AppTek GmbH
The VietMed-NER dataset, the first publicly available medical spoken Named Entity Recognition (NER) resource, was developed from real-world Vietnamese medical conversations and features 18 distinct entity types. This work established baseline performance using state-of-the-art models, with XLM-R_large achieving an F1 score of 0.58 on ASR output, and provided detailed error analysis specific to medical entity extraction.
Multi-speaker automatic speech recognition (ASR) is crucial for many
real-world applications, but it requires dedicated modeling techniques.
Existing approaches can be divided into modular and end-to-end methods. Modular
approaches separate speakers and recognize each of them with a single-speaker
ASR system. End-to-end models process overlapped speech directly in a single,
powerful neural network. This work proposes a middle-ground approach that
leverages explicit speech separation similarly to the modular approach but also
incorporates mixture speech information directly into the ASR module in order
to mitigate the propagation of errors made by the speech separator. We also
explore a way to exchange cross-speaker context information through a layer
that combines information of the individual speakers. Our system is optimized
through separate and joint training stages and achieves a relative improvement
of 7% in word error rate over a purely modular setup on the SMS-WSJ task.
As one of the most popular sequence-to-sequence modeling approaches for
speech recognition, the RNN-Transducer has achieved evolving performance with
more and more sophisticated neural network models of growing size and
increasing training epochs. While strong computation resources seem to be the
prerequisite of training superior models, we try to overcome it by carefully
designing a more efficient training pipeline. In this work, we propose an
efficient 3-stage progressive training pipeline to build highly-performing
neural transducer models from scratch with very limited computation resources
in a reasonable short time period. The effectiveness of each stage is
experimentally verified on both Librispeech and Switchboard corpora. The
proposed pipeline is able to train transducer models approaching
state-of-the-art performance with a single GPU in just 2-3 weeks. Our best
conformer transducer achieves 4.1% WER on Librispeech test-other with only 35
epochs of training.
In this work, we compare from-scratch sequence-level cross-entropy (full-sum)
training of Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and Connectionist Temporal Classification
(CTC) topologies for automatic speech recognition (ASR). Besides accuracy, we
further analyze their capability for generating high-quality time alignment
between the speech signal and the transcription, which can be crucial for many
subsequent applications. Moreover, we propose several methods to improve
convergence of from-scratch full-sum training by addressing the alignment
modeling issue. Systematic comparison is conducted on both Switchboard and
LibriSpeech corpora across CTC, posterior HMM with and w/o transition
probabilities, and standard hybrid HMM. We also provide a detailed analysis of
both Viterbi forced-alignment and Baum-Welch full-sum occupation probabilities.
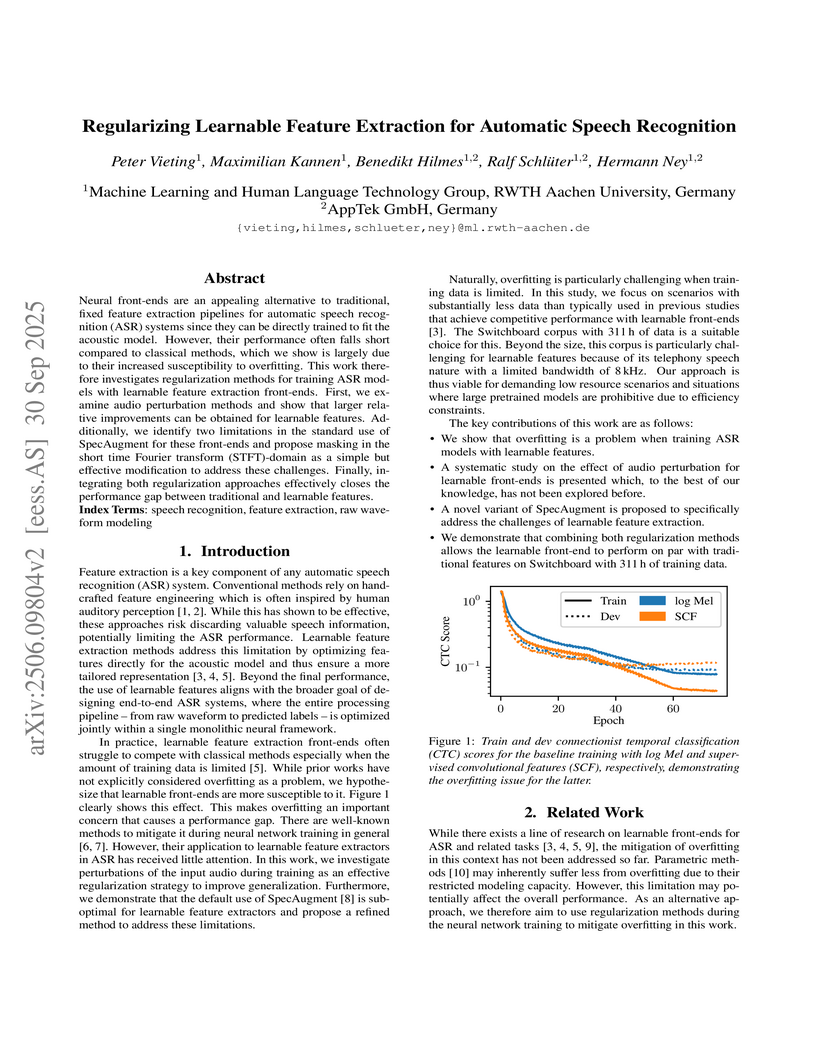
Neural front-ends are an appealing alternative to traditional, fixed feature extraction pipelines for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems since they can be directly trained to fit the acoustic model. However, their performance often falls short compared to classical methods, which we show is largely due to their increased susceptibility to overfitting. This work therefore investigates regularization methods for training ASR models with learnable feature extraction front-ends. First, we examine audio perturbation methods and show that larger relative improvements can be obtained for learnable features. Additionally, we identify two limitations in the standard use of SpecAugment for these front-ends and propose masking in the short time Fourier transform (STFT)-domain as a simple but effective modification to address these challenges. Finally, integrating both regularization approaches effectively closes the performance gap between traditional and learnable features.
02 Jun 2025
With the rise of large pre-trained foundation models for automatic speech
recognition new challenges appear. While the performance of these models is
good, runtime and cost of inference increases. One approach to make use of
their strength while retaining efficiency is to distill their knowledge to
smaller models during training. In this work, we explore different CTC-based
distillation variants, focusing on blank token handling. We show that common
approaches like blank elimination do not always work off the shelf. We explore
new blank selection patterns as a potential sweet spot between standard
knowledge distillation and blank elimination mechanisms. Through the
introduction of a symmetric selection method, we are able to remove the CTC
loss during knowledge distillation with minimal to no performance degradation.
With this, we make the training independent from target labels, potentially
allowing for distillation on untranscribed audio data.
Researchers from RWTH Aachen University and AppTek GmbH challenge the long-standing assumption that CTC-based ASR models operate under strict label context independence, revealing through knowledge distillation experiments that modern CTC models with powerful Conformer encoders implicitly learn context-dependent internal language models despite their theoretical formulation, introducing label-level knowledge distillation methods with smoothing and masking regularization techniques where a single-layer LSTM student model learns to approximate the CTC teacher's internal linguistic biases, achieving over 13% relative WER improvement compared to shallow fusion on cross-domain TED-LIUM evaluation while demonstrating that context-dependent ILM estimation consistently outperforms traditional frame-level priors and context-independent approximations, with the surprising finding that ILM perplexity shows no correlation with final ASR performance unlike external language models, necessitating task-specific evaluation metrics for internal language model quality assessment.
09 Oct 2023
We investigate a novel modeling approach for end-to-end neural network
training using hidden Markov models (HMM) where the transition probabilities
between hidden states are modeled and learned explicitly. Most contemporary
sequence-to-sequence models allow for from-scratch training by summing over all
possible label segmentations in a given topology. In our approach there are
explicit, learnable probabilities for transitions between segments as opposed
to a blank label that implicitly encodes duration statistics. We implement a
GPU-based forward-backward algorithm that enables the simultaneous training of
label and transition probabilities. We investigate recognition results and
additionally Viterbi alignments of our models. We find that while the
transition model training does not improve recognition performance, it has a
positive impact on the alignment quality. The generated alignments are shown to
be viable targets in state-of-the-art Viterbi trainings.
Meeting transcription is a field of high relevance and remarkable progress in recent years. Still, challenges remain that limit its performance. In this work, we extend a previously proposed framework for analyzing leakage in speech separation with proper sensitivity to temporal locality. We show that there is significant leakage to the cross channel in areas where only the primary speaker is active. At the same time, the results demonstrate that this does not affect the final performance much as these leaked parts are largely ignored by the voice activity detection (VAD). Furthermore, different segmentations are compared showing that advanced diarization approaches are able to reduce the gap to oracle segmentation by a third compared to a simple energy-based VAD. We additionally reveal what factors contribute to the remaining difference. The results represent state-of-the-art performance on LibriCSS among systems that train the recognition module on LibriSpeech data only.
We study a streamable attention-based encoder-decoder model in which either the decoder, or both the encoder and decoder, operate on pre-defined, fixed-size windows called chunks. A special end-of-chunk (EOC) symbol advances from one chunk to the next chunk, effectively replacing the conventional end-of-sequence symbol. This modification, while minor, situates our model as equivalent to a transducer model that operates on chunks instead of frames, where EOC corresponds to the blank symbol. We further explore the remaining differences between a standard transducer and our model. Additionally, we examine relevant aspects such as long-form speech generalization, beam size, and length normalization. Through experiments on Librispeech and TED-LIUM-v2, and by concatenating consecutive sequences for long-form trials, we find that our streamable model maintains competitive performance compared to the non-streamable variant and generalizes very well to long-form speech.
To join the advantages of classical and end-to-end approaches for speech
recognition, we present a simple, novel and competitive approach for
phoneme-based neural transducer modeling. Different alignment label topologies
are compared and word-end-based phoneme label augmentation is proposed to
improve performance. Utilizing the local dependency of phonemes, we adopt a
simplified neural network structure and a straightforward integration with the
external word-level language model to preserve the consistency of seq-to-seq
modeling. We also present a simple, stable and efficient training procedure
using frame-wise cross-entropy loss. A phonetic context size of one is shown to
be sufficient for the best performance. A simplified scheduled sampling
approach is applied for further improvement and different decoding approaches
are briefly compared. The overall performance of our best model is comparable
to state-of-the-art (SOTA) results for the TED-LIUM Release 2 and Switchboard
corpora.
While generative methods have progressed rapidly in recent years, generating expressive prosody for an utterance remains a challenging task in text-to-speech synthesis. This is particularly true for systems that model prosody explicitly through parameters such as pitch, energy, and duration, which is commonly done for the sake of interpretability and controllability. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of stochastic methods for this task, including Normalizing Flows, Conditional Flow Matching, and Rectified Flows. We compare these methods to a traditional deterministic baseline, as well as to real human realizations. Our extensive subjective and objective evaluations demonstrate that stochastic methods produce natural prosody on par with human speakers by capturing the variability inherent in human speech. Further, they open up additional controllability options by allowing the sampling temperature to be tuned.
We present a complete training pipeline to build a state-of-the-art hybrid HMM-based ASR system on the 2nd release of the TED-LIUM corpus. Data augmentation using SpecAugment is successfully applied to improve performance on top of our best SAT model using i-vectors. By investigating the effect of different maskings, we achieve improvements from SpecAugment on hybrid HMM models without increasing model size and training time. A subsequent sMBR training is applied to fine-tune the final acoustic model, and both LSTM and Transformer language models are trained and evaluated. Our best system achieves a 5.6% WER on the test set, which outperforms the previous state-of-the-art by 27% relative.
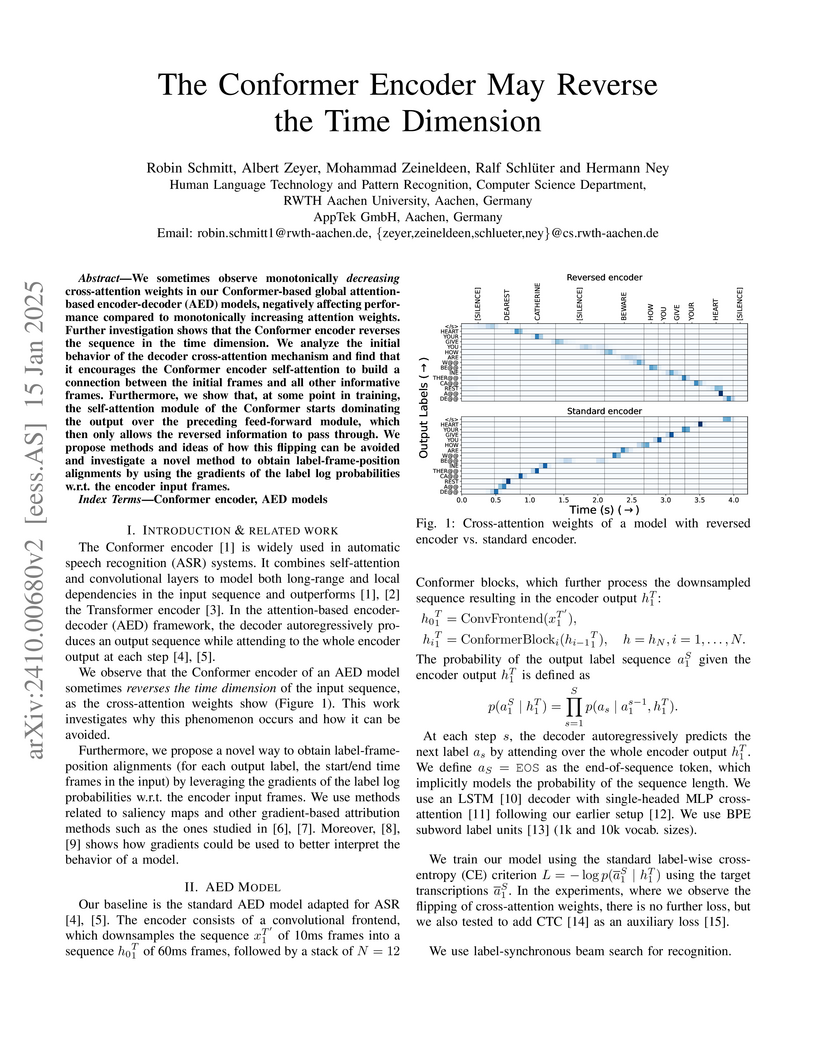
We sometimes observe monotonically decreasing cross-attention weights in our Conformer-based global attention-based encoder-decoder (AED) models, Further investigation shows that the Conformer encoder reverses the sequence in the time dimension. We analyze the initial behavior of the decoder cross-attention mechanism and find that it encourages the Conformer encoder self-attention to build a connection between the initial frames and all other informative frames. Furthermore, we show that, at some point in training, the self-attention module of the Conformer starts dominating the output over the preceding feed-forward module, which then only allows the reversed information to pass through. We propose methods and ideas of how this flipping can be avoided and investigate a novel method to obtain label-frame-position alignments by using the gradients of the label log probabilities w.r.t. the encoder input frames.
This paper summarizes our work on the first track of the ninth Dialog System
Technology Challenge (DSTC 9), "Beyond Domain APIs: Task-oriented
Conversational Modeling with Unstructured Knowledge Access". The goal of the
task is to generate responses to user turns in a task-oriented dialog that
require knowledge from unstructured documents. The task is divided into three
subtasks: detection, selection and generation. In order to be compute
efficient, we formulate the selection problem in terms of hierarchical
classification steps. We achieve our best results with this model.
Alternatively, we employ siamese sequence embedding models, referred to as
Dense Knowledge Retrieval, to retrieve relevant documents. This method further
reduces the computation time by a factor of more than 100x at the cost of
degradation in R@1 of 5-6% compared to the first model. Then for either
approach, we use Retrieval Augmented Generation to generate responses based on
multiple selected snippets and we show how the method can be used to fine-tune
trained embeddings.
ASR systems are deployed across diverse environments, each with specific
hardware constraints. We use supernet training to jointly train multiple
encoders of varying sizes, enabling dynamic model size adjustment to fit
hardware constraints without redundant training. Moreover, we introduce a novel
method called OrthoSoftmax, which applies multiple orthogonal softmax functions
to efficiently identify optimal subnets within the supernet, avoiding
resource-intensive search. This approach also enables more flexible and precise
subnet selection by allowing selection based on various criteria and levels of
granularity. Our results with CTC on Librispeech and TED-LIUM-v2 show that
FLOPs-aware component-wise selection achieves the best overall performance.
With the same number of training updates from one single job, WERs for all
model sizes are comparable to or slightly better than those of individually
trained models. Furthermore, we analyze patterns in the selected components and
reveal interesting insights.
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems typically use handcrafted feature extraction pipelines. To avoid their inherent information loss and to achieve more consistent modeling from speech to transcribed text, neural raw waveform feature extractors (FEs) are an appealing approach. Also the wav2vec 2.0 model, which has recently gained large popularity, uses a convolutional FE which operates directly on the speech waveform. However, it is not yet studied extensively in the literature. In this work, we study its capability to replace the standard feature extraction methods in a connectionist temporal classification (CTC) ASR model and compare it to an alternative neural FE. We show that both are competitive with traditional FEs on the LibriSpeech benchmark and analyze the effect of the individual components. Furthermore, we analyze the learned filters and show that the most important information for the ASR system is obtained by a set of bandpass filters.
The peaky behavior of CTC models is well known experimentally. However, an
understanding about why peaky behavior occurs is missing, and whether this is a
good property. We provide a formal analysis of the peaky behavior and gradient
descent convergence properties of the CTC loss and related training criteria.
Our analysis provides a deep understanding why peaky behavior occurs and when
it is suboptimal. On a simple example which should be trivial to learn for any
model, we prove that a feed-forward neural network trained with CTC from
uniform initialization converges towards peaky behavior with a 100% error rate.
Our analysis further explains why CTC only works well together with the blank
label. We further demonstrate that peaky behavior does not occur on other
related losses including a label prior model, and that this improves
convergence.
This paper summarizes our contributions to the document-grounded dialog tasks at the 9th and 10th Dialog System Technology Challenges (DSTC9 and DSTC10). In both iterations the task consists of three subtasks: first detect whether the current turn is knowledge seeking, second select a relevant knowledge document, and third generate a response grounded on the selected document. For DSTC9 we proposed different approaches to make the selection task more efficient. The best method, Hierarchical Selection, actually improves the results compared to the original baseline and gives a speedup of 24x. In the DSTC10 iteration of the task, the challenge was to adapt systems trained on written dialogs to perform well on noisy automatic speech recognition transcripts. Therefore, we proposed data augmentation techniques to increase the robustness of the models as well as methods to adapt the style of generated responses to fit well into the proceeding dialog. Additionally, we proposed a noisy channel model that allows for increasing the factuality of the generated responses. In addition to summarizing our previous contributions, in this work, we also report on a few small improvements and reconsider the automatic evaluation metrics for the generation task which have shown a low correlation to human judgments.
In hybrid HMM based speech recognition, LSTM language models have been widely applied and achieved large improvements. The theoretical capability of modeling any unlimited context suggests that no recombination should be applied in decoding. This motivates to reconsider full summation over the HMM-state sequences instead of Viterbi approximation in decoding. We explore the potential gain from more accurate probabilities in terms of decision making and apply the full-sum decoding with a modified prefix-tree search framework. The proposed full-sum decoding is evaluated on both Switchboard and Librispeech corpora. Different models using CE and sMBR training criteria are used. Additionally, both MAP and confusion network decoding as approximated variants of general Bayes decision rule are evaluated. Consistent improvements over strong baselines are achieved in almost all cases without extra cost. We also discuss tuning effort, efficiency and some limitations of full-sum decoding.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.