dialogue length and quickly becomes the bottleneck in resource-constrained environments. An active line of research for reducing memory bottleneck is KV cache compression, which seeks to limit cache size while preserving accuracy. Yet existing methods face two major limitations: (i) evicting the KV cache after full-context prefill causes unbounded peak memory, and (ii) query-dependent eviction narrows the cache to a single query, leading to failure cases in multi-turn conversations. We introduce EpiCache, a training-free KV cache management framework for long conversational question answering (LongConvQA) under fixed memory budgets. EpiCache bounds cache growth through block-wise prefill and preserves topic-relevant context via episodic KV compression, which clusters conversation history into coherent episodes and applies episode-specific KV cache eviction. We further design an adaptive layer-wise budget allocation strategy that measures each layer's sensitivity to eviction and distributes the memory budget across layers accordingly. Across three LongConvQA benchmarks, EpiCache improves accuracy by up to 40%, maintains near-full KV accuracy under 4-6x compression, and reduces latency/memory by up to 2.4x/3.5x, enabling efficient multi-turn interaction under strict resource limits. Our code is available at this https URL.
FastVLM, an efficient Vision Language Model developed by Apple, employs a novel FastViTHD vision encoder designed for rapid high-resolution image processing. This approach achieves over 2.5 points higher average performance on VLM benchmarks while being up to 3 times faster on an M1 MacBook Pro, significantly improving on-device VLM efficiency.
A method enables efficient scaling of Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) up to 7B parameters by adapting pre-trained autoregressive models, achieving state-of-the-art performance among DLMs and demonstrating capabilities competitive with AR models, particularly excelling in text infilling.
LADIR introduces a framework that integrates continuous latent representations with latent diffusion models to enhance text reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models. This approach achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, generates more diverse reasoning paths, and provides improved interpretability across various mathematical reasoning and puzzle planning benchmarks.
Apple researchers introduced Pico-Banana-400K, a large-scale dataset of approximately 400,000 text-guided image editing examples built from real OpenImages photographs. This resource features MLLM-based quality assessment and includes specialized subsets for multi-turn editing and preference learning to advance model training for improved instruction following and visual fidelity.
08 Oct 2025
RL4HS is a reinforcement learning framework that trains Large Language Models to precisely identify hallucinated text segments within generated content. It achieves this by using a span-level reward function and Class-Aware Policy Optimization (CAPO), significantly improving factual consistency detection over existing methods on the RAGTruth benchmark.
Language models must be adapted to understand and follow user instructions. Reinforcement learning is widely used to facilitate this -- typically using fixed criteria such as "helpfulness" and "harmfulness". In our work, we instead propose using flexible, instruction-specific criteria as a means of broadening the impact that reinforcement learning can have in eliciting instruction following. We propose "Reinforcement Learning from Checklist Feedback" (RLCF). From instructions, we extract checklists and evaluate how well responses satisfy each item - using both AI judges and specialized verifier programs - then combine these scores to compute rewards for RL. We compare RLCF with other alignment methods applied to a strong instruction following model (Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct) on five widely-studied benchmarks -- RLCF is the only method to improve performance on every benchmark, including a 4-point boost in hard satisfaction rate on FollowBench, a 6-point increase on InFoBench, and a 3-point rise in win rate on Arena-Hard. These results establish checklist feedback as a key tool for improving language models' support of queries that express a multitude of needs.
Johns Hopkins University and Apple researchers developed DeepMMSearch-R1, a multimodal large language model capable of performing on-demand, multi-turn web searches using both text and a novel cropped image search tool. This system achieves superior performance on knowledge-intensive visual question answering tasks by dynamically accessing and reasoning over external, up-to-date web information.
DataComp-LM introduces a standardized, large-scale benchmark for evaluating language model training data curation strategies, complete with an openly released corpus, framework, and models. Its DCLM-BASELINE 7B model, trained on carefully filtered Common Crawl data, achieves 64% MMLU 5-shot accuracy, outperforming previous open-data state-of-the-art models while requiring substantially less compute.
CLaRa, developed by Apple and the University of Edinburgh, introduces a unified framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation that utilizes continuous latent document representations to enable joint optimization and efficient context handling. It achieved superior performance on question answering benchmarks, including an F1 score improvement on NQ from 51.01 to 51.41 with 16x context compression, and its retriever surpassed supervised baselines by over 10 percentage points on HotpotQA.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.