Chinese Academy of Engineering
Heterogeneous hardware and dynamic workloads worsen long-standing OS bottlenecks in scalability, adaptability, and manageability. At the same time, advances in machine learning (ML), large language models (LLMs), and agent-based methods enable automation and self-optimization, but current efforts lack a unifying view. This survey reviews techniques, architectures, applications, challenges, and future directions at the AI-OS intersection. We chart the shift from heuristic- and rule-based designs to AI-enhanced systems, outlining the strengths of ML, LLMs, and agents across the OS stack. We summarize progress in AI for OS (core components and the wider ecosystem) and in OS for AI (component- and architecture-level support for short- and long-context inference, distributed training, and edge inference). For practice, we consolidate evaluation dimensions, methodological pipelines, and patterns that balance real-time constraints with predictive accuracy. We identify key challenges, such as complexity, overhead, model drift, limited explainability, and privacy and safety risks, and recommend modular, AI-ready kernel interfaces; unified toolchains and benchmarks; hybrid rules-plus-AI decisions with guardrails; and verifiable in-kernel inference. Finally, we propose a three-stage roadmap including AI-powered, AI-refactored, and AI-driven OSs, to bridge prototypes and production and to enable scalable, reliable AI deployment.
02 Dec 2025
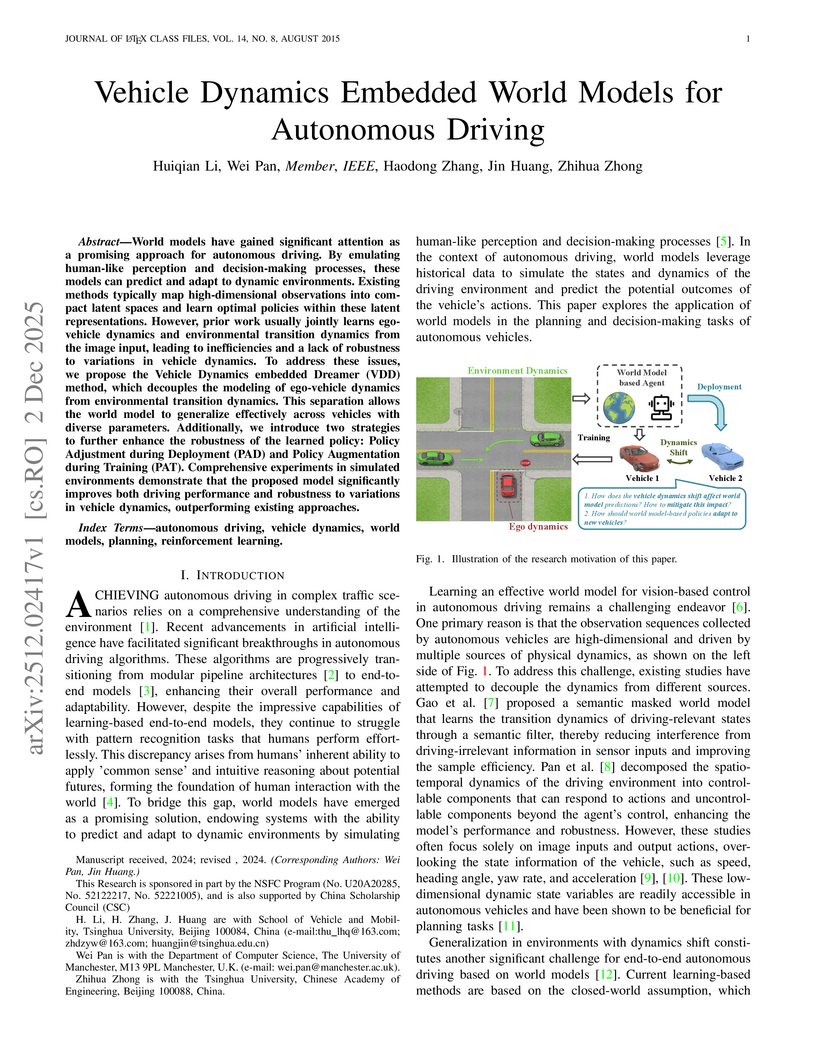
The Vehicle Dynamics embedded Dreamer (VDD) method introduces a world model that explicitly decouples ego-vehicle and environmental dynamics to improve the robustness and generalization of autonomous driving policies. It achieved superior performance in environments with varied vehicle dynamics, demonstrating higher success rates and cumulative rewards compared to prior models.
 Imperial College London
Imperial College London Zhejiang UniversityZhejiang LabNational University of Defense TechnologyBielefeld UniversityShanghai UniversityUniversity of StrathclydeTU WienUniversity of ManitobaSorbonne UniversityChinese Academy of EngineeringNational Digital Switching System Engineering & Technological R&D Center
Zhejiang UniversityZhejiang LabNational University of Defense TechnologyBielefeld UniversityShanghai UniversityUniversity of StrathclydeTU WienUniversity of ManitobaSorbonne UniversityChinese Academy of EngineeringNational Digital Switching System Engineering & Technological R&D CenterComputing is a critical driving force in the development of human civilization. In recent years, we have witnessed the emergence of intelligent computing, a new computing paradigm that is reshaping traditional computing and promoting digital revolution in the era of big data, artificial intelligence and internet-of-things with new computing theories, architectures, methods, systems, and applications. Intelligent computing has greatly broadened the scope of computing, extending it from traditional computing on data to increasingly diverse computing paradigms such as perceptual intelligence, cognitive intelligence, autonomous intelligence, and human-computer fusion intelligence. Intelligence and computing have undergone paths of different evolution and development for a long time but have become increasingly intertwined in recent years: intelligent computing is not only intelligence-oriented but also intelligence-driven. Such cross-fertilization has prompted the emergence and rapid advancement of intelligent computing. Intelligent computing is still in its infancy and an abundance of innovations in the theories, systems, and applications of intelligent computing are expected to occur soon. We present the first comprehensive survey of literature on intelligent computing, covering its theory fundamentals, the technological fusion of intelligence and computing, important applications, challenges, and future perspectives. We believe that this survey is highly timely and will provide a comprehensive reference and cast valuable insights into intelligent computing for academic and industrial researchers and practitioners.
The rapid evolution of edge computing has exposed fundamental limitations in traditional operating system and hypervisor architectures, particularly in managing heterogeneous platforms and meeting the constraints of limited resources. Existing solutions often rely on monolithic or layered combinations of hypervisors and guest OSes, which are difficult to tailor for the diverse and dynamic requirements of edge scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose TenonOS, a demand-driven, self-generating, and lightweight operating system framework that fundamentally rethinks and reconstructs both the hypervisor and OS architectures. TenonOS introduces a novel LibOS-on-LibOS approach, in which both virtualization and OS functionalities are modularized into fine-grained, reusable micro-libraries. A dynamic orchestration engine composes these modules on demand to construct customized, application-specific runtime environments. At the core of TenonOS are two key components: Mortise, a minimal, modularized hypervisor, and Tenon, a real-time LibOS. Mortise provides low-overhead resource isolation, fast inter-VM communication, and manages the full lifecycle of Tenon instances - including on-demand creation, suspension, and termination - enabling TenonOS to flexibly adapt its runtime layout to workload variations. Tenon delivers deterministic scheduling and multi-process support for time-critical applications. Through this unified and modular architecture, TenonOS eliminates redundant layers, reduces system overhead, and enhances scalability, security, and maintainability. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that TenonOS achieves superior real-time scheduling (40.28% improvement), a compact memory footprint (361 KiB), and high adaptability to dynamic edge workloads, making it an ideal foundation for heterogeneous, resource-constrained edge systems.
17 Feb 2025
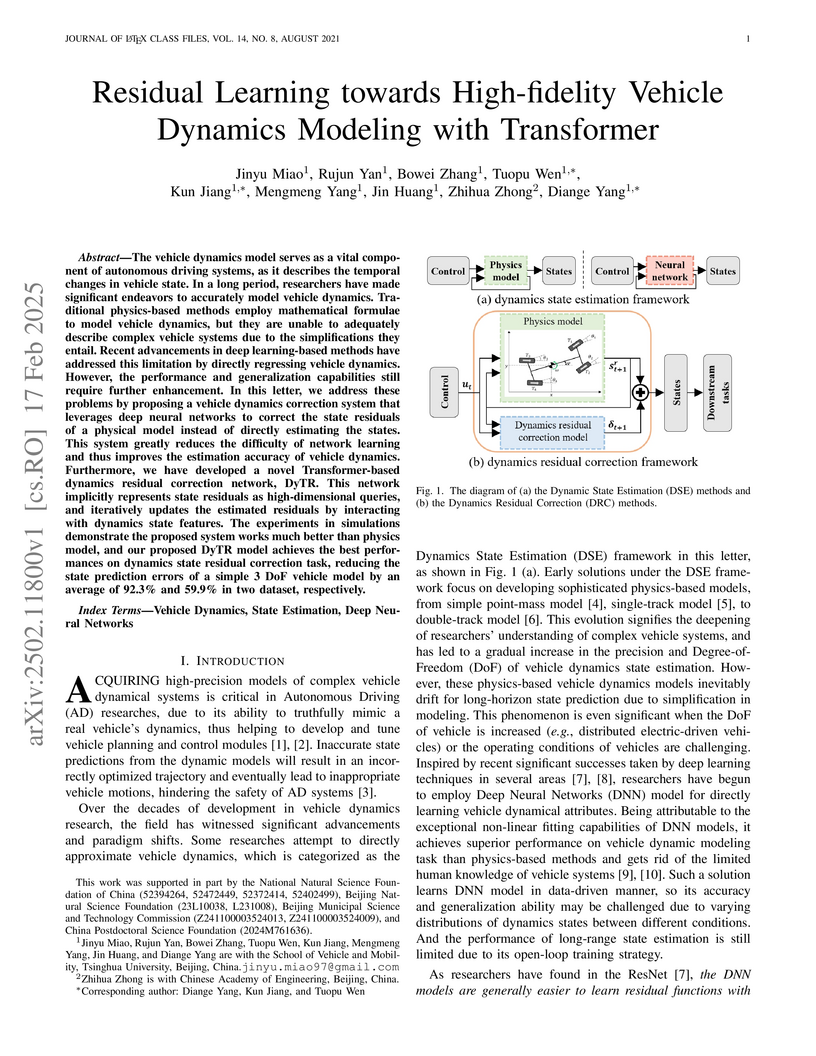
The vehicle dynamics model serves as a vital component of autonomous driving
systems, as it describes the temporal changes in vehicle state. In a long
period, researchers have made significant endeavors to accurately model vehicle
dynamics. Traditional physics-based methods employ mathematical formulae to
model vehicle dynamics, but they are unable to adequately describe complex
vehicle systems due to the simplifications they entail. Recent advancements in
deep learning-based methods have addressed this limitation by directly
regressing vehicle dynamics. However, the performance and generalization
capabilities still require further enhancement. In this letter, we address
these problems by proposing a vehicle dynamics correction system that leverages
deep neural networks to correct the state residuals of a physical model instead
of directly estimating the states. This system greatly reduces the difficulty
of network learning and thus improves the estimation accuracy of vehicle
dynamics. Furthermore, we have developed a novel Transformer-based dynamics
residual correction network, DyTR. This network implicitly represents state
residuals as high-dimensional queries, and iteratively updates the estimated
residuals by interacting with dynamics state features. The experiments in
simulations demonstrate the proposed system works much better than physics
model, and our proposed DyTR model achieves the best performances on dynamics
state residual correction task, reducing the state prediction errors of a
simple 3 DoF vehicle model by an average of 92.3% and 59.9% in two dataset,
respectively.
University of Oslo University of Waterloo
University of Waterloo Imperial College London
Imperial College London Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University College London
University College London Fudan UniversityPurple Mountain Laboratories
Fudan UniversityPurple Mountain Laboratories Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua UniversityXidian UniversityThe University of EdinburghUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaZhejiang LabPeng Cheng LaboratoryTechnology Innovation InstituteThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenShanghaiTech University
Tsinghua UniversityXidian UniversityThe University of EdinburghUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaZhejiang LabPeng Cheng LaboratoryTechnology Innovation InstituteThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenShanghaiTech University Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Huazhong University of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSoutheast UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Huawei TechnologiesBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsEast China Normal UniversityTU WienUniversity of KentChina Academy of Information and Communications TechnologyChina MobileZTE CorporationVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandChinese Academy of EngineeringChina UnicomChina Academy of Telecommunication TechnologyTerminus GroupFuzhou Internet of Things Open LabShenzhen Smart City Technology Development Group
King’s College LondonSoutheast UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Huawei TechnologiesBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsEast China Normal UniversityTU WienUniversity of KentChina Academy of Information and Communications TechnologyChina MobileZTE CorporationVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandChinese Academy of EngineeringChina UnicomChina Academy of Telecommunication TechnologyTerminus GroupFuzhou Internet of Things Open LabShenzhen Smart City Technology Development Group
 University of Waterloo
University of Waterloo Imperial College London
Imperial College London Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University College London
University College London Fudan UniversityPurple Mountain Laboratories
Fudan UniversityPurple Mountain Laboratories Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua UniversityXidian UniversityThe University of EdinburghUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaZhejiang LabPeng Cheng LaboratoryTechnology Innovation InstituteThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenShanghaiTech University
Tsinghua UniversityXidian UniversityThe University of EdinburghUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaZhejiang LabPeng Cheng LaboratoryTechnology Innovation InstituteThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenShanghaiTech University Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Huazhong University of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSoutheast UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Huawei TechnologiesBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsEast China Normal UniversityTU WienUniversity of KentChina Academy of Information and Communications TechnologyChina MobileZTE CorporationVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandChinese Academy of EngineeringChina UnicomChina Academy of Telecommunication TechnologyTerminus GroupFuzhou Internet of Things Open LabShenzhen Smart City Technology Development Group
King’s College LondonSoutheast UniversityHarbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)Huawei TechnologiesBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsEast China Normal UniversityTU WienUniversity of KentChina Academy of Information and Communications TechnologyChina MobileZTE CorporationVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandChinese Academy of EngineeringChina UnicomChina Academy of Telecommunication TechnologyTerminus GroupFuzhou Internet of Things Open LabShenzhen Smart City Technology Development GroupMobile communication standards were developed for enhancing transmission and
network performance by using more radio resources and improving spectrum and
energy efficiency. How to effectively address diverse user requirements and
guarantee everyone's Quality of Experience (QoE) remains an open problem. The
Sixth Generation (6G) mobile systems will solve this problem by utilizing
heterogenous network resources and pervasive intelligence to support
everyone-centric customized services anywhere and anytime. In this article, we
first coin the concept of Service Requirement Zone (SRZ) on the user side to
characterize and visualize the integrated service requirements and preferences
of specific tasks of individual users. On the system side, we further introduce
the concept of User Satisfaction Ratio (USR) to evaluate the system's overall
service ability of satisfying a variety of tasks with different SRZs. Then, we
propose a network Artificial Intelligence (AI) architecture with integrated
network resources and pervasive AI capabilities for supporting customized
services with guaranteed QoEs. Finally, extensive simulations show that the
proposed network AI architecture can consistently offer a higher USR
performance than the cloud AI and edge AI architectures with respect to
different task scheduling algorithms, random service requirements, and dynamic
network conditions.
23 Sep 2025
Accurate localization serves as an important component in autonomous driving systems. Traditional rule-based localization involves many standalone modules, which is theoretically fragile and requires costly hyperparameter tuning, therefore sacrificing the accuracy and generalization. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end visual localization system, RAVE, in which the surrounding images are associated with the HD map data to estimate pose. To ensure high-quality observations for localization, a low-rank flow-based prior fusion module (FLORA) is developed to incorporate misaligned map prior into the perceived BEV features. Pursuing a balance among efficiency, interpretability, and accuracy, a hierarchical localization module is proposed, which efficiently estimates poses through a decoupled BEV neural matching-based pose solver (DEMA) using rasterized HD map, and then refines the estimation through a Transformer-based pose regressor (POET) using vectorized HD map. The experimental results demonstrate that our method can perform robust and accurate localization under varying environmental conditions while running efficiently.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.